| MeSH term | MeSH ID | Detail |
|---|---|---|
| Lung Neoplasms | D008175 | 171 associated lipids |
| Adenocarcinoma | D000230 | 166 associated lipids |
| Neoplasms | D009369 | 13 associated lipids |
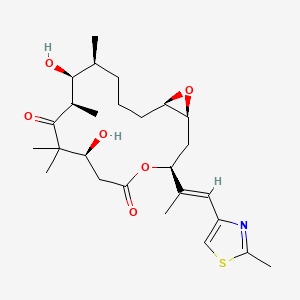
Epothilone A
Epothilone a is a lipid of Polyketides (PK) class. Epothilone a is associated with abnormalities such as abnormal fragmented structure and Hyperostosis, Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal. The involved functions are known as Polymerization, Mutation, Depolymerization, Musculoskeletal torsion, function and Negative Regulation of Microtubule Depolymerization. Epothilone a often locates in Microtubules, soluble, Nuclear Structure and Microtubule cytoskeleton. The associated genes with Epothilone A are C9 gene, SLC33A1 gene, KIF2C gene and HMHA1 gene.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of Epothilone A, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with Epothilone A?
Epothilone A is suspected in and other diseases in descending order of the highest number of associated sentences.
Related references are mostly published in these journals:
| Disease | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literature |
|---|
Possible diseases from mapped MeSH terms on references
We collected disease MeSH terms mapped to the references associated with Epothilone A
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with Epothilone A
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with Epothilone A?
Visualization in cellular structure
Associated locations are in red color. Not associated locations are in black.
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Location | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What functions are associated with Epothilone A?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with Epothilone A?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
What genes are associated with Epothilone A?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Gene | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What common seen animal models are associated with Epothilone A?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
NCBI Entrez Crosslinks
All references with Epothilone A
Download all related citations| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wang YL et al. | Microbial transformation of epothilone A by Aspergillus niger AS 3.739. | 2009 | J Asian Nat Prod Res | pmid:19431017 |
| Jiménez VA | Quantum-chemical study on the bioactive conformation of epothilones. | 2010 | J Chem Inf Model | pmid:21077585 |
| Rusinska-Roszak D et al. | Extended and clustered conformers of epothilone A. | 2011 | J Phys Chem B | pmid:21405036 |
| Bode JW and Carreira EM | Stereoselective syntheses of epothilones A and B via directed nitrile oxide cycloaddition. | 2001 | J. Am. Chem. Soc. | pmid:11472140 |
| Gerth K et al. | Epothilons A and B: antifungal and cytotoxic compounds from Sorangium cellulosum (Myxobacteria). Production, physico-chemical and biological properties. | 1996 | J. Antibiot. | pmid:8698639 |
| Gerth K et al. | Studies on the biosynthesis of epothilones: hydroxylation of Epo A and B to epothilones E and F. | 2002 | J. Antibiot. | pmid:11918064 |
| Gerth K et al. | Studies on the biosynthesis of epothilones: the PKS and Epothilone C/D monooxygenase. | 2001 | J. Antibiot. | pmid:11302486 |
| Kowalski RJ et al. | Activities of the microtubule-stabilizing agents epothilones A and B with purified tubulin and in cells resistant to paclitaxel (Taxol(R)). | 1997 | J. Biol. Chem. | pmid:8999970 |
| Shi G et al. | Structural insight into the mechanism of epothilone A bound to beta-tubulin and its mutants at Arg282Gln and Thr274Ile. | 2012 | J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. | pmid:22731768 |
| Jiménez VA et al. | Structural insight into epothilones antitumor activity based on the conformational preferences and tubulin binding modes of epothilones A and B obtained from molecular dynamics simulations. | 2015 | J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. | pmid:24773261 |