| MeSH term | MeSH ID | Detail |
|---|---|---|
| Temporomandibular Joint Disorders | D013705 | 4 associated lipids |
| Arthralgia | D018771 | 8 associated lipids |
| Osteophyte | D054850 | 2 associated lipids |
| Glycogen Storage Disease | D006008 | 4 associated lipids |
| Hypertrophy, Left Ventricular | D017379 | 12 associated lipids |
| Retinitis | D012173 | 4 associated lipids |
| Theileriasis | D013801 | 7 associated lipids |
| Muscle Cramp | D009120 | 3 associated lipids |
| Rigor Mortis | D012298 | 1 associated lipids |
| Thrombophilia | D019851 | 6 associated lipids |
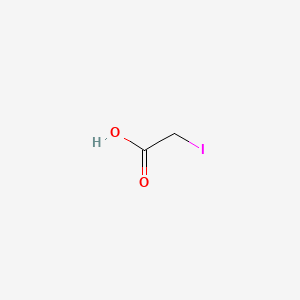
Iodoacetic acid
Iodoacetic acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. Iodoacetic acid is associated with abnormalities such as Photoreceptor degeneration and Post MI. The involved functions are known as Hypoxia, Glycolysis, Metabolic Inhibition, Oxidation and PTPS activity. Iodoacetic acid often locates in Extracellular, Muscle, Mitochondria, Cytoplasmic matrix and Tissue membrane. The associated genes with Iodoacetic acid are SLC33A1 gene, GTF2I gene, Mutant Proteins, TRIM33 gene and oxytocin, 1-desamino-(O-Et-Tyr)(2)-.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of Iodoacetic acid, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with Iodoacetic acid?
Iodoacetic acid is suspected in Photoreceptor degeneration, Post MI and other diseases in descending order of the highest number of associated sentences.
Related references are mostly published in these journals:
| Disease | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literature |
|---|
Possible diseases from mapped MeSH terms on references
We collected disease MeSH terms mapped to the references associated with Iodoacetic acid
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with Iodoacetic acid
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with Iodoacetic acid?
Visualization in cellular structure
Associated locations are in red color. Not associated locations are in black.
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Location | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What functions are associated with Iodoacetic acid?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with Iodoacetic acid?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
What genes are associated with Iodoacetic acid?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Gene | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What common seen animal models are associated with Iodoacetic acid?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
NCBI Entrez Crosslinks
All references with Iodoacetic acid
Download all related citations| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Li LC and Cosgrove DJ | Grass group I pollen allergens (beta-expansins) lack proteinase activity and do not cause wall loosening via proteolysis. | 2001 | Eur. J. Biochem. | pmid:11488915 |
| Okamoto K et al. | ATP from glycolysis is required for normal sodium homeostasis in resting fast-twitch rodent skeletal muscle. | 2001 | Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. | pmid:11500303 |
| Kishida F et al. | A type kappa Bence Jones protein containing a cysteinyl residue in the variable region. | 1975 | J. Biochem. | pmid:1150631 |
| Trinchieri G and De Marchi M | Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity in humans. II. Energy requirement. | 1975 | J. Immunol. | pmid:1151059 |
| Boja ES and Fales HM | Overalkylation of a protein digest with iodoacetamide. | 2001 | Anal. Chem. | pmid:11510821 |
| Delgado EF et al. | Properties of myofibril-bound calpain activity in longissimus muscle of callipyge and normal sheep. | 2001 | J. Anim. Sci. | pmid:11518218 |
| pmid:11521884 | ||||
| Leach RM et al. | Divergent roles of glycolysis and the mitochondrial electron transport chain in hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction of the rat: identity of the hypoxic sensor. | 2001 | J. Physiol. (Lond.) | pmid:11579170 |
| Lawrence CL et al. | The KATP channel opener diazoxide protects cardiac myocytes during metabolic inhibition without causing mitochondrial depolarization or flavoprotein oxidation. | 2001 | Br. J. Pharmacol. | pmid:11588107 |
| pmid:11594466 | ||||
| pmid:11640901 | ||||
| Zervos C and Adams E | Hydroxyproline-2-epimerase of Pseudomonas: active-site peptides. | 1975 | Mol. Cell. Biochem. | pmid:1165763 |
| Ayala E and Canonico PG | Aminoisobutyric acid transport in primary cultures of normal adult rat hepatocytes. | 1975 | Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. | pmid:1166067 |
| Tavazzi B et al. | Oxidative stress induces impairment of human erythrocyte energy metabolism through the oxygen radical-mediated direct activation of AMP-deaminase. | 2001 | J. Biol. Chem. | pmid:11675377 |
| Nijweide PJ and van der Plas A | Regulation of calcium transport in isolated periosteal cells, effects of hormones and metabolic inhibitors. | 1979 | Calcif. Tissue Int. | pmid:116755 |
| Walker WS and Demus A | Antibody-dependent cytolysis of chicken erythrocytes by an in vitro-established line of mouse peritoneal macrophages. | 1975 | J. Immunol. | pmid:1167563 |
| Guo Z et al. | Iodoacetate protects hippocampal neurons against excitotoxic and oxidative injury: involvement of heat-shock proteins and Bcl-2. | 2001 | J. Neurochem. | pmid:11677264 |
| pmid:11693549 | ||||
| pmid:11695393 | ||||
| Bubis J et al. | Chemical modification of transducin with iodoacetic acid: transducin-alpha carboxymethylated at Cys(347) allows transducin binding to Light-activated rhodopsin but prevents its release in the presence of GTP. | 2001 | Arch. Biochem. Biophys. | pmid:11697851 |