| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bhatt V et al. | Simultaneous quantification and identification of flavonoids, lignans, coumarin and amides in leaves of Zanthoxylum armatum using UPLC-DAD-ESI-QTOF-MS/MS. | 2017 | J Pharm Biomed Anal | pmid:27693952 |
| Kuroki S et al. | Sanshool on The Fingertip Interferes with Vibration Detection in a Rapidly-Adapting (RA) Tactile Channel. | 2016 | PLoS ONE | pmid:27935970 |
| Hagura N et al. | Food vibrations: Asian spice sets lips trembling. | 2013 | Proc. Biol. Sci. | pmid:24026819 |
| Tsunozaki M et al. | A 'toothache tree' alkylamide inhibits Aδ mechanonociceptors to alleviate mechanical pain. | 2013 | J. Physiol. (Lond.) | pmid:23652591 |
| Igarashi Y et al. | Total synthesis of hydroxy-α- and hydroxy-β-sanshool using Suzuki-Miyaura coupling. | 2012 | Chem. Pharm. Bull. | pmid:22863716 |
| Klein AH et al. | A tingling sanshool derivative excites primary sensory neurons and elicits nocifensive behavior in rats. | 2011 | J. Neurophysiol. | pmid:21273322 |
| Lennertz RC et al. | Physiological basis of tingling paresthesia evoked by hydroxy-alpha-sanshool. | 2010 | J. Neurosci. | pmid:20335471 |
| Albin KC and Simons CT | Psychophysical evaluation of a sanshool derivative (alkylamide) and the elucidation of mechanisms subserving tingle. | 2010 | PLoS ONE | pmid:20209090 |
| Gerhold KA and Bautista DM | Molecular and cellular mechanisms of trigeminal chemosensation. | 2009 | Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. | pmid:19686135 |
| Riera CE et al. | Compounds from Sichuan and Melegueta peppers activate, covalently and non-covalently, TRPA1 and TRPV1 channels. | 2009 | Br. J. Pharmacol. | pmid:19594761 |
| Sawyer CM et al. | Activation of lumbar spinal wide-dynamic range neurons by a sanshool derivative. | 2009 | J. Neurophysiol. | pmid:19164099 |
| Bautista DM et al. | Pungent agents from Szechuan peppers excite sensory neurons by inhibiting two-pore potassium channels. | 2008 | Nat. Neurosci. | pmid:18568022 |
| Park YD et al. | Human acyl-CoA: cholesterol acyltransferase inhibitory activities of aliphatic acid amides from Zanthoxylum piperitum DC. | 2007 | Biol. Pharm. Bull. | pmid:17202689 |
| Sugai E et al. | Quantitative analysis of sanshool compounds in Japanese pepper (Xanthoxylum piperitum DC.) and their pungent characteristics. | 2005 | Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. | pmid:16244448 |
| Sugai E et al. | Pungent qualities of sanshool-related compounds evaluated by a sensory test and activation of rat TRPV1. | 2005 | Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. | pmid:16244447 |
| pmid: | ||||
| pmid:23537660 | ||||
| pmid:17767493 | ||||
| pmid:28821179 | ||||
| pmid:27284001 | ||||
| pmid:27233468 | ||||
| pmid:24759050 | ||||
| pmid:24175626 | ||||
| pmid:24106759 | ||||
| pmid:21846099 | ||||
| pmid:21808981 | ||||
| pmid:19209861 | ||||
| pmid:18481010 | ||||
| pmid:11301873 | ||||
| pmid:8693039 |
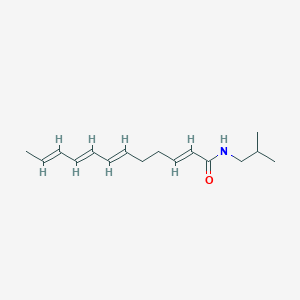
Beta-sanshool
Beta-sanshool is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class.