| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pmid: | ||||
| Iio T and Yoden K | Fluorescence formation from hydroperoxide of phosphatidylcholine with amino compound. | 1988 | Lipids | pmid:3352475 |
| Keough KM et al. | Phosphatidylcholine-cholesterol interactions: bilayers of heteroacid lipids containing linoleate lose calorimetric transitions at low cholesterol concentration. | 1989 | Biochim. Biophys. Acta | pmid:2758050 |
| Kojima I et al. | Insulin-like growth factor-I stimulates diacylglycerol production via multiple pathways in Balb/c 3T3 cells. | 1990 | J. Biol. Chem. | pmid:2120207 |
| Ninomiya H et al. | Biomodulator-mediated susceptibility of endogenous lipid droplets from rat adipocytes to hormone-sensitive lipase. | 1990 | Biochem. Med. Metab. Biol. | pmid:2161247 |
| Marques-Vidal P et al. | Hepatic lipase-mediated hydrolysis versus liver uptake of HDL phospholipids and triacylglycerols by the perfused rat liver. | 1991 | Biochim. Biophys. Acta | pmid:2007182 |
| Scagnelli GP et al. | Plasma 1-palmitoyl-2-linoleoyl phosphatidylcholine. Evidence for extensive phospholipase A1 hydrolysis and hepatic metabolism of the products. | 1991 | J. Biol. Chem. | pmid:1917938 |
| Wratten ML et al. | Structural and dynamic effects of oxidatively modified phospholipids in unsaturated lipid membranes. | 1992 | Biochemistry | pmid:1329957 |
| Vanloo B et al. | LCAT activation properties of apo A-I CNBr fragments and conversion of discoidal complexes into spherical particles. | 1992 | Biochim. Biophys. Acta | pmid:1420299 |
| Shamburek RD and Schwartz CC | Selective composition of biliary phosphatidylcholines is affected by secretion rate but not by bile acid hydrophobicity. | 1993 | J. Lipid Res. | pmid:8263408 |
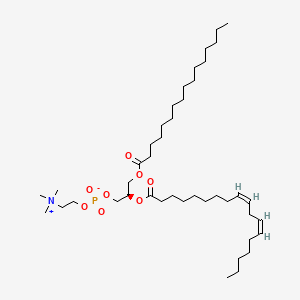
Soybean phospholipid
Soybean phospholipid is a lipid of Glycerophospholipids (GP) class. The involved functions are known as 5-(carboxyamino)imidazole ribonucleotide mutase activity, Laser-generated electromagnetic radiation, physiological aspects, Genetic Translation Process and Saturated. Soybean phospholipid often locates in Head, Tissue membrane, Membrane, extrinsic to membrane and Cytoplasmic matrix. The associated genes with Soybean phospholipid are THEMIS gene, C10orf27 gene and G-substrate. The related lipids are Unilamellar Vesicles, LYSO-PC, Phosphatidic Acid, Lysophosphatidylcholines and palmitoyl lysophosphatidylcholine.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of Soybean phospholipid, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with Soybean phospholipid?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
No disease MeSH terms mapped to the current reference collection.
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with Soybean phospholipid
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with Soybean phospholipid?
Visualization in cellular structure
Associated locations are in red color. Not associated locations are in black.
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Location | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What functions are associated with Soybean phospholipid?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with Soybean phospholipid?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Lipid concept | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What genes are associated with Soybean phospholipid?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Gene | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What common seen animal models are associated with Soybean phospholipid?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.