| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pmid: | ||||
| Ferguson JE and Hanley MR | Phosphatidic acid and lysophosphatidic acid stimulate receptor-regulated membrane currents in the Xenopus laevis oocyte. | 1992 | Arch. Biochem. Biophys. | pmid:1379791 |
| Chang YJ et al. | Dioleoyl phosphatidic acid induces morphological changes through an endogenous LPA receptor in C6 glioma cells. | 2008 | Arch. Pharm. Res. | pmid:18481020 |
| Farren SB et al. | Polymorphic phase preferences of phosphatidic acid: A 31P and 2H NMR study. | 1983 | Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. | pmid:6838577 |
| Woźniak M et al. | The influence of phosphatidate bilayers on pig heart AMP deaminase. Crucial role of pH-dependent lipid-phase transition. | 1988 | Biochem. J. | pmid:3214434 |
| Houslay MD et al. | Acidic phospholipid species inhibit adenylate cyclase activity in rat liver plasma membranes. | 1986 | Biochem. J. | pmid:3741383 |
| Dalton KA et al. | Anionic phospholipids decrease the rate of slippage on the Ca(2+)-ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum. | 1999 | Biochem. J. | pmid:10455031 |
| Dalton KA et al. | Anionic lipids and accumulation of Ca2+ by a Ca(2+)-ATPase. | 1998 | Biochem. Soc. Trans. | pmid:9765953 |
| Kooijman EE et al. | Spontaneous curvature of phosphatidic acid and lysophosphatidic acid. | 2005 | Biochemistry | pmid:15697235 |
| Kooijman EE et al. | What makes the bioactive lipids phosphatidic acid and lysophosphatidic acid so special? | 2005 | Biochemistry | pmid:16363814 |
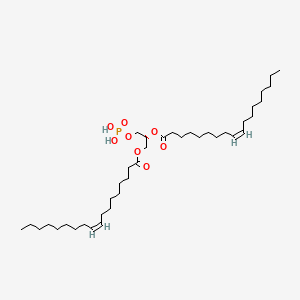
PA(18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z))
PA(18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z)) is a lipid of Glycerophospholipids (GP) class. The involved functions are known as adenylate cyclase activity, inhibitors, Drug Interactions, Membrane Fluidity and Force. Pa(18:1(9z)/18:1(9z)) often locates in Cell membrane, Tissue membrane, Epidermis, Connective Tissue and Back. The associated genes with PA(18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z)) are growth promoting activity and RAF1 gene. The related lipids are Phosphatidic Acid, Lysophospholipids, lysophosphatidic acid, Lysophosphatidylcholines and dioleoyl phosphate.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of PA(18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z)), we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with PA(18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z))?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
No disease MeSH terms mapped to the current reference collection.
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with PA(18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z))
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with PA(18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z))?
Visualization in cellular structure
Associated locations are in red color. Not associated locations are in black.
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Location | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What functions are associated with PA(18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z))?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with PA(18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z))?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Lipid concept | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What genes are associated with PA(18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z))?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Gene | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What common seen animal models are associated with PA(18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z))?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.