| MeSH term | MeSH ID | Detail |
|---|---|---|
| Abnormalities, Multiple | D000015 | 13 associated lipids |
| Abnormalities, Drug-Induced | D000014 | 10 associated lipids |
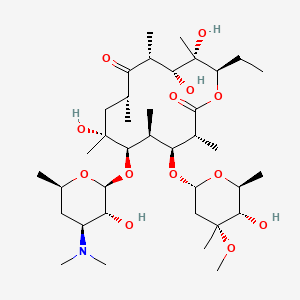
erythromycin
erythromycin is a lipid of Polyketides (PK) class. Erythromycin is associated with abnormalities such as Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome, Pneumonia, Infection, Pneumococcal Infections and Exanthema. The involved functions are known as Pharmacodynamics, Sterility, Agent, Drug Kinetics and Adjudication. Erythromycin often locates in Blood, peritoneal, Extracellular, Ribosomes and apicoplast. The associated genes with erythromycin are P4HTM gene, SLC33A1 gene, FAM3B gene, Operon and Homologous Gene. The related lipids are Hydroxytestosterones, Steroids, Propionate, Mycolic Acids and campesterol. The related experimental models are Mouse Model and Knock-out.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of erythromycin, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with erythromycin?
erythromycin is suspected in Pneumonia, Infection, Gonorrhea, Cystic Fibrosis, Respiratory Tract Infections, Influenza and other diseases in descending order of the highest number of associated sentences.
Related references are mostly published in these journals:
- Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. (35)
- J. Antimicrob. Chemother. (18)
- Clin. Infect. Dis. (2)
- Others (29)
| Disease | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literature |
|---|
Possible diseases from mapped MeSH terms on references
We collected disease MeSH terms mapped to the references associated with erythromycin
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with erythromycin
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with erythromycin?
Visualization in cellular structure
Associated locations are in red color. Not associated locations are in black.
Related references are published most in these journals:
- Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. (20)
- J. Antimicrob. Chemother. (9)
- FEMS Microbiol. Lett. (2)
- Others (20)
| Location | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What functions are associated with erythromycin?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with erythromycin?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Lipid concept | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What genes are associated with erythromycin?
Related references are published most in these journals:
- Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. (19)
- J. Antimicrob. Chemother. (10)
- Drug Metab. Dispos. (5)
- Others (29)
| Gene | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What common seen animal models are associated with erythromycin?
Mouse Model
Mouse Model are used in the study 'In vitro and in vivo activities of macrolide derivatives against Mycobacterium tuberculosis.' (Falzari K et al., 2005) and Mouse Model are used in the study 'Activity of ABT-773 against Mycobacterium avium complex in the beige mouse model.' (Cynamon MH et al., 2000).
Knock-out
Knock-out are used in the study 'Functional expression and comparative characterization of nine murine cytochromes P450 by fluorescent inhibition screening.' (McLaughlin LA et al., 2008).
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Model | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
NCBI Entrez Crosslinks
All references with erythromycin
Download all related citations| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Suzuki H et al. | [Il-8 secretion by cultured epithelial cells of human nasal mucosa and its suppression by macrolide antibiotics]. | 1997 | Jpn J Antibiot | pmid:9597442 |
| Nakada J et al. | [Effects of erythromycin and roxithromycin on airway goblet cell secretion]. | 1997 | Jpn J Antibiot | pmid:9597441 |
| Ieshiro R et al. | [Effect of clarithromycin in extending the life expectancy of patients with non-small-cell lung cancer]. | 1997 | Jpn J Antibiot | pmid:9597440 |
| Sakata K et al. | [Effects of macrolide antibiotics to inhibit infiltration and proliferation of malignant tumor cells--in vitro evaluation]. | 1997 | Jpn J Antibiot | pmid:9597435 |
| Hoover J | "Antibiotic selection for endodontic infections". | 1995 | J Gt Houst Dent Soc | pmid:9594808 |
| de Bethune MP and Nierhaus KH | Characterisation of the binding of virginiamycin S to Escherichia coli ribosomes. | 1978 | Eur. J. Biochem. | pmid:95947 |
| Dodhia H and Miller E | Review of the evidence for the use of erythromycin in the management of persons exposed to pertussis. | 1998 | Epidemiol. Infect. | pmid:9593483 |
| Spangler SK et al. | Postantibiotic effect and postantibiotic sub-MIC effect of levofloxacin compared to those of ofloxacin, ciprofloxacin, erythromycin, azithromycin, and clarithromycin against 20 pneumococci. | 1998 | Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. | pmid:9593160 |
| Goldstein EJ et al. | Activities of HMR 3004 (RU 64004) and HMR 3647 (RU 66647) compared to those of erythromycin, azithromycin, clarithromycin, roxithromycin, and eight other antimicrobial agents against unusual aerobic and anaerobic human and animal bite pathogens isolated from skin and soft tissue infections in humans. | 1998 | Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. | pmid:9593139 |
| Wieteska M | [Legionnaires' diseases]. | 1998 | Pol. Merkur. Lekarski | pmid:9591446 |
| Boiron M et al. | Erythromycin elicits opposite effects on antro-bulbar and duodenal motility: analysis in diabetics by cineradiography. | 1997 | Arch. Physiol. Biochem. | pmid:9587651 |
| Bertho G et al. | Solution conformation of methylated macrolide antibiotics roxithromycin and erythromycin using NMR and molecular modelling. Ribosome-bound conformation determined by TRNOE and formation of cytochrome P450-metabolite complex. | 1998 | Int. J. Biol. Macromol. | pmid:9585888 |
| Bouvier d'Yvoire MJ et al. | Computer-aided prediction of macrolide antibiotic concentrations in human circulating polymorphonuclear leucocytes. | 1998 | J. Antimicrob. Chemother. | pmid:9579715 |
| Malizia T et al. | Synergic interactions of macrolides and proton-pump inhibitors against Helicobacter pylori: a comparative in-vitro study. | 1998 | J. Antimicrob. Chemother. | pmid:9579710 |
| Brett M et al. | The comparative in-vitro activity of roxithromycin and other antibiotics against Bordetella pertussis. | 1998 | J. Antimicrob. Chemother. | pmid:9579709 |
| Ednie LM et al. | Anti-anaerobic activity of erythromycin, azithromycin and clarithromycin: effect of pH adjustment of media to compensate for pH shift caused by incubation in CO2. | 1998 | J. Antimicrob. Chemother. | pmid:9578166 |
| Bassotti G et al. | Effect of different doses of erythromycin on colonic motility in patients with slow transit constipation. | 1998 | Z Gastroenterol | pmid:9577904 |
| Hoppe JE | Susceptibility testing of Bordetella pertussis. | 1998 | J. Clin. Microbiol. | pmid:9574735 |
| Higa F et al. | Simplified quantitative assay system for measuring activities of drugs against intracellular Legionella pneumophila. | 1998 | J. Clin. Microbiol. | pmid:9574712 |
| Piccolomini R et al. | In vitro antimicrobial susceptibility of periodontopathic Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans to roxithromycin and erythromycin. | 1997 | Oral Microbiol. Immunol. | pmid:9573812 |