| MeSH term | MeSH ID | Detail |
|---|---|---|
| Drug Overdose | D062787 | 2 associated lipids |
| Carcinoma, Small Cell | D018288 | 21 associated lipids |
| Malaria, Falciparum | D016778 | 22 associated lipids |
| Lymphoma, B-Cell | D016393 | 24 associated lipids |
| Prostatic Neoplasms | D011471 | 126 associated lipids |
| Pancreatic Neoplasms | D010190 | 77 associated lipids |
| Metabolism, Inborn Errors | D008661 | 46 associated lipids |
| Lung Neoplasms | D008175 | 171 associated lipids |
| Hemolysis | D006461 | 131 associated lipids |
| Eye Diseases | D005128 | 12 associated lipids |
| Edema | D004487 | 152 associated lipids |
| Diabetic Retinopathy | D003930 | 39 associated lipids |
| Adenocarcinoma | D000230 | 166 associated lipids |
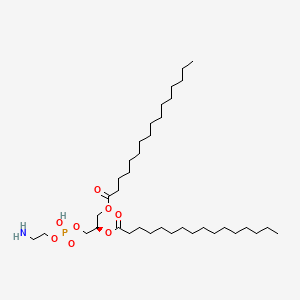
923-61-5
923-61-5 is a lipid of Glycerophospholipids (GP) class. 923-61-5 is associated with abnormalities such as Gigantism, Hyperostosis of skull, BOSLEY-SALIH-ALORAINY SYNDROME, Anemia, Sickle Cell and Amyloidosis. The involved functions are known as Protein Binding, Anabolism, Signal Transduction, Detergents and Genetic Translation Process. 923-61-5 often locates in soluble, Tissue membrane, brush border membrane, Mouse Kidney and Plasma membrane. The associated genes with 923-61-5 are THEMIS gene, SLC33A1 gene, P4HTM gene, Integral Membrane Proteins and Protein Structure. The related lipids are 1,2-oleoylphosphatidylcholine, Unilamellar Vesicles, Membrane Lipids, DOPE and Micelles.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of 923-61-5, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with 923-61-5?
923-61-5 is suspected in Gigantism, BOSLEY-SALIH-ALORAINY SYNDROME, Anemia, Sickle Cell, Amyloidosis, Cholera, Hyperostosis of skull and other diseases in descending order of the highest number of associated sentences.
Related references are mostly published in these journals:
| Disease | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literature |
|---|
Possible diseases from mapped MeSH terms on references
We collected disease MeSH terms mapped to the references associated with 923-61-5
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with 923-61-5
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with 923-61-5?
Visualization in cellular structure
Associated locations are in red color. Not associated locations are in black.
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Location | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What functions are associated with 923-61-5?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with 923-61-5?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Lipid concept | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What genes are associated with 923-61-5?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Gene | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What common seen animal models are associated with 923-61-5?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
NCBI Entrez Crosslinks
All references with 923-61-5
Download all related citations| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sostarecz AG et al. | Influence of molecular environment on the analysis of phospholipids by time-of-flight secondary ion mass spectrometry. | 2004 | Langmuir | pmid:15984252 |
| Ichikawa T et al. | Immobilizing single lipid and channel molecules in artificial lipid bilayers with annexin A5. | 2006 | Langmuir | pmid:16800690 |
| McBee TW and Saavedra SS | Stability of lipid films formed on gamma-aminopropyl monolayers. | 2005 | Langmuir | pmid:15807579 |
| Czapla K et al. | Differentiating oxicam nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in phosphoglyceride monolayers. | 2010 | Langmuir | pmid:20030324 |
| Wiecław K et al. | Meloxicam and meloxicam-beta-cyclodextrin complex in model membranes: effects on the properties and enzymatic lipolysis of phospholipid monolayers in relation to anti-inflammatory activity. | 2009 | Langmuir | pmid:19123793 |
| Stidder B et al. | Effect of low amounts of cholesterol on the swelling behavior of floating bilayers. | 2005 | Langmuir | pmid:16171350 |
| Koo KA et al. | Acteoside and its aglycones protect primary cultures of rat cortical cells from glutamate-induced excitotoxicity. | 2006 | Life Sci. | pmid:16566948 |
| Sleight RG and Dao HN | Synergistic activation of CTP:phosphocholine cytidylyltransferase by phosphatidylethanolamine and oleic acid. | 1990 | Lipids | pmid:2158609 |
| Karlik S et al. | Comparative evaluation of two membrane-based liposomal MRI contrast agents. | 1991 | Magn Reson Med | pmid:2046538 |
| Grant CW et al. | A liposomal MRI contrast agent: phosphatidylethanolamine-DTPA. | 1989 | Magn Reson Med | pmid:2779414 |
| Løkling KE et al. | Novel pH-sensitive paramagnetic liposomes with improved MR properties. | 2004 | Magn Reson Med | pmid:15065240 |
| Jones MN | Use of liposomes to deliver bactericides to bacterial biofilms. | 2005 | Meth. Enzymol. | pmid:15721384 |
| Helm CA and Israelachvili JN | Forces between phospholipid bilayers and relationship to membrane fusion. | 1993 | Meth. Enzymol. | pmid:8350750 |
| Bagatolli LA | Thermotropic behavior of lipid mixtures studied at the level of single vesicles: giant unilamellar vesicles and two-photon excitation fluorescence microscopy. | 2003 | Meth. Enzymol. | pmid:14611068 |
| Zhang H et al. | Chemically selective liposome surface glyco-functionalization. | 2011 | Methods Mol. Biol. | pmid:21674336 |
| Zidovetzki R et al. | A nuclear magnetic resonance study of the interactions of the antimalarials chloroquine, quinacrine, quinine and mefloquine with lipids extracted from normal human erythrocytes. | 1990 | Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. | pmid:2320052 |
| Okada N et al. | Differing reactivities of human and guinea-pig complement on haptenized liposomes via the alternative pathway. | 1983 | Mol. Immunol. | pmid:6194429 |
| Peetla C and Labhasetwar V | Biophysical characterization of nanoparticle-endothelial model cell membrane interactions. | 2008 May-Jun | Mol. Pharm. | pmid:18271547 |
| Zuhorn IS et al. | Nonbilayer phase of lipoplex-membrane mixture determines endosomal escape of genetic cargo and transfection efficiency. | 2005 | Mol. Ther. | pmid:15851018 |
| Wang M et al. | Structure of asteroid bodies in the vitreous of galactose-fed dogs. | 2006 | Mol. Vis. | pmid:16617295 |