| MeSH term | MeSH ID | Detail |
|---|---|---|
| Hemolysis | D006461 | 131 associated lipids |
| Neuroblastoma | D009447 | 66 associated lipids |
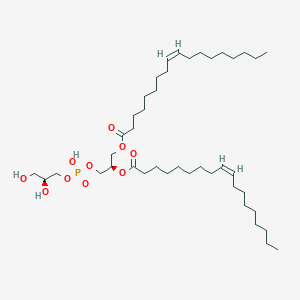
PG(18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z))
PG(18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z)) is a lipid of Glycerophospholipids (GP) class. Pg(18:1(9z)/18:1(9z)) is associated with abnormalities such as Neonatal hemochromatosis, Renal tubular disorder, Hereditary pancreatitis and UDPglucose 4-epimerase deficiency disease. The involved functions are known as Genetic Translation Process, Regulation, Saturated, enzyme activity and Cytokinesis. Pg(18:1(9z)/18:1(9z)) often locates in Membrane, soluble, Tissue membrane, membrane fraction and Thylakoid Membrane. The associated genes with PG(18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z)) are COIL gene, P4HTM gene, GRAP2 gene, Integral Membrane Proteins and synthetic peptide. The related lipids are Liposomes, Fatty Acids, Sphingolipids, DOPE and 1,2-oleoylphosphatidylcholine.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of PG(18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z)), we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with PG(18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z))?
PG(18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z)) is suspected in Renal tubular disorder, Hereditary pancreatitis, Neonatal hemochromatosis, UDPglucose 4-epimerase deficiency disease and other diseases in descending order of the highest number of associated sentences.
Related references are mostly published in these journals:
| Disease | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literature |
|---|
Possible diseases from mapped MeSH terms on references
We collected disease MeSH terms mapped to the references associated with PG(18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z))
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with PG(18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z))
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with PG(18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z))?
Visualization in cellular structure
Associated locations are in red color. Not associated locations are in black.
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Location | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What functions are associated with PG(18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z))?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with PG(18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z))?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Lipid concept | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What genes are associated with PG(18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z))?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Gene | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What common seen animal models are associated with PG(18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z))?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
NCBI Entrez Crosslinks
All references with PG(18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z))
Download all related citations| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nazarov PV et al. | FRET study of membrane proteins: simulation-based fitting for analysis of membrane protein embedment and association. | 2006 | Biophys. J. | pmid:16632512 |
| Fallon MS and Chauhan A | Sequestration of amitriptyline by liposomes. | 2006 | J Colloid Interface Sci | pmid:16643936 |
| Park JW and Lee GU | Properties of mixed lipid monolayers assembled on hydrophobic surfaces through vesicle adsorption. | 2006 | Langmuir | pmid:16700594 |
| Pérez S et al. | Influence of the saturation chain and head group charge of phospholipids in the interaction of hepatitis G virus synthetic peptides. | 2005 | J Phys Chem B | pmid:16853582 |
| Droghetti E et al. | Heme coordination states of unfolded ferrous cytochrome C. | 2006 | Biophys. J. | pmid:16877519 |
| Koynova R et al. | An intracellular lamellar-nonlamellar phase transition rationalizes the superior performance of some cationic lipid transfection agents. | 2006 | Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. | pmid:16983097 |
| Raghuraman H and Chattopadhyay A | Orientation and dynamics of melittin in membranes of varying composition utilizing NBD fluorescence. | 2007 | Biophys. J. | pmid:17114219 |
| Nazarov PV et al. | FRET study of membrane proteins: determination of the tilt and orientation of the N-terminal domain of M13 major coat protein. | 2007 | Biophys. J. | pmid:17114224 |
| Sun C et al. | Chloroplast SecA and Escherichia coli SecA have distinct lipid and signal peptide preferences. | 2007 | J. Bacteriol. | pmid:17142391 |
| Christ K et al. | The role of lipid II in membrane binding of and pore formation by nisin analyzed by two combined biosensor techniques. | 2007 | Biochim. Biophys. Acta | pmid:17254547 |
| Caracciolo G et al. | Structural stability against disintegration by anionic lipids rationalizes the efficiency of cationic liposome/DNA complexes. | 2007 | Langmuir | pmid:17341104 |
| Biswas N et al. | Structure and conformation of the disulfide bond in dimeric lung surfactant peptides SP-B1-25 and SP-B8-25. | 2007 | Biochim. Biophys. Acta | pmid:17349612 |
| Meleleo D et al. | Acetyl-[Asn30,Tyr32]-calcitonin fragment 8-32 forms channels in phospholipid planar lipid membranes. | 2007 | Eur. Biophys. J. | pmid:17393160 |
| Claessens MM et al. | Opposing effects of cation binding and hydration on the bending rigidity of anionic lipid bilayers. | 2007 | J Phys Chem B | pmid:17530881 |
| Dahlberg M | Polymorphic phase behavior of cardiolipin derivatives studied by coarse-grained molecular dynamics. | 2007 | J Phys Chem B | pmid:17542632 |
| Yang L et al. | Synthetic antimicrobial oligomers induce a composition-dependent topological transition in membranes. | 2007 | J. Am. Chem. Soc. | pmid:17880067 |
| Arnusch CJ et al. | Enhanced membrane pore formation by multimeric/oligomeric antimicrobial peptides. | 2007 | Biochemistry | pmid:17944489 |
| Parisot J et al. | Molecular mechanism of target recognition by subtilin, a class I lanthionine antibiotic. | 2008 | Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. | pmid:17999970 |
| Howell B and Chauhan A | Uptake of amitriptyline and nortriptyline with liposomes, proteins, and serum: implications for drug detoxification. | 2008 | J Colloid Interface Sci | pmid:18076894 |
| Stöckl M et al. | Alpha-synuclein selectively binds to anionic phospholipids embedded in liquid-disordered domains. | 2008 | J. Mol. Biol. | pmid:18082181 |