| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Birukov KG et al. | Epoxycyclopentenone-containing oxidized phospholipids restore endothelial barrier function via Cdc42 and Rac. | 2004 | Circ. Res. | pmid:15472119 |
| Minto RE et al. | A 2H solid-state NMR spectroscopic investigation of biomimetic bicelles containing cholesterol and polyunsaturated phosphatidylcholine. | 2004 | Chem. Phys. Lipids | pmid:15530448 |
| Milne GL et al. | Identification and analysis of products formed from phospholipids in the free radical oxidation of human low density lipoproteins. | 2005 | J. Lipid Res. | pmid:15547297 |
| Reis A et al. | Separation of peroxidation products of diacyl-phosphatidylcholines by reversed-phase liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. | 2005 | Biomed. Chromatogr. | pmid:15558686 |
| Samocha-Bonet D et al. | Lipid peroxidation in the presence of albumin, inhibitory and prooxidative effects. | 2004 | Free Radic. Res. | pmid:15621694 |
| Hyvönen MT and Kovanen PT | Molecular dynamics simulations of unsaturated lipid bilayers: effects of varying the numbers of double bonds. | 2005 | Eur. Biophys. J. | pmid:15688184 |
| Adibhatla RM and Hatcher JF | Cytidine 5'-diphosphocholine (CDP-choline) in stroke and other CNS disorders. | 2005 | Neurochem. Res. | pmid:15756928 |
| Ahn T et al. | Involvement of nonlamellar-prone lipids in the stability increase of human cytochrome P450 1A2 in reconstituted membranes. | 2005 | Biochemistry | pmid:15966743 |
| Zhang L and Granick S | Slaved diffusion in phospholipid bilayers. | 2005 | Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. | pmid:15967988 |
| Ishikado A et al. | Liposomalization of lactoferrin enhanced it's anti-inflammatory effects via oral administration. | 2005 | Biol. Pharm. Bull. | pmid:16141546 |
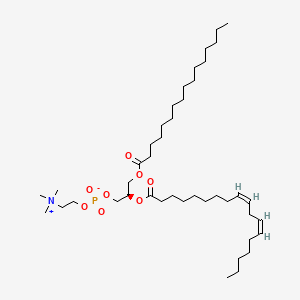
Soybean phospholipid
Soybean phospholipid is a lipid of Glycerophospholipids (GP) class. The involved functions are known as 5-(carboxyamino)imidazole ribonucleotide mutase activity, Laser-generated electromagnetic radiation, physiological aspects, Genetic Translation Process and Saturated. Soybean phospholipid often locates in Head, Tissue membrane, Membrane, extrinsic to membrane and Cytoplasmic matrix. The associated genes with Soybean phospholipid are THEMIS gene, C10orf27 gene and G-substrate. The related lipids are Unilamellar Vesicles, LYSO-PC, Phosphatidic Acid, Lysophosphatidylcholines and palmitoyl lysophosphatidylcholine.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of Soybean phospholipid, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with Soybean phospholipid?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
No disease MeSH terms mapped to the current reference collection.
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with Soybean phospholipid
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with Soybean phospholipid?
Visualization in cellular structure
Associated locations are in red color. Not associated locations are in black.
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Location | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What functions are associated with Soybean phospholipid?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with Soybean phospholipid?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Lipid concept | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What genes are associated with Soybean phospholipid?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Gene | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What common seen animal models are associated with Soybean phospholipid?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.