| MeSH term | MeSH ID | Detail |
|---|---|---|
| Adenocarcinoma | D000230 | 166 associated lipids |
| Neoplasms | D009369 | 13 associated lipids |
| Lung Neoplasms | D008175 | 171 associated lipids |
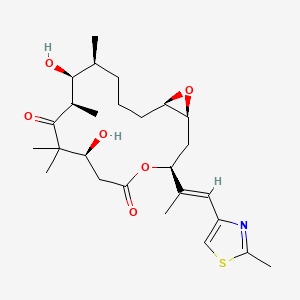
Epothilone A
Epothilone a is a lipid of Polyketides (PK) class. Epothilone a is associated with abnormalities such as abnormal fragmented structure and Hyperostosis, Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal. The involved functions are known as Polymerization, Mutation, Depolymerization, Musculoskeletal torsion, function and Negative Regulation of Microtubule Depolymerization. Epothilone a often locates in Microtubules, soluble, Nuclear Structure and Microtubule cytoskeleton. The associated genes with Epothilone A are C9 gene, SLC33A1 gene, KIF2C gene and HMHA1 gene.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of Epothilone A, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with Epothilone A?
Epothilone A is suspected in and other diseases in descending order of the highest number of associated sentences.
Related references are mostly published in these journals:
| Disease | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literature |
|---|
Possible diseases from mapped MeSH terms on references
We collected disease MeSH terms mapped to the references associated with Epothilone A
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with Epothilone A
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with Epothilone A?
Visualization in cellular structure
Associated locations are in red color. Not associated locations are in black.
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Location | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What functions are associated with Epothilone A?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with Epothilone A?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
What genes are associated with Epothilone A?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Gene | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What common seen animal models are associated with Epothilone A?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
NCBI Entrez Crosslinks
All references with Epothilone A
Download all related citations| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sefkow M et al. | Derivatization of the C12-C13 functional groups of epothilones A, B and C. | 1998 | Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. | pmid:9873670 |
| Sefkow M et al. | Oxidative and reductive transformations of epothilone A. | 1998 | Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. | pmid:9873669 |
| Sinha SC et al. | The antibody catalysis route to the total synthesis of epothilones. | 1998 | Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. | pmid:9843936 |
| Finney NS | Enantioselective epoxide hydrolysis: catalysis involving microbes, mammals and metals. | 1998 | Chem. Biol. | pmid:9571210 |
| Taraschi TF et al. | Plasmodium falciparum: characterization of organelle migration during merozoite morphogenesis in asexual malaria infections. | 1998 | Exp. Parasitol. | pmid:9562421 |
| Nicolaou KC et al. | Synthesis of epothilones A and B in solid and solution phase. | 1997 | Nature | pmid:9153390 |
| Cowden CJ and Paterson I | Synthetic chemistry. Cancer drugs better than taxol? | 1997 | Nature | pmid:9153384 |
| Kowalski RJ et al. | Activities of the microtubule-stabilizing agents epothilones A and B with purified tubulin and in cells resistant to paclitaxel (Taxol(R)). | 1997 | J. Biol. Chem. | pmid:8999970 |
| Mann J | Myxobacterial bounty. | 1997 | Nature | pmid:8990108 |
| Service RF | Tumor-killer made; how does it work? | 1996 | Science | pmid:8984658 |
| Gerth K et al. | Epothilons A and B: antifungal and cytotoxic compounds from Sorangium cellulosum (Myxobacteria). Production, physico-chemical and biological properties. | 1996 | J. Antibiot. | pmid:8698639 |
