| MeSH term | MeSH ID | Detail |
|---|---|---|
| Arrhythmias, Cardiac | D001145 | 42 associated lipids |
| Lupus Erythematosus, Systemic | D008180 | 43 associated lipids |
| Lung Neoplasms | D008175 | 171 associated lipids |
| Insulinoma | D007340 | 28 associated lipids |
| Diabetes Mellitus, Type 1 | D003922 | 56 associated lipids |
| Diabetic Retinopathy | D003930 | 39 associated lipids |
| Pulmonary Edema | D011654 | 23 associated lipids |
| Peritonitis | D010538 | 38 associated lipids |
| Proteinuria | D011507 | 30 associated lipids |
| Arteriosclerosis | D001161 | 86 associated lipids |
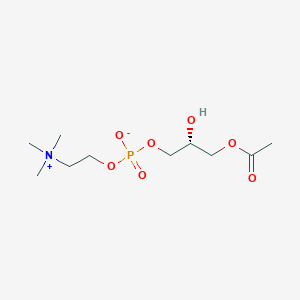
Lysophosphatidylcholine
Lysophosphatidylcholine is a lipid of Glycerophospholipids (GP) class. Lysophosphatidylcholine is associated with abnormalities such as Ischemia, Obesity, Diabetes Mellitus, Non-Insulin-Dependent, Fatty Liver and Atherosclerosis. The involved functions are known as Inflammation, antagonists, Signal Transduction, Signal Pathways and Saturated. Lysophosphatidylcholine often locates in Body tissue, Head, integral to membrane, Membrane and Extracellular. The associated genes with Lysophosphatidylcholine are RHOA gene, Homologous Gene, GPR4 gene, GPR68 gene and TRPV2 gene. The related lipids are Nonesterified Fatty Acids, lysophosphatidylethanolamine, Lysophosphatidylcholines, Phosphatidylserines and 25-hydroxycholesterol. The related experimental models are Knock-out and Disease model.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of Lysophosphatidylcholine, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with Lysophosphatidylcholine?
Lysophosphatidylcholine is suspected in Atherosclerosis, Ischemia, Septicemia, Obesity, Exanthema, hypercholesterolemia and other diseases in descending order of the highest number of associated sentences.
Related references are mostly published in these journals:
| Disease | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literature |
|---|
Possible diseases from mapped MeSH terms on references
We collected disease MeSH terms mapped to the references associated with Lysophosphatidylcholine
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with Lysophosphatidylcholine
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with Lysophosphatidylcholine?
Visualization in cellular structure
Associated locations are in red color. Not associated locations are in black.
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Location | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What functions are associated with Lysophosphatidylcholine?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with Lysophosphatidylcholine?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Lipid concept | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What genes are associated with Lysophosphatidylcholine?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Gene | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What common seen animal models are associated with Lysophosphatidylcholine?
Knock-out
Knock-out are used in the study 'Loss of G2A promotes macrophage accumulation in atherosclerotic lesions of low density lipoprotein receptor-deficient mice.' (Parks BW et al., 2005) and Knock-out are used in the study 'Altered lung phospholipid metabolism in mice with targeted deletion of lysosomal-type phospholipase A2.' (Fisher AB et al., 2005).
Disease model
Disease model are used in the study 'Dissociation of pentameric to monomeric C-reactive protein localizes and aggravates inflammation: in vivo proof of a powerful proinflammatory mechanism and a new anti-inflammatory strategy.' (Thiele JR et al., 2014).
