| MeSH term | MeSH ID | Detail |
|---|---|---|
| Anemia, Hemolytic | D000743 | 4 associated lipids |
| Multiple Myeloma | D009101 | 13 associated lipids |
| Melanoma | D008545 | 69 associated lipids |
| Osteoporosis | D010024 | 12 associated lipids |
| Kidney Diseases | D007674 | 29 associated lipids |
| Gingival Hemorrhage | D005884 | 5 associated lipids |
| Hematuria | D006417 | 13 associated lipids |
| Blood Coagulation Disorders | D001778 | 4 associated lipids |
| Glioma | D005910 | 112 associated lipids |
| Cell Transformation, Neoplastic | D002471 | 126 associated lipids |
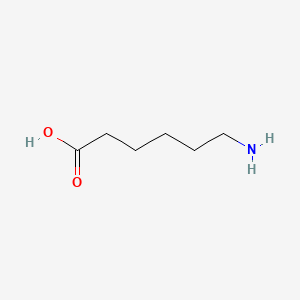
6-aminohexanoic acid
6-aminohexanoic acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. 6-aminohexanoic acid is associated with abnormalities such as Blood Clot, Myocardial Infarction, Cerebrovascular accident, Renal impairment and Scoliosis, unspecified. The involved functions are known as Fibrinolysis, Agent, Hemorrhage, plasminogen activation and inhibitors. 6-aminohexanoic acid often locates in Chest, Blood, Body tissue, peritoneal and Plasma membrane. The associated genes with 6-aminohexanoic acid are P4HTM gene, BSND gene, MTPN gene, NDUFS4 gene and Homologous Gene. The related lipids are Phosphatidylserines and Butyric Acid.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of 6-aminohexanoic acid, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with 6-aminohexanoic acid?
6-aminohexanoic acid is suspected in Cerebrovascular accident, Blood Clot, Myocardial Infarction, Renal impairment, Thromboembolism, Postoperative myocardial infarction and other diseases in descending order of the highest number of associated sentences.
Related references are mostly published in these journals:
| Disease | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literature |
|---|
Possible diseases from mapped MeSH terms on references
We collected disease MeSH terms mapped to the references associated with 6-aminohexanoic acid
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with 6-aminohexanoic acid
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with 6-aminohexanoic acid?
Visualization in cellular structure
Associated locations are in red color. Not associated locations are in black.
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Location | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What functions are associated with 6-aminohexanoic acid?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with 6-aminohexanoic acid?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Lipid concept | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What genes are associated with 6-aminohexanoic acid?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Gene | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What common seen animal models are associated with 6-aminohexanoic acid?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
NCBI Entrez Crosslinks
All references with 6-aminohexanoic acid
Download all related citations| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Slatter JG et al. | Pharmacokinetics, metabolism, and excretion of irinotecan (CPT-11) following I.V. infusion of [(14)C]CPT-11 in cancer patients. | 2000 | Drug Metab. Dispos. | pmid:10725311 |
| Deussen HJ et al. | A novel biotinylated suicide inhibitor for directed molecular evolution of lipolytic enzymes. | 2000 | Bioorg. Med. Chem. | pmid:10732966 |
| Lin LF et al. | Epsilon amino caproic acid inhibits streptokinase-plasminogen activator complex formation and substrate binding through kringle-dependent mechanisms. | 2000 | Biochemistry | pmid:10769130 |
| Southern LJ et al. | Glutaraldehyde-induced cross-links: a study of model compounds and commercial bioprosthetic valves. | 2000 | J. Heart Valve Dis. | pmid:10772042 |
| Walsh PN et al. | The therapeutic role of epsilon-aminocaproic acid (EACA) for dental extractions in hemophiliacs. | 1975 | Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. | pmid:1078619 |
| Tang H et al. | Altered expression of tissue-type plasminogen activator and type 1 inhibitor in astrocytes of mouse cortex following scratch injury in culture. | 2000 | Neurosci. Lett. | pmid:10793247 |
| Roos YB et al. | Antifibrinolytic therapy for aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage. | 2000 | Cochrane Database Syst Rev | pmid:10796425 |
| Barker JL et al. | Studies on convulsants in the isolated frog spinal cord. I. Antagonism of amino acid responses. | 1975 | J. Physiol. (Lond.) | pmid:1079871 |
| Graham ID et al. | The use of technologies to minimize exposure to perioperative allogeneic blood transfusion in elective surgery. A survey of Canadian hospitals. | 2000 | Int J Technol Assess Health Care | pmid:10815367 |
| Hruby Z et al. | Mechanism of antinephritic effect of proteinase inhibitors in experimental anti-GBM glomerulopathy. | 2000 | Res Exp Med (Berl) | pmid:10815758 |