| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pmid: | ||||
| Farren SB et al. | Polymorphic phase preferences of phosphatidic acid: A 31P and 2H NMR study. | 1983 | Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. | pmid:6838577 |
| Nayar R et al. | Phosphatidic acid as a calcium ionophore in large unilamellar vesicle systems. | 1984 | Biochim. Biophys. Acta | pmid:6435674 |
| Miner VW and Prestegard JH | Structure of divalent cation-phosphatidic acid complexes as determined by 31P-NMR. | 1984 | Biochim. Biophys. Acta | pmid:6743656 |
| Brasseur R et al. | Mode of organization of lipid aggregates: a conformational analysis. | 1984 | Biosci. Rep. | pmid:6547066 |
| Smaal EB et al. | Essential adaptation of the calcium influx assay into liposomes with entrapped arsenazo III for studies on the possible calcium translocating properties of acidic phospholipids. | 1985 | Biochim. Biophys. Acta | pmid:3924100 |
| Nicolay K et al. | Ethylene glycol causes acyl chain disordering in liquid-crystalline, unsaturated phospholipid model membranes, as measured by 2H NMR. | 1986 | FEBS Lett. | pmid:3803574 |
| Houslay MD et al. | Acidic phospholipid species inhibit adenylate cyclase activity in rat liver plasma membranes. | 1986 | Biochem. J. | pmid:3741383 |
| Smaal EB et al. | Consequences of the interaction of calcium with dioleoylphosphatidate-containing model membranes: changes in membrane permeability. | 1986 | Biochim. Biophys. Acta | pmid:3730389 |
| Smaal EB et al. | 2H-NMR, 31P-NMR and DSC characterization of a novel lipid organization in calcium-dioleoylphosphatidate membranes. Implications for the mechanism of the phosphatidate calcium transmembrane shuttle. | 1987 | Biochim. Biophys. Acta | pmid:3814595 |
| Smaal EB et al. | Consequences of the interaction of calcium with dioleoylphosphatidate-containing model membranes: calcium-membrane and membrane-membrane interactions. | 1987 | Biochim. Biophys. Acta | pmid:3099843 |
| Woźniak M et al. | The influence of phosphatidate bilayers on pig heart AMP deaminase. Crucial role of pH-dependent lipid-phase transition. | 1988 | Biochem. J. | pmid:3214434 |
| Lebeau L et al. | Two-dimensional crystallization of DNA gyrase B subunit on specifically designed lipid monolayers. | 1990 | FEBS Lett. | pmid:2163898 |
| Lin YP and Carman GM | Kinetic analysis of yeast phosphatidate phosphatase toward Triton X-100/phosphatidate mixed micelles. | 1990 | J. Biol. Chem. | pmid:2152917 |
| McGhee JG and Shoback DM | Effects of phosphatidic acid on parathyroid hormone release, intracellular free Ca2+, and inositol phosphates in dispersed bovine parathyroid cells. | 1990 | Endocrinology | pmid:2153532 |
| Sun J and Petersheim M | Lanthanide(III)-phosphatidic acid complexes: binding site heterogeneity and phase separation. | 1990 | Biochim. Biophys. Acta | pmid:2110832 |
| Spruijt RB et al. | Interaction of non-enveloped plant viruses and their viral coat proteins with phospholipid vesicles. | 1991 | Biochim. Biophys. Acta | pmid:2059653 |
| Ferguson JE and Hanley MR | Phosphatidic acid and lysophosphatidic acid stimulate receptor-regulated membrane currents in the Xenopus laevis oocyte. | 1992 | Arch. Biochem. Biophys. | pmid:1379791 |
| McCarthy MP and Moore MA | Effects of lipids and detergents on the conformation of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo californica. | 1992 | J. Biol. Chem. | pmid:1560000 |
| Oja CD et al. | Influence of dose on liposome clearance: critical role of blood proteins. | 1996 | Biochim. Biophys. Acta | pmid:8652601 |
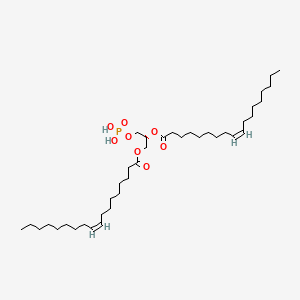
PA(18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z))
PA(18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z)) is a lipid of Glycerophospholipids (GP) class. The involved functions are known as adenylate cyclase activity, inhibitors, Drug Interactions, Membrane Fluidity and Force. Pa(18:1(9z)/18:1(9z)) often locates in Cell membrane, Tissue membrane, Epidermis, Connective Tissue and Back. The associated genes with PA(18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z)) are growth promoting activity and RAF1 gene. The related lipids are Phosphatidic Acid, Lysophospholipids, lysophosphatidic acid, Lysophosphatidylcholines and dioleoyl phosphate.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of PA(18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z)), we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with PA(18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z))?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
No disease MeSH terms mapped to the current reference collection.
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with PA(18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z))
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with PA(18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z))?
Visualization in cellular structure
Associated locations are in red color. Not associated locations are in black.
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Location | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What functions are associated with PA(18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z))?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with PA(18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z))?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Lipid concept | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What genes are associated with PA(18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z))?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Gene | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What common seen animal models are associated with PA(18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z))?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.