| Bollag DM et al. | Epothilones, a new class of microtubule-stabilizing agents with a taxol-like mechanism of action. | 1995 | Cancer Res. | pmid:7757983 |
| Rogalska A et al. | Metformin and epothilone A treatment up regulate pro-apoptotic PARP-1, Casp-3 and H2AX genes and decrease of AKT kinase level to control cell death of human hepatocellular carcinoma and ovary adenocarcinoma cells. | 2018 | Toxicol In Vitro | pmid:29117515 |
| Jiménez VA et al. | Molecular modeling study on the tubulin-binding modes of epothilone derivatives: Insight into the structural basis for epothilones activity. | 2017 | Chem Biol Drug Des | pmid:28632973 |
| Rogalska A et al. | Effects of Epothilone A in Combination with the Antidiabetic Drugs Metformin and Sitagliptin in HepG2 Human Hepatocellular Cancer Cells: Role of Transcriptional Factors NF-κB and p53. | 2016 | Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. | pmid:27039825 |
| Ranade AR et al. | Characterizing the Epothilone Binding Site on β-Tubulin by Photoaffinity Labeling: Identification of β-Tubulin Peptides TARGSQQY and TSRGSQQY as Targets of an Epothilone Photoprobe for Polymerized Tubulin. | 2016 | J. Med. Chem. | pmid:26986898 |
| Parajuli P et al. | Enzymatic synthesis of lactosylated and sialylated derivatives of epothilone A. | 2016 | Glycoconj. J. | pmid:26852037 |
| Borrelli S et al. | New class of squalene-based releasable nanoassemblies of paclitaxel, podophyllotoxin, camptothecin and epothilone A. | 2014 | Eur J Med Chem | pmid:25084144 |
| Jiménez VA et al. | Structural insight into epothilones antitumor activity based on the conformational preferences and tubulin binding modes of epothilones A and B obtained from molecular dynamics simulations. | 2015 | J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. | pmid:24773261 |
| Xiao CF et al. | Investigation of inclusion complex of epothilone A with cyclodextrins. | 2014 | Carbohydr Polym | pmid:24507285 |
| Prota AE et al. | Molecular mechanism of action of microtubule-stabilizing anticancer agents. | 2013 | Science | pmid:23287720 |
| Yu D et al. | Mechanical and functional properties of epothilone-stabilized microtubules. | 2013 | Cytoskeleton (Hoboken) | pmid:23135951 |
| Rogalska A et al. | Induction of apoptosis in human ovarian cancer cells by new anticancer compounds, epothilone A and B. | 2013 | Toxicol In Vitro | pmid:22995584 |
| Shi G et al. | Structural insight into the mechanism of epothilone A bound to beta-tubulin and its mutants at Arg282Gln and Thr274Ile. | 2012 | J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. | pmid:22731768 |
| Kamel K and Kolinski A | Computational study of binding of epothilone A to β-tubulin. | 2011 | Acta Biochim. Pol. | pmid:21633729 |
| Ganguly A et al. | Overexpression of mitotic centromere-associated Kinesin stimulates microtubule detachment and confers resistance to paclitaxel. | 2011 | Mol. Cancer Ther. | pmid:21471284 |
| Rusinska-Roszak D et al. | Extended and clustered conformers of epothilone A. | 2011 | J Phys Chem B | pmid:21405036 |
| Jiménez VA | Quantum-chemical study on the bioactive conformation of epothilones. | 2010 | J Chem Inf Model | pmid:21077585 |
| Passarella D et al. | Synthesis and biological evaluation of epothilone A dimeric compounds. | 2009 | Bioorg. Med. Chem. | pmid:19804980 |
| Pfeiffer B et al. | Synthesis and SAR of C12-C13-oxazoline derivatives of epothilone A. | 2009 | Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. | pmid:19433359 |
| Wang YL et al. | Microbial transformation of epothilone A by Aspergillus niger AS 3.739. | 2009 | J Asian Nat Prod Res | pmid:19431017 |
| Zhan W et al. | Design and synthesis of C6-C8 bridged epothilone A. | 2008 | Org. Lett. | pmid:18355076 |
| Erdélyi M et al. | Conformational preferences of natural and C3-modified epothilones in aqueous solution. | 2008 | J. Med. Chem. | pmid:18271516 |
| Sakaushi S et al. | Differential responses of mitotic spindle pole formation to microtubule-stabilizing agents epothilones A and B at low concentrations. | 2008 | Cell Cycle | pmid:18235240 |
| Reese M et