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Model | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
NCBI Entrez Crosslinks
All references with Lysophosphatidylcholine
Download all related citations| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pmid: | ||||
| Vuong TD et al. | Hypoalbuminemia increases lysophosphatidylcholine in low-density lipoprotein of normocholesterolemic subjects. | 1999 | Kidney Int. | pmid:10027937 |
| Tokumura A et al. | Substrate specificity of lysophospholipase D which produces bioactive lysophosphatidic acids in rat plasma. | 1999 | Biochim. Biophys. Acta | pmid:10064906 |
| Kita T | [Aging and atherosclerosis]. | 1998 | Nihon Ronen Igakkai Zasshi | pmid:10064965 |
| Ma H et al. | Protective effect of quinaprilat, an active metabolite of quinapril, on Ca2+-overload induced by lysophosphatidylcholine in isolated rat cardiomyocytes. | 1999 | Jpn. J. Pharmacol. | pmid:10082313 |
| Fazeli A et al. | Sperm-oviduct interaction: induction of capacitation and preferential binding of uncapacitated spermatozoa to oviductal epithelial cells in porcine species. | 1999 | Biol. Reprod. | pmid:10084961 |
| Anttinen H | Stimulation of collagen galactosyltransferase and glucosyltransferase activities by lysophosphatidylcholine. | 1976 | Biochem. J. | pmid:1008844 |
| Rydström J et al. | The topology of the mitochondrial 11beta-hydroxylase system in bovine adrenal cortex. | 1976 | Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. | pmid:1008873 |
| Taniyama Y et al. | Cloning and expression of a novel lysophospholipase which structurally resembles lecithin cholesterol acyltransferase. | 1999 | Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. | pmid:10092508 |
| Shoda J et al. | Secretory low-molecular-weight phospholipases A2 and their specific receptor in bile ducts of patients with intrahepatic calculi: factors of chronic proliferative cholangitis. | 1999 | Hepatology | pmid:10094942 |
| Saunders DR and Sillery J | Lecithin inhibits fatty acid and bile salt absorption from rat small intestine in vivo. | 1976 | Lipids | pmid:1011937 |
| Sasagawa T et al. | Abnormal serum lysophospholipids in multiple myeloma patients. | 1999 | Lipids | pmid:10188592 |
| Wu R et al. | Antibodies against lysophosphatidylcholine and oxidized LDL in patients with SLE. | 1999 | Lupus | pmid:10192509 |
| Wu R et al. | Antibodies to adult human endothelial cells cross-react with oxidized low-density lipoprotein and beta 2-glycoprotein I (beta 2-GPI) in systemic lupus erythematosus. | 1999 | Clin. Exp. Immunol. | pmid:10193434 |
| Hunter GW et al. | Lysophosphatidylcholine modulates catalytically important motions of the Ca-ATPase phosphorylation domain. | 1999 | Biochemistry | pmid:10194382 |
| Martens JS et al. | A modification of apolipoprotein B accounts for most of the induction of macrophage growth by oxidized low density lipoprotein. | 1999 | J. Biol. Chem. | pmid:10196168 |
| Galle J et al. | Lp(a) and LDL induce apoptosis in human endothelial cells and in rabbit aorta: role of oxidative stress. | 1999 | Kidney Int. | pmid:10201010 |
| Lamarche B et al. | Triglyceride enrichment of HDL enhances in vivo metabolic clearance of HDL apo A-I in healthy men. | 1999 | J. Clin. Invest. | pmid:10207171 |
| Kugiyama K et al. | Burst production of superoxide anion in human endothelial cells by lysophosphatidylcholine. | 1999 | Atherosclerosis | pmid:10208496 |
| Zetterberg G et al. | Lysophosphatidylcholine abrogates the CR1 preserving effect of surfactant on quartz-exposed human granulocytes. | 1999 | Inflammation | pmid:10213273 |
| Ozaki H et al. | Lysophosphatidylcholine activates mitogen-activated protein kinases by a tyrosine kinase-dependent pathway in bovine aortic endothelial cells. | 1999 | Atherosclerosis | pmid:10217354 |
| Huang A et al. | Lipid hydroperoxides inhibit nitric oxide production in RAW264.7 macrophages. | 1999 | Free Radic. Biol. Med. | pmid:10218641 |
| William Taeusch H et al. | Nonionic polymers reverse inactivation of surfactant by meconium and other substances. | 1999 | Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. | pmid:10228100 |
| Riffo M and Nieto A | Lysophosphatidylcholine induces changes in physicochemical, morphological, and functional properties of mouse zona pellucida: a possible role of phospholipase A2 in sperm-zona pellucida interaction. | 1999 | Mol. Reprod. Dev. | pmid:10230818 |
| Fyrst H et al. | The PLB2 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae confers resistance to lysophosphatidylcholine and encodes a phospholipase B/lysophospholipase. | 1999 | Biochemistry | pmid:10231538 |
| Jones RC | The nature of ultrastructural changes induced by exposure of spermatozoa to lysolecithin. | 1976 | Theriogenology | pmid:1029673 |
