| MeSH term | MeSH ID | Detail |
|---|---|---|
| Arrhythmias, Cardiac | D001145 | 42 associated lipids |
| Lupus Erythematosus, Systemic | D008180 | 43 associated lipids |
| Lung Neoplasms | D008175 | 171 associated lipids |
| Insulinoma | D007340 | 28 associated lipids |
| Diabetes Mellitus, Type 1 | D003922 | 56 associated lipids |
| Diabetic Retinopathy | D003930 | 39 associated lipids |
| Pulmonary Edema | D011654 | 23 associated lipids |
| Peritonitis | D010538 | 38 associated lipids |
| Proteinuria | D011507 | 30 associated lipids |
| Arteriosclerosis | D001161 | 86 associated lipids |
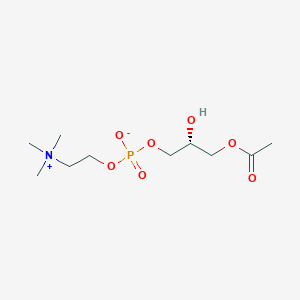
Lysophosphatidylcholine
Lysophosphatidylcholine is a lipid of Glycerophospholipids (GP) class. Lysophosphatidylcholine is associated with abnormalities such as Ischemia, Obesity, Diabetes Mellitus, Non-Insulin-Dependent, Fatty Liver and Atherosclerosis. The involved functions are known as Inflammation, antagonists, Signal Transduction, Signal Pathways and Saturated. Lysophosphatidylcholine often locates in Body tissue, Head, integral to membrane, Membrane and Extracellular. The associated genes with Lysophosphatidylcholine are RHOA gene, Homologous Gene, GPR4 gene, GPR68 gene and TRPV2 gene. The related lipids are Nonesterified Fatty Acids, lysophosphatidylethanolamine, Lysophosphatidylcholines, Phosphatidylserines and 25-hydroxycholesterol. The related experimental models are Knock-out and Disease model.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of Lysophosphatidylcholine, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with Lysophosphatidylcholine?
Lysophosphatidylcholine is suspected in Atherosclerosis, Ischemia, Septicemia, Obesity, Exanthema, hypercholesterolemia and other diseases in descending order of the highest number of associated sentences.
Related references are mostly published in these journals:
| Disease | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literature |
|---|
Possible diseases from mapped MeSH terms on references
We collected disease MeSH terms mapped to the references associated with Lysophosphatidylcholine
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with Lysophosphatidylcholine
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with Lysophosphatidylcholine?
Visualization in cellular structure
Associated locations are in red color. Not associated locations are in black.
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Location | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What functions are associated with Lysophosphatidylcholine?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with Lysophosphatidylcholine?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Lipid concept | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What genes are associated with Lysophosphatidylcholine?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Gene | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What common seen animal models are associated with Lysophosphatidylcholine?
Knock-out
Knock-out are used in the study 'Loss of G2A promotes macrophage accumulation in atherosclerotic lesions of low density lipoprotein receptor-deficient mice.' (Parks BW et al., 2005) and Knock-out are used in the study 'Altered lung phospholipid metabolism in mice with targeted deletion of lysosomal-type phospholipase A2.' (Fisher AB et al., 2005).
Disease model
Disease model are used in the study 'Dissociation of pentameric to monomeric C-reactive protein localizes and aggravates inflammation: in vivo proof of a powerful proinflammatory mechanism and a new anti-inflammatory strategy.' (Thiele JR et al., 2014).
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Model | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
NCBI Entrez Crosslinks
All references with Lysophosphatidylcholine
Download all related citations| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Egelandsdal B et al. | The denaturing action of lysophosphatidylcholine as studied by calorimetric and rheological techniques. | Chem. Phys. Lipids | pmid:2060066 | |
| Hawcroft DM and Martin PA | Studies on age related changes in the lipids of mouse liver microsomes. | Mech. Ageing Dev. | pmid:4437211 | |
| Hou WY et al. | Effect of inhibition of neuropathy target esterase in mouse nervous tissues in vitro on phosphatidylcholine and lysophosphatidylcholine homeostasis. | Int. J. Toxicol. | pmid:19620706 | |
| Killian JA and de Kruijff B | The influence of proteins and peptides on the phase properties of lipids. | Chem. Phys. Lipids | pmid:2427235 | |
| Herrmann W et al. | [The permeability of isolated phosphatides from normal and atherosclerotic human aortas]. | Atherosclerosis | pmid:4458690 | |
| Garçon DP et al. | Removal from the membrane affects the interaction of rat osseous plate ecto-nucleosidetriphosphate diphosphohydrolase-1 with substrates and ions. | J. Membr. Biol. | pmid:18841405 | |
| Ryborg AK et al. | Intracutaneous injection of lysophosphatidylcholine induces skin inflammation and accumulation of leukocytes. | Acta Derm. Venereol. | pmid:11028854 | |
| Besterman EM and Gillett MP | Inhibition of platelet aggregation by lysolecithin. | Atherosclerosis | pmid:5135227 | |
| Moyon S et al. | Efficient Remyelination Requires DNA Methylation. | eNeuro | pmid:28451635 | |
| Kim HY et al. | Lysophospholipid profile in serum and liver by high-fat diet and tumor induction in obesity-resistant BALB/c mice. | Nutrition | pmid:25280424 |