| MeSH term | MeSH ID | Detail |
|---|---|---|
| Hemolysis | D006461 | 131 associated lipids |
| Uremia | D014511 | 33 associated lipids |
| Stomach Ulcer | D013276 | 75 associated lipids |
| Diabetes Mellitus | D003920 | 90 associated lipids |
| Sarcoma, Experimental | D012513 | 13 associated lipids |
| Adenocarcinoma | D000230 | 166 associated lipids |
| Lupus Erythematosus, Systemic | D008180 | 43 associated lipids |
| Hyperglycemia | D006943 | 21 associated lipids |
| Wounds and Injuries | D014947 | 20 associated lipids |
| Kidney Neoplasms | D007680 | 29 associated lipids |
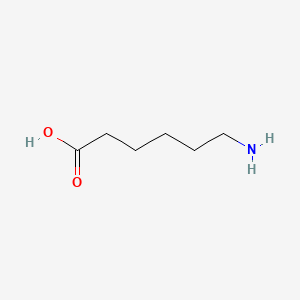
6-aminohexanoic acid
6-aminohexanoic acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. 6-aminohexanoic acid is associated with abnormalities such as Blood Clot, Myocardial Infarction, Cerebrovascular accident, Renal impairment and Scoliosis, unspecified. The involved functions are known as Fibrinolysis, Agent, Hemorrhage, plasminogen activation and inhibitors. 6-aminohexanoic acid often locates in Chest, Blood, Body tissue, peritoneal and Plasma membrane. The associated genes with 6-aminohexanoic acid are P4HTM gene, BSND gene, MTPN gene, NDUFS4 gene and Homologous Gene. The related lipids are Phosphatidylserines and Butyric Acid.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of 6-aminohexanoic acid, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with 6-aminohexanoic acid?
6-aminohexanoic acid is suspected in Cerebrovascular accident, Blood Clot, Myocardial Infarction, Renal impairment, Thromboembolism, Postoperative myocardial infarction and other diseases in descending order of the highest number of associated sentences.
Related references are mostly published in these journals:
| Disease | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literature |
|---|
Possible diseases from mapped MeSH terms on references
We collected disease MeSH terms mapped to the references associated with 6-aminohexanoic acid
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with 6-aminohexanoic acid
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with 6-aminohexanoic acid?
Visualization in cellular structure
Associated locations are in red color. Not associated locations are in black.
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Location | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What functions are associated with 6-aminohexanoic acid?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with 6-aminohexanoic acid?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Lipid concept | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What genes are associated with 6-aminohexanoic acid?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Gene | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What common seen animal models are associated with 6-aminohexanoic acid?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
NCBI Entrez Crosslinks
All references with 6-aminohexanoic acid
Download all related citations| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ljungh A | Helicobacter pylori interactions with plasminogen. | 2000 | Methods | pmid:10816376 |
| Reuter SR et al. | Selective arterial embolization for control of massive upper gastrointestinal bleeding. | 1975 | Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med | pmid:1081839 |
| Wang W et al. | Cyclic peptides incorporating 4-carboxyphenylalanine and phosphotyrosine are potent inhibitors of pp60(c-)(src). | 2000 | Biochemistry | pmid:10819990 |
| Koutský J et al. | [Plasminogen activator and other trypsin-like proteases in the uterus wall and their participation on the tissue bleeding (author's transl)]. | 1975 | Arch Gynakol | pmid:1082328 |
| Rao BH et al. | Epsilon aminocaproic acid in paediatric cardiac surgery to reduce postoperative blood loss. | 2000 | Indian J. Med. Res. | pmid:10824468 |
