| MeSH term | MeSH ID | Detail |
|---|---|---|
| Coronary Disease | D003327 | 70 associated lipids |
| Coronary Artery Disease | D003324 | 47 associated lipids |
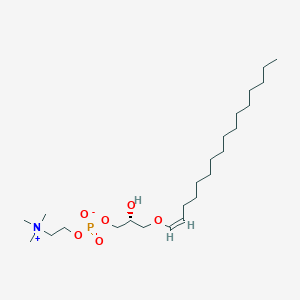
Lysoplasmenylcholine
Lysoplasmenylcholine is a lipid of Glycerophospholipids (GP) class. Lysoplasmenylcholine is associated with abnormalities such as Ischemia, Congenital Abnormality and Myocardial Ischemia. The involved functions are known as membrane activity, Action Potentials, Hypoxia, Energy Absorption and Cell Death. Lysoplasmenylcholine often locates in Myocardium, Membrane, Extracellular, Axon and Sarcolemma. The associated genes with Lysoplasmenylcholine are THOC4 gene, POLE gene, SFLL and CA1 gene. The related lipids are Plasmalogens, Phosphatidylserines, Lysophospholipids, plasmenylcholine and lysoplasmenylcholine.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of Lysoplasmenylcholine, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with Lysoplasmenylcholine?
Lysoplasmenylcholine is suspected in Myocardial Ischemia, Ischemia, Congenital Abnormality and other diseases in descending order of the highest number of associated sentences.
Related references are mostly published in these journals:
- Am. J. Physiol. (2)
- Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. (1)
- Am. J. Physiol., Cell Physiol. (1)
- Others (1)
| Disease | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literature |
|---|
Possible diseases from mapped MeSH terms on references
We collected disease MeSH terms mapped to the references associated with Lysoplasmenylcholine
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with Lysoplasmenylcholine
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with Lysoplasmenylcholine?
Visualization in cellular structure
Associated locations are in red color. Not associated locations are in black.
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Location | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What functions are associated with Lysoplasmenylcholine?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with Lysoplasmenylcholine?
Related references are published most in these journals:
- Am. J. Physiol. (2)
- Am. J. Physiol., Cell Physiol. (2)
- Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. (1)
- Others (1)
| Lipid concept | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What genes are associated with Lysoplasmenylcholine?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Gene | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What common seen animal models are associated with Lysoplasmenylcholine?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
NCBI Entrez Crosslinks
All references with Lysoplasmenylcholine
Download all related citations| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pmid: | ||||
| McHowat J et al. | Selective hydrolysis of plasmalogen phospholipids by Ca2+-independent PLA2 in hypoxic ventricular myocytes. | 1998 | Am. J. Physiol. | pmid:9611139 |
| Creer MH and McHowat J | Selective hydrolysis of plasmalogens in endothelial cells following thrombin stimulation. | 1998 | Am. J. Physiol. | pmid:9843711 |
| Williams SD and Ford DA | Calcium-independent phospholipase A(2) mediates CREB phosphorylation and c-fos expression during ischemia. | 2001 | Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. | pmid:11406482 |
| Liu SJ et al. | Alterations in Ca2+ cycling by lysoplasmenylcholine in adult rabbit ventricular myocytes. | 2003 | Am. J. Physiol., Cell Physiol. | pmid:12456398 |
| White MC et al. | Lysoplasmenylcholine increases neutrophil adherence to human coronary artery endothelial cells. | 2007 | Am. J. Physiol., Cell Physiol. | pmid:17728394 |
| Meyer MC and McHowat J | Calcium-independent phospholipase A2-catalyzed plasmalogen hydrolysis in hypoxic human coronary artery endothelial cells. | 2007 | Am. J. Physiol., Cell Physiol. | pmid:16943248 |
| HARTREE EF and MANN T | Crystalline lysoplasmalogen (lysophosphatidal choline): preparation from heart muscle and action on erythrocytes and spermatozoa. | 1960 | Biochem. J. | pmid:14400186 |
| Turini ME and Holub BJ | Eicosanoid/thromboxane A2-independent and -dependent generation of lysoplasmenylethanolamine via phospholipase A2 in collagen-stimulated human platelets. | 1993 | Biochem. J. | pmid:8435063 |
| Reiss D et al. | Delayed oxidative degradation of polyunsaturated diacyl phospholipids in the presence of plasmalogen phospholipids in vitro. | 1997 | Biochem. J. | pmid:9169616 |
| Rahman IA et al. | Calcium-dependent generation of N-acylethanolamines and lysophosphatidic acids by glycerophosphodiesterase GDE7. | 2016 | Biochim. Biophys. Acta | pmid:27637550 |
| Jurkowitz MS et al. | The YhhN protein of Legionella pneumophila is a Lysoplasmalogenase. | 2015 | Biochim. Biophys. Acta | pmid:25445671 |
| Jurkowitz-Alexander M et al. | Solubilization, purification and characterization of lysoplasmalogen alkenylhydrolase (lysoplasmalogenase) from rat liver microsomes. | 1989 | Biochim. Biophys. Acta | pmid:2930768 |
| Jurkowitz MS et al. | Identification and characterization of alkenyl hydrolase (lysoplasmalogenase) in microsomes and identification of a plasmalogen-active phospholipase A2 in cytosol of small intestinal epithelium. | 1999 | Biochim. Biophys. Acta | pmid:10064898 |
| Davies NJ et al. | Lysoplasmenylethanolamine accumulation in ischemic/reperfused isolated fatty acid-perfused hearts. | 1992 | Circ. Res. | pmid:1576737 |
| Caldwell RA and Baumgarten CM | Plasmalogen-derived lysolipid induces a depolarizing cation current in rabbit ventricular myocytes. | 1998 | Circ. Res. | pmid:9734476 |
| Nishimukai M et al. | Lymphatic absorption of choline plasmalogen is much higher than that of ethanolamine plasmalogen in rats. | 2011 | Eur J Nutr | pmid:21152926 |
| Williams SD and Ford DA | Activation of myocardial cAMP-dependent protein kinase by lysoplasmenylcholine. | 1997 | FEBS Lett. | pmid:9450545 |
| Illig HK et al. | Phospholipid metabolism of glial cell primary cultures, IV. Metabolism of 1-alkenyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine between 1 and 20 hours incubation. | 1982 | Hoppe-Seyler's Z. Physiol. Chem. | pmid:7129362 |
| Gunawan J and Debuch H | Liberation of free aldehyde from 1-(1-alkenyl)-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine (lysoplasmalogen) by rat liver microsomes. | 1981 | Hoppe-Seyler's Z. Physiol. Chem. | pmid:7239443 |