| MeSH term | MeSH ID | Detail |
|---|---|---|
| Adenocarcinoma | D000230 | 166 associated lipids |
| Body Weight | D001835 | 333 associated lipids |
| Colonic Neoplasms | D003110 | 161 associated lipids |
| Gastrointestinal Hemorrhage | D006471 | 27 associated lipids |
| Carcinoma, Hepatocellular | D006528 | 140 associated lipids |
| Hyperlipidemias | D006949 | 73 associated lipids |
| Malabsorption Syndromes | D008286 | 16 associated lipids |
| Stomach Ulcer | D013276 | 75 associated lipids |
| Werner Syndrome | D014898 | 4 associated lipids |
| Myoclonic Epilepsies, Progressive | D020191 | 3 associated lipids |
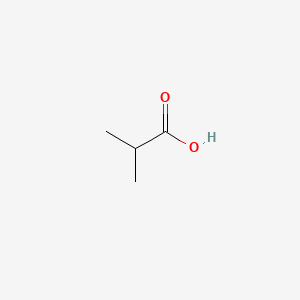
ISOBUTYRIC ACID
ISOBUTYRIC ACID is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. Isobutyric acid is associated with abnormalities such as Atrophy, Muscular, Spinobulbar. The involved functions are known as Signal Transduction, Oxidation, Vmax, Metabolic Inhibition and Regulation. Isobutyric acid often locates in Cytoplasm, Plasma membrane, peroxisome, Mouse Embryonic Fibroblast and Protoplasm. The associated genes with ISOBUTYRIC ACID are Candidate Disease Gene, CDKN1A gene, MYC gene, E2F1 gene and HBP1 gene. The related lipids are butyrate, Butyrates, lipid structure, Fatty Acids and Propionate. The related experimental models are Knock-out.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of ISOBUTYRIC ACID, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with ISOBUTYRIC ACID?
ISOBUTYRIC ACID is suspected in Atrophy, Muscular, Spinobulbar and other diseases in descending order of the highest number of associated sentences.
Related references are mostly published in these journals:
| Disease | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literature |
|---|
Possible diseases from mapped MeSH terms on references
We collected disease MeSH terms mapped to the references associated with ISOBUTYRIC ACID
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with ISOBUTYRIC ACID
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with ISOBUTYRIC ACID?
Visualization in cellular structure
Associated locations are in red color. Not associated locations are in black.
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Location | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What functions are associated with ISOBUTYRIC ACID?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with ISOBUTYRIC ACID?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Lipid concept | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What genes are associated with ISOBUTYRIC ACID?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Gene | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What common seen animal models are associated with ISOBUTYRIC ACID?
Knock-out
Knock-out are used in the study 'G1/S arrest induced by histone deacetylase inhibitor sodium butyrate in E1A + Ras-transformed cells is mediated through down-regulation of E2F activity and stabilization of beta-catenin.' (Abramova MV et al., 2006).
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Model | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
NCBI Entrez Crosslinks
All references with ISOBUTYRIC ACID
Download all related citations| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Huys G et al. | Aeromonas hydrophila subsp. ranae subsp. nov., isolated from septicaemic farmed frogs in Thailand. | 2003 | Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. | pmid:12807217 |
| Gabler MT and Heinrichs AJ | Altering soluble and potentially rumen degradable protein for prepubertal Holstein heifers. | 2003 | J. Dairy Sci. | pmid:12836949 |
| Noftsger SM et al. | Effects of 2-hydroxy-4-(methylthio) butanoic acid (HMB) on microbial growth in continuous culture. | 2003 | J. Dairy Sci. | pmid:12939087 |
| Batstone DJ et al. | Kinetics of thermophilic, anaerobic oxidation of straight and branched chain butyrate and valerate. | 2003 | Biotechnol. Bioeng. | pmid:12966576 |
| Shigematsu T et al. | Delftia tsuruhatensis sp. nov., a terephthalate-assimilating bacterium isolated from activated sludge. | 2003 | Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. | pmid:13130036 |
| Grenier D | Nutritional interactions between two suspected periodontopathogens, Treponema denticola and Porphyromonas gingivalis. | 1992 | Infect. Immun. | pmid:1333450 |
| Wang SS et al. | Cleavage and deprotection of peptides on MBHA-resin with hydrogen bromide. | 1992 Sep-Oct | Int. J. Pept. Protein Res. | pmid:1335998 |
| WEGNER GH and FOSTER EM | Incorporation of isobutyrate and valerate into cellular plasmalogen by Bacteroides succinogenes. | 1963 | J. Bacteriol. | pmid:13999496 |
| SOCRANSKY SS et al. | DEPENDENCY OF TREPONEMA MICRODENTIUM ON OTHER ORAL ORGANISMS FOR ISOBUTYRATE, POLYAMINES, AND A CONTROLLED OXIDATION-REDUCTION POTENTIAL. | 1964 | J. Bacteriol. | pmid:14197888 |
| Lemoff AS et al. | Binding energies of water to sodiated valine and structural isomers in the gas phase: the effect of proton affinity on zwitterion stability. | 2003 | J. Am. Chem. Soc. | pmid:14583055 |