| Saleem R et al. | The effect of epsilon-aminocaproic acid on HemoSTATUS and kaolin-activated clotting time measurements. | 2000 | Anesth. Analg. | pmid:10825308 |
| Rajamohan G and Dikshit KL | Role of the N-terminal region of staphylokinase (SAK): evidence for the participation of the N-terminal region of SAK in the enzyme-substrate complex formation. | 2000 | FEBS Lett. | pmid:10838076 |
| Ghosh K et al. | Epsilon-aminocaproic acid inhibits the activity of factor VIII inhibitors in patients with severe haemophilia A in vivo and in vitro. | 2000 | Acta Haematol. | pmid:10838448 |
| Wells TJ | A new concept in the control of acute gingival hemorrhage. | 1976 | J Oral Surg | pmid:1083898 |
| Fatah-Ardalani K et al. | More porous fibrin gel structure obtained by interaction with Lys-plasminogen than with Glu-plasminogen. | 2000 | Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis | pmid:10847420 |
| Kimura I et al. | Vascular endothelial growth factor- and platelet-derived growth factor-angiogenesis depressed but fetal bovine serum-angiogenesis enhanced choroidal tissue cultures of streptozotocin-diabetic Wistar and GK rats. | 2000 | Int Angiol | pmid:10853682 |
| Lawiński M et al. | [E-aminocaproic acid in the treatment of acute pancreatitis]. | 1976 | Pol Przegl Chir | pmid:1085930 |
| North MJ and Ashworth JM | Inhibition of the development of the cellular slime mould Dictyostelium discoideum by omega-aminocarboxylic acids. | 1976 | J. Gen. Microbiol. | pmid:1086340 |
| North MJ and Campbell AJ | The effect of epsilon-aminocaproic acid on biochemical changes in the development of the cellular slime mould Dictyostelium discoideum. | 1976 | J. Gen. Microbiol. | pmid:1086341 |
| Dalmau A et al. | Tranexamic acid reduces red cell transfusion better than epsilon-aminocaproic acid or placebo in liver transplantation. | 2000 | Anesth. Analg. | pmid:10866882 |
| Vergoz D et al. | Kasabach-kasabach-. | 1976 Jan-Mar | Phlebologie | pmid:1087029 |
| Kallmes DF et al. | Adjuvant use of epsilon-aminocaproic acid (Amicar) in the endovascular treatment of cranial arteriovenous fistulae. | 2000 | Neuroradiology | pmid:10872177 |
| MacDonald M et al. | Synthesis and conformation of Gly-Gly dipeptides constrained with phenylalanine-like aminocaproic acid linkers. | 2000 | Org. Lett. | pmid:10880193 |
| Kleking GR and Viurbakh G | [Antifibrinolytic and antimycotic properties of 2-thiontetrahydro-1,3,5-thiadiazine]. | 1976 Jun-Aug | Farmakol Toksikol | pmid:1088410 |
| Ledoux D et al. | Human plasmin enzymatic activity is inhibited by chemically modified dextrans. | 2000 | J. Biol. Chem. | pmid:10889187 |
| Goretzki L et al. | Binding of the NG2 proteoglycan to kringle domains modulates the functional properties of angiostatin and plasmin(ogen). | 2000 | J. Biol. Chem. | pmid:10889192 |
| Gruber EM et al. | Synthetic antifibrinolytics are not associated with an increased incidence of baffle fenestration closure after the modified Fontan procedure. | 2000 | J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. | pmid:10890476 |
| Takahashi R et al. | Affinity chromatography for purification of two urokinases from human urine. | 2000 | J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. | pmid:10892585 |
| Romano PE and Robinson JA | Traumatic hyphema: a comprehensive review of the past half century yields 8076 cases for which specific medical treatment reduces rebleeding 62%, from 13% to 5% (P<.0001). | 2000 | Binocul Vis Strabismus Q | pmid:10893461 |
| Fukao H et al. | Binding of mutant tissue-type plasminogen activators to human endothelial cells and their extracellular matrix. | 2000 | Life Sci. | pmid:10894090 |
| Cattaneo M and Mannucci PM | Current status of non-transfusional haemostatic agents. | 1999 | Haematologica | pmid:10907488 |
| Zajicek J et al. | The effects of ligand binding on the backbone dynamics of the kringle 1 domain of human plasminogen. | 2000 | J. Mol. Biol. | pmid:10926513 |
| Zhang WY et al. | Plasmin-mediated macrophage reversal of low density lipoprotein aggregation. | 2000 | J. Biol. Chem. | pmid:10942782 |
| Horne MK et al. | Comparison of the effect of histidine-rich glycoprotein and 6-aminohexanoic acid on plasmin production and fibrinolysis in vitro. | 2000 | Thromb. Res. | pmid:10946092 |
| Dekkers DW et al. | Multidrug resistance protein 1 regulates lipid asymmetry in erythrocyte membranes. | 2000 | Biochem. J. | pmid:10947968 |
| Kornblatt JA | Understanding the fluorescence changes of human plasminogen when it binds the ligand, 6-aminohexanoate: a synthesis. | 2000 | Biochim. Biophys. Acta | pmid:10962086 |
| Yarzábal A et al. | A study of the interaction between Helicobacter pylori and components of the human fibrinolytic system. | 2000 | Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. | pmid:10973131 |
| Hoffmann K et al. | First non-radioactive assay for in vitro screening of histone deacetylase inhibitors. | 2000 | Pharmazie | pmid:10989838 |
| Hu B et al. | Intervesicle cross-linking with integrin alpha IIb beta 3 and cyclic-RGD-lipopeptide. A model of cell-adhesion processes. | 2000 | Biochemistry | pmid:11015207 |
| Hawley SB et al. | Purification, cloning, and characterization of a profibrinolytic plasminogen-binding protein, TIP49a. | 2001 | J. Biol. Chem. | pmid:11027681 |
| Maineri P et al. | Postoperative bleeding after coronary revascularization. Comparison between tranexamic acid and epsilon-aminocaproic acid. | 2000 | Minerva Cardioangiol | pmid:11048468 |
| Stafford-Smith M et al. | The association of epsilon-aminocaproic acid with postoperative decrease in creatinine clearance in 1502 coronary bypass patients. | 2000 | Anesth. Analg. | pmid:11049888 |
| Avilan L et al. | Interaction of Leishmania mexicana promastigotes with the plasminogen-plasmin system. | 2000 | Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. | pmid:11071275 |
| Boxrud PD and Bock PE | Streptokinase binds preferentially to the extended conformation of plasminogen through lysine binding site and catalytic domain interactions. | 2000 | Biochemistry | pmid:11076540 |
| Chauhan S et al. | Efficacy of aprotinin, epsilon aminocaproic acid, or combination in cyanotic heart disease. | 2000 | Ann. Thorac. Surg. | pmid:11081890 |
| Hrabálek A et al. | Esters of 6-dimethylaminohexanoic acid as skin penetration enhancers. | 2000 | Pharmazie | pmid:11082838 |
| Elliott JT and Prestwich GD | Maleimide-functionalized lipids that anchor polypeptides to lipid bilayers and membranes. | 2000 Nov-Dec | Bioconjug. Chem. | pmid:11087332 |
| Mullan S | Conservative management of the recently ruptured aneurysm. | 1975 | Surg Neurol | pmid:1111142 |
| Muneer E et al. | Mechanism of enhancement by fucoidan and CNBr-fibrinogen digest of the activation of glu-plasminogen by tissue plasminogen activator. | 2000 Apr-Jun | Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet | pmid:11112095 |
| Ries M et al. | Differences between neonates and adults in the urokinase-plasminogen activator (u-PA) pathway of the fibrinolytic system. | 2000 | Thromb. Res. | pmid:11113278 |
| Minn SK and Mandel EE | Experimental disseminated intravascular coagulation effect of heparin and epsilon-aminocaproic acid on tests of hemostatic function. | 1975 | Thromb. Res. | pmid:1114490 |
| Herren T et al. | Regulation of plasminogen binding to neutrophils. | 2001 | Blood | pmid:11159539 |
| Khatib AM et al. | Regulation of urokinase plasminogen activator/plasmin-mediated invasion of melanoma cells by the integrin vitronectin receptor alphaVbeta3. | 2001 | Int. J. Cancer | pmid:11169951 |
| Caster WO and Bleecker S | Hyperglycemic effect of amino compounds structurally related to caproate in rats. | 1975 | J. Nutr. | pmid:1117341 |
| Vang SN et al. | Co-administration of aprotinin and epsilon-aminocaproic acid during cardiopulmonary bypass in a swine model. | 2000 | J Extra Corpor Technol | pmid:11194056 |