| Ramanadham S et al. | Studies of the role of group VI phospholipase A2 in fatty acid incorporation, phospholipid remodeling, lysophosphatidylcholine generation, and secretagogue-induced arachidonic acid release in pancreatic islets and insulinoma cells. | 1999 | J. Biol. Chem. | pmid:10318801 |
| Baker RR and Chang HY | Evidence for two distinct lysophospholipase activities that degrade lysophosphatidylcholine and lysophosphatidic acid in neuronal nuclei of cerebral cortex. | 1999 | Biochim. Biophys. Acta | pmid:10320808 |
| Tang YH et al. | Effect of calcitonin gene-related peptide-induced preconditioning on attenuated endothelium-dependent vasorelaxation induced by lysophosphatidylcholine. | 1997 | Zhongguo Yao Li Xue Bao | pmid:10322927 |
| Longo WE et al. | Synthetic pathways of gallbladder mucosal prostanoids: the role of cyclooxygenase-1 and 2. | 1999 | Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fatty Acids | pmid:10328326 |
| Shi AH et al. | Lysophosphatidylcholine molecular species in low density lipoprotein of type 2 diabetes. | 1999 | Horm. Metab. Res. | pmid:10333086 |
| Huang YH et al. | Lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC) induces proinflammatory cytokines by a platelet-activating factor (PAF) receptor-dependent mechanism. | 1999 | Clin. Exp. Immunol. | pmid:10337026 |
| Gómez-Muñoz A et al. | Lysophosphatidylcholine stimulates phospholipase D activity in mouse peritoneal macrophages. | 1999 | J. Lipid Res. | pmid:10357830 |
| Goldman R et al. | Calcium-dependent PAF-stimulated generation of reactive oxygen species in a human keratinocyte cell line. | 1999 | Biochim. Biophys. Acta | pmid:10366777 |
| Chen JX et al. | Protective effects of Ginkgo biloba extract against lysophosphatidylcholine-induced vascular endothelial cell damage. | 1998 | Zhongguo Yao Li Xue Bao | pmid:10375785 |
| Tokumura A et al. | Production of lysophosphatidic acids by lysophospholipase D in human follicular fluids of In vitro fertilization patients. | 1999 | Biol. Reprod. | pmid:10377049 |
| Si Y and Olds-Clarke P | Mice carrying two t haplotypes: sperm populations with reduced Zona pellucida binding are deficient in capacitation. | 1999 | Biol. Reprod. | pmid:10377063 |
| Subramanian VS et al. | Role of lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase in the metabolism of oxidized phospholipids in plasma: studies with platelet-activating factor-acetyl hydrolase-deficient plasma. | 1999 | Biochim. Biophys. Acta | pmid:10395969 |
| Sakai M et al. | Glucocorticoid inhibits oxidized LDL-induced macrophage growth by suppressing the expression of granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor. | 1999 | Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. | pmid:10397691 |
| Holm BA et al. | Multiple mechanisms of lung surfactant inhibition. | 1999 | Pediatr. Res. | pmid:10400140 |
| Daleau P | Lysophosphatidylcholine, a metabolite which accumulates early in myocardium during ischemia, reduces gap junctional coupling in cardiac cells. | 1999 | J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. | pmid:10403756 |
| Mokgobu I et al. | The ketolide antimicrobial agent HMR-3004 inhibits neutrophil superoxide production by a membrane-stabilizing mechanism. | 1999 | Int. J. Immunopharmacol. | pmid:10405872 |
| Sakuma S et al. | Existence of acyl-CoA hydrolase-mediated pathway supplying arachidonic acid for prostaglandin synthesis in microsomes from rabbit kidney medulla. | 1999 | Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. | pmid:10410378 |
| Woodruff RH and Franklin RJ | The expression of myelin protein mRNAs during remyelination of lysolecithin-induced demyelination. | 1999 | Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. | pmid:10417664 |
| Bryson EA et al. | Folding of apocytochrome c in lipid micelles: formation of alpha-helix precedes membrane insertion. | 1999 | Biochemistry | pmid:10423256 |
| Trotta M | Influence of phase transformation on indomethacin release from microemulsions. | 1999 | J Control Release | pmid:10425344 |
| Odgren PR et al. | The toothless osteopetrotic rat has a normal vitamin D-binding protein-macrophage activating factor (DBP-MAF) cascade and chondrodysplasia resistant to treatments with colony stimulating factor-1 (CSF-1) and/or DBP-MAF. | 1999 | Bone | pmid:10456382 |
| Ueno Y et al. | Lysophosphatidylcholine phosphorylates CREB and activates the jun2TRE site of c-jun promoter in vascular endothelial cells. | 1999 | FEBS Lett. | pmid:10471787 |
| Suenaga H and Kamata K | Marked dissociation between intracellular Ca2+ level and contraction on exposure of rat aorta to lysophosphatidylcholine. | 1999 | Eur. J. Pharmacol. | pmid:10478630 |
| Bassa BV et al. | Lysophosphatidylcholine activates mesangial cell PKC and MAP kinase by PLCgamma-1 and tyrosine kinase-Ras pathways. | 1999 | Am. J. Physiol. | pmid:10484515 |