| MeSH term | MeSH ID | Detail |
|---|---|---|
| Hemolysis | D006461 | 131 associated lipids |
| Uremia | D014511 | 33 associated lipids |
| Stomach Ulcer | D013276 | 75 associated lipids |
| Diabetes Mellitus | D003920 | 90 associated lipids |
| Sarcoma, Experimental | D012513 | 13 associated lipids |
| Adenocarcinoma | D000230 | 166 associated lipids |
| Lupus Erythematosus, Systemic | D008180 | 43 associated lipids |
| Hyperglycemia | D006943 | 21 associated lipids |
| Wounds and Injuries | D014947 | 20 associated lipids |
| Kidney Neoplasms | D007680 | 29 associated lipids |
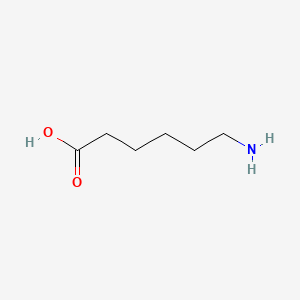
6-aminohexanoic acid
6-aminohexanoic acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. 6-aminohexanoic acid is associated with abnormalities such as Blood Clot, Myocardial Infarction, Cerebrovascular accident, Renal impairment and Scoliosis, unspecified. The involved functions are known as Fibrinolysis, Agent, Hemorrhage, plasminogen activation and inhibitors. 6-aminohexanoic acid often locates in Chest, Blood, Body tissue, peritoneal and Plasma membrane. The associated genes with 6-aminohexanoic acid are P4HTM gene, BSND gene, MTPN gene, NDUFS4 gene and Homologous Gene. The related lipids are Phosphatidylserines and Butyric Acid.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of 6-aminohexanoic acid, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with 6-aminohexanoic acid?
6-aminohexanoic acid is suspected in Cerebrovascular accident, Blood Clot, Myocardial Infarction, Renal impairment, Thromboembolism, Postoperative myocardial infarction and other diseases in descending order of the highest number of associated sentences.
Related references are mostly published in these journals:
| Disease | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literature |
|---|
Possible diseases from mapped MeSH terms on references
We collected disease MeSH terms mapped to the references associated with 6-aminohexanoic acid
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with 6-aminohexanoic acid
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with 6-aminohexanoic acid?
Visualization in cellular structure
Associated locations are in red color. Not associated locations are in black.
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Location | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What functions are associated with 6-aminohexanoic acid?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with 6-aminohexanoic acid?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Lipid concept | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What genes are associated with 6-aminohexanoic acid?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Gene | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What common seen animal models are associated with 6-aminohexanoic acid?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
NCBI Entrez Crosslinks
All references with 6-aminohexanoic acid
Download all related citations| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Daoudal P et al. | [So-called refractory hypoxemia: treatment with acexamic acid]. | 1979 | Nouv Presse Med | pmid:95046 |
| Arai K et al. | Role of the kringle domain in plasminogen activation with staphylokinase. | 1998 | J. Biochem. | pmid:9504411 |
| Hardy JF et al. | Prophylactic tranexamic acid and epsilon-aminocaproic acid for primary myocardial revascularization. | 1998 | Ann. Thorac. Surg. | pmid:9485231 |
| Poon MC and Ratnoff OD | Evidence that functional subunits of antihemophilic factor (Factor VIII) are linked by noncovalent bonds. | 1976 | Blood | pmid:947407 |
| Okamoto S et al. | Enzyme-controlling medicines: introduction. | 1997 | Semin. Thromb. Hemost. | pmid:9469621 |
| Young KC et al. | Plasminogen activation by streptokinase via a unique mechanism. | 1998 | J. Biol. Chem. | pmid:9446629 |
| Pyun JC et al. | Modification of short peptides using epsilon-aminocaproic acid for improved coating efficiency in indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA). | 1997 | J. Immunol. Methods | pmid:9433469 |
| Bennett-Guerrero E et al. | Cost-benefit and efficacy of aprotinin compared with epsilon-aminocaproic acid in patients having repeated cardiac operations: a randomized, blinded clinical trial. | 1997 | Anesthesiology | pmid:9416723 |
| Takayasu R et al. | Enhancement of fibrin binding and activation of plasminogen by staplabin through induction of a conformational change in plasminogen. | 1997 | FEBS Lett. | pmid:9414095 |
| Laupacis A and Fergusson D | Drugs to minimize perioperative blood loss in cardiac surgery: meta-analyses using perioperative blood transfusion as the outcome. The International Study of Peri-operative Transfusion (ISPOT) Investigators. | 1997 | Anesth. Analg. | pmid:9390590 |