| MeSH term | MeSH ID | Detail |
|---|---|---|
| Leukemia P388 | D007941 | 43 associated lipids |
| Seizures | D012640 | 87 associated lipids |
| Varicose Ulcer | D014647 | 4 associated lipids |
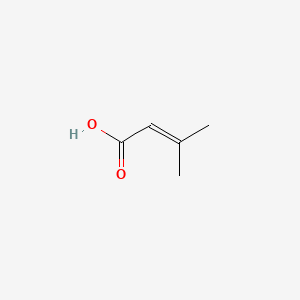
3-methylbut-2-enoic acid
3-methylbut-2-enoic acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. The involved functions are known as volatile substances, Anabolism, Pressure- physical agent, Adaptation and mevalonate pathway. 3-methylbut-2-enoic acid often locates in Cell membrane and Membrane. The associated genes with 3-methylbut-2-enoic acid are tryptones. The related lipids are Butyric Acids.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of 3-methylbut-2-enoic acid, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with 3-methylbut-2-enoic acid?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
Possible diseases from mapped MeSH terms on references
We collected disease MeSH terms mapped to the references associated with 3-methylbut-2-enoic acid
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with 3-methylbut-2-enoic acid
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with 3-methylbut-2-enoic acid?
Visualization in cellular structure
Associated locations are in red color. Not associated locations are in black.
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Location | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What functions are associated with 3-methylbut-2-enoic acid?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with 3-methylbut-2-enoic acid?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Lipid concept | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What genes are associated with 3-methylbut-2-enoic acid?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Gene | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What common seen animal models are associated with 3-methylbut-2-enoic acid?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
NCBI Entrez Crosslinks
All references with 3-methylbut-2-enoic acid
Download all related citations| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Taglialatela-Scafati O et al. | STAT-3 inhibitory bisabolanes from Carthamus glaucus. | 2012 | J. Nat. Prod. | pmid:22309250 |
| Schuller JM et al. | Structure and catalytic mechanism of a cyclic dipeptide prenyltransferase with broad substrate promiscuity. | 2012 | J. Mol. Biol. | pmid:22683356 |
| Hayati AA et al. | Optic neuritis in a child with biotinidase deficiency: case report and literature review. | 2012 | Clin Ophthalmol | pmid:22457589 |
| Wortmann SB et al. | The 3-methylglutaconic acidurias: what's new? | 2012 | J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. | pmid:20882351 |
| Schmidt J et al. | Selective orthosteric free fatty acid receptor 2 (FFA2) agonists: identification of the structural and chemical requirements for selective activation of FFA2 versus FFA3. | 2011 | J. Biol. Chem. | pmid:21220428 |
| Sorek N et al. | Differential effects of prenylation and s-acylation on type I and II ROPS membrane interaction and function. | 2011 | Plant Physiol. | pmid:21139084 |
| Jouneau S et al. | Anti-inflammatory effect of fluvastatin on IL-8 production induced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Aspergillus fumigatus antigens in cystic fibrosis. | 2011 | PLoS ONE | pmid:21826199 |
| van Veldhoven JP et al. | Structure-activity relationships of trans-substituted-propenoic acid derivatives on the nicotinic acid receptor HCA2 (GPR109A). | 2011 | Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. | pmid:21167710 |
| Schaafsma D et al. | Simvastatin inhibits TGFβ1-induced fibronectin in human airway fibroblasts. | 2011 | Respir. Res. | pmid:21864337 |
| Jost M et al. | Structure-function analysis of an enzymatic prenyl transfer reaction identifies a reaction chamber with modifiable specificity. | 2010 | J. Am. Chem. Soc. | pmid:21105662 |