| MeSH term | MeSH ID | Detail |
|---|---|---|
| Arrhythmias, Cardiac | D001145 | 42 associated lipids |
| Lupus Erythematosus, Systemic | D008180 | 43 associated lipids |
| Lung Neoplasms | D008175 | 171 associated lipids |
| Insulinoma | D007340 | 28 associated lipids |
| Diabetes Mellitus, Type 1 | D003922 | 56 associated lipids |
| Diabetic Retinopathy | D003930 | 39 associated lipids |
| Pulmonary Edema | D011654 | 23 associated lipids |
| Peritonitis | D010538 | 38 associated lipids |
| Proteinuria | D011507 | 30 associated lipids |
| Arteriosclerosis | D001161 | 86 associated lipids |
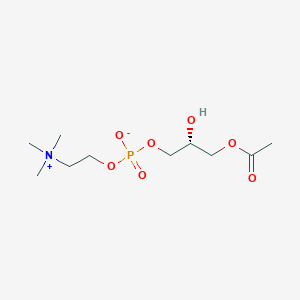
Lysophosphatidylcholine
Lysophosphatidylcholine is a lipid of Glycerophospholipids (GP) class. Lysophosphatidylcholine is associated with abnormalities such as Ischemia, Obesity, Diabetes Mellitus, Non-Insulin-Dependent, Fatty Liver and Atherosclerosis. The involved functions are known as Inflammation, antagonists, Signal Transduction, Signal Pathways and Saturated. Lysophosphatidylcholine often locates in Body tissue, Head, integral to membrane, Membrane and Extracellular. The associated genes with Lysophosphatidylcholine are RHOA gene, Homologous Gene, GPR4 gene, GPR68 gene and TRPV2 gene. The related lipids are Nonesterified Fatty Acids, lysophosphatidylethanolamine, Lysophosphatidylcholines, Phosphatidylserines and 25-hydroxycholesterol. The related experimental models are Knock-out and Disease model.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of Lysophosphatidylcholine, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with Lysophosphatidylcholine?
Lysophosphatidylcholine is suspected in Atherosclerosis, Ischemia, Septicemia, Obesity, Exanthema, hypercholesterolemia and other diseases in descending order of the highest number of associated sentences.
Related references are mostly published in these journals:
| Disease | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literature |
|---|
Possible diseases from mapped MeSH terms on references
We collected disease MeSH terms mapped to the references associated with Lysophosphatidylcholine
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with Lysophosphatidylcholine
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with Lysophosphatidylcholine?
Visualization in cellular structure
Associated locations are in red color. Not associated locations are in black.
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Location | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What functions are associated with Lysophosphatidylcholine?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with Lysophosphatidylcholine?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Lipid concept | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What genes are associated with Lysophosphatidylcholine?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Gene | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What common seen animal models are associated with Lysophosphatidylcholine?
Knock-out
Knock-out are used in the study 'Loss of G2A promotes macrophage accumulation in atherosclerotic lesions of low density lipoprotein receptor-deficient mice.' (Parks BW et al., 2005) and Knock-out are used in the study 'Altered lung phospholipid metabolism in mice with targeted deletion of lysosomal-type phospholipase A2.' (Fisher AB et al., 2005).
Disease model
Disease model are used in the study 'Dissociation of pentameric to monomeric C-reactive protein localizes and aggravates inflammation: in vivo proof of a powerful proinflammatory mechanism and a new anti-inflammatory strategy.' (Thiele JR et al., 2014).
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Model | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
NCBI Entrez Crosslinks
All references with Lysophosphatidylcholine
Download all related citations| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sánchez-Villalba E et al. | Improved exogenous DNA uptake in bovine spermatozoa and gene expression in embryos using membrane destabilizing agents in ICSI-SMGT. | 2018 | Zygote | pmid:29334034 |
| Huang Y et al. | [Metformin prevents non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in rats: role of phospholipase A2/lysophosphatidylcholine lipoapoptosis pathway in hepatocytes]. | 2011 | Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi | pmid:21426695 |
| Niu N et al. | [Effects of niacin on cell adhesion and early atherogenesis: involvement of the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinases pathway]. | 2013 | Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi | pmid:24484556 |
| Chen JX et al. | Protective effects of Ginkgo biloba extract against lysophosphatidylcholine-induced vascular endothelial cell damage. | 1998 | Zhongguo Yao Li Xue Bao | pmid:10375785 |
| Peng CF et al. | Protective effects of 17 beta-estradiol on endothelial function injured by oxidized low-density lipoproteins. | 1996 | Zhongguo Yao Li Xue Bao | pmid:9812750 |
| Tang YH et al. | Effect of calcitonin gene-related peptide-induced preconditioning on attenuated endothelium-dependent vasorelaxation induced by lysophosphatidylcholine. | 1997 | Zhongguo Yao Li Xue Bao | pmid:10322927 |
| Wang BJ et al. | [Association of ORMDL3 single nucleotide polymorphisms with lysophosphatidylcholine and apolipoprotein B levels in children with asthma]. | 2015 | Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi | pmid:25815492 |
| Sun GJ et al. | [Effects of fenofibrate on the proliferation and apoptosis and nitric oxide synthase expression of cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells induced by lysophosphatidylcholine]. | 2006 | Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban | pmid:16859127 |
| Voelz H | Site of ATPase activity in Myxococcus xanthus: lipid requirement for enzyme activity. Dedicated to Professor Dr. W. Schwartz on his 80th birthday. | 1978 | Z. Allg. Mikrobiol. | pmid:151387 |
| Kudo Y | [Binding Characterizations of Asp-hemolysin to Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein]. | 2005 | Yakugaku Zasshi | pmid:16079612 |