| MeSH term | MeSH ID | Detail |
|---|---|---|
| Adenocarcinoma | D000230 | 166 associated lipids |
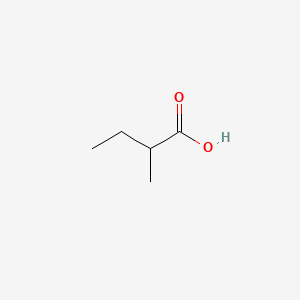
2-Methylbutanoic acid
2-Methylbutanoic acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. The involved functions are known as Binding (Molecular Function), Oxidation, isoleucine catabolic process, Anabolism and physiological aspects. 2-methylbutanoic acid often locates in Membrane, soluble and host. The associated genes with 2-Methylbutanoic acid are Homologous Gene, Genome, NKS1 gene, HM13 gene and ACSM1 gene. The related lipids are Fatty Acids, Butyric Acids, branched chain fatty acid, Propionate and 2-methylvalerate.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of 2-Methylbutanoic acid, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with 2-Methylbutanoic acid?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
Possible diseases from mapped MeSH terms on references
We collected disease MeSH terms mapped to the references associated with 2-Methylbutanoic acid
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with 2-Methylbutanoic acid
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with 2-Methylbutanoic acid?
Visualization in cellular structure
Associated locations are in red color. Not associated locations are in black.
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Location | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What functions are associated with 2-Methylbutanoic acid?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with 2-Methylbutanoic acid?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Lipid concept | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What genes are associated with 2-Methylbutanoic acid?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Gene | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What common seen animal models are associated with 2-Methylbutanoic acid?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
NCBI Entrez Crosslinks
All references with 2-Methylbutanoic acid
Download all related citations| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| El Amine Dib M et al. | Characterization of volatile compounds of Daucus crinitus Desf. Headspace Solid Phase Microextraction as alternative technique to Hydrodistillation. | 2010 | Chem Cent J | pmid:20858266 |
| Verhulst NO et al. | Cultured skin microbiota attracts malaria mosquitoes. | 2009 | Malar. J. | pmid:20017925 |
| Xie X et al. | Acyltransferase mediated polyketide release from a fungal megasynthase. | 2009 | J. Am. Chem. Soc. | pmid:19530726 |
| Reineri F et al. | Effect of low and zero magnetic field on the hyperpolarization lifetime in parahydrogenated perdeuterated molecules. | 2009 | J. Magn. Reson. | pmid:19535274 |
| MurÃn R et al. | Glial metabolism of isoleucine. | 2009 | Neurochem. Res. | pmid:18787950 |
| Hajhashemi V et al. | Anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties of Heracleum persicum essential oil and hydroalcoholic extract in animal models. | 2009 | J Ethnopharmacol | pmid:19467316 |
| Ho HY et al. | Identification and synthesis of the sex pheromone of the Madeira mealybug, Phenacoccus madeirensis Green. | 2009 | J. Chem. Ecol. | pmid:19529970 |
| Ferreira L et al. | Characterization of volatile substances in apples from Rosaceae family by headspace solid-phase microextraction followed by GC-qMS. | 2009 | J Sep Sci | pmid:19425016 |
| Lee GH et al. | Aroma-active components of Lycii fructus (kukija). | 2008 | J. Food Sci. | pmid:19241541 |
| Hayashida-Soiza G et al. | Purification and characterization of antibacterial substances produced by a marine bacterium Pseudoalteromonas haloplanktis strain. | 2008 | J. Appl. Microbiol. | pmid:18828792 |