| MeSH term | MeSH ID | Detail |
|---|---|---|
| Bacterial Infections | D001424 | 21 associated lipids |
| Body Weight | D001835 | 333 associated lipids |
| Drug Hypersensitivity | D004342 | 20 associated lipids |
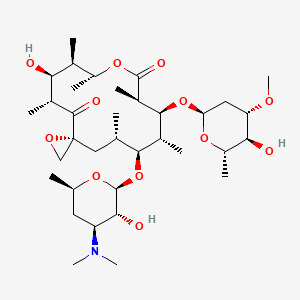
oleandomycin
oleandomycin is a lipid of Polyketides (PK) class. The involved functions are known as 5-(carboxyamino)imidazole ribonucleotide mutase activity, Methylation, enzyme activity, Anabolism and Biosynthetic Pathways. Oleandomycin often locates in Chromosomes and Protoplasm. The associated genes with oleandomycin are resistance genes, Open Reading Frames, CTTNBP2 gene, Gene Feature and Gene Clusters.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of oleandomycin, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with oleandomycin?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
Possible diseases from mapped MeSH terms on references
We collected disease MeSH terms mapped to the references associated with oleandomycin
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with oleandomycin
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with oleandomycin?
Visualization in cellular structure
Associated locations are in red color. Not associated locations are in black.
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Location | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What functions are associated with oleandomycin?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with oleandomycin?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
What genes are associated with oleandomycin?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Gene | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What common seen animal models are associated with oleandomycin?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
NCBI Entrez Crosslinks
All references with oleandomycin
Download all related citations| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kimura Y et al. | Characterization of the mac-1 gene encoding a putative ABC transporter from Myxococcus xanthus. | 2001 | J. Biochem. | pmid:11226873 |
| Smirnov VV et al. | [Gram-negative eubacteria isolated from the water, molluscs and algae of the Black Sea]. | 2001 Jul-Aug | Mikrobiol. Z. | pmid:11692675 |
| Long PF et al. | Engineering specificity of starter unit selection by the erythromycin-producing polyketide synthase. | 2002 | Mol. Microbiol. | pmid:11918808 |
| Gaisser S et al. | Parallel pathways for oxidation of 14-membered polyketide macrolactones in Saccharopolyspora erythraea. | 2002 | Mol. Microbiol. | pmid:11994157 |
| Kim YH et al. | Purification and characterization of an erythromycin esterase from an erythromycin-resistant Pseudomonas sp. | 2002 | FEMS Microbiol. Lett. | pmid:12044681 |
| Milanova A and Lashev L | Pharmacokinetics of oleandomycin in dogs after intravenous or oral administration alone and after pretreatment with metamizole or dexamethasone. | 2002 | Vet. Res. Commun. | pmid:11860088 |
| Di Modugno V et al. | Low level resistance to oleandomycin as a marker of ermA in staphylococci. | 2002 | J. Antimicrob. Chemother. | pmid:11815596 |
| Schlüsener MP et al. | Determination of antibiotics from soil by pressurized liquid extraction and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. | 2003 | J Chromatogr A | pmid:12899294 |
| González de la Huebra MJ et al. | Comparative study of coulometric and amperometric detection for the determination of macrolides in human urine using high-performance liquid chromatography. | 2003 | Anal Bioanal Chem | pmid:12733015 |
| Wang J | Determination of five macrolide antibiotic residues in honey by LC-ESI-MS and LC-ESI-MS/MS. | 2004 | J. Agric. Food Chem. | pmid:14733491 |