| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pmid: | ||||
| Stutzman JR et al. | Gas-phase transformation of phosphatidylcholine cations to structurally informative anions via ion/ion chemistry. | 2013 | Anal. Chem. | pmid:23469867 |
| Melzak KA and Gizeli E | Relative activity of cholesterol in OPPC/cholesterol/sphingomyelin mixtures measured with an acoustic sensor. | 2009 | Analyst | pmid:19238301 |
| Bagheri M et al. | Immobilization reduces the activity of surface-bound cationic antimicrobial peptides with no influence upon the activity spectrum. | 2009 | Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. | pmid:19104020 |
| Jiménez-Monreal AM et al. | Influence of the physical state of the membrane on the enzymatic activity and energy of activation of protein kinase C alpha. | 1999 | Biochemistry | pmid:10387014 |
| Chen L et al. | The cytoplasmic region of mouse Fc gamma RIIb1, but not Fc gamma RIIb2, binds phospholipid membranes. | 1999 | Biochemistry | pmid:10026293 |
| Santaren JF et al. | Thermal and 13C-NMR study of the dynamic structure of 1-palmitoyl-2-oleyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine and 1-oleyl-2-palmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine in aqueous dispersions. | 1982 | Biochim. Biophys. Acta | pmid:7093254 |
| Tada K et al. | Barotropic and thermotropic bilayer phase behavior of positional isomers of unsaturated mixed-chain phosphatidylcholines. | 2009 | Biochim. Biophys. Acta | pmid:19233121 |
| Wang C et al. | Push and pull forces in lipid raft formation: the push can be as important as the pull. | 2015 | J. Am. Chem. Soc. | pmid:25561007 |
| Kuge H et al. | Functional compartmentalization of the plasma membrane of neurons by a unique acyl chain composition of phospholipids. | 2014 | J. Biol. Chem. | pmid:25096572 |
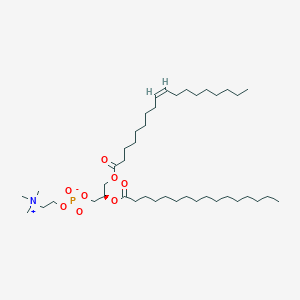
PC(18:1(9Z)/16:0)
PC(18:1(9Z)/16:0) is a lipid of Glycerophospholipids (GP) class. Pc(18:1(9z)/16:0) is associated with abnormalities such as protrusion. The involved functions are known as Process, phospholipase A1 activity, Immunoreactivity, Collision and Chromosome Pairing. Pc(18:1(9z)/16:0) often locates in Membrane, Cell membrane and membrane fraction. The related lipids are 1-oleoyl-2-palmitoylphosphatidylcholine, LYSO-PC, dioleoyl phosphatidylethanolamine, lysophosphatidic acid and Phosphatidic Acid.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of PC(18:1(9Z)/16:0), we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with PC(18:1(9Z)/16:0)?
PC(18:1(9Z)/16:0) is suspected in protrusion and other diseases in descending order of the highest number of associated sentences.
Related references are mostly published in these journals:
| Disease | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literature |
|---|
No disease MeSH terms mapped to the current reference collection.
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with PC(18:1(9Z)/16:0)
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with PC(18:1(9Z)/16:0)?
Visualization in cellular structure
Associated locations are in red color. Not associated locations are in black.
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Location | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What functions are associated with PC(18:1(9Z)/16:0)?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with PC(18:1(9Z)/16:0)?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Lipid concept | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What genes are associated with PC(18:1(9Z)/16:0)?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
What common seen animal models are associated with PC(18:1(9Z)/16:0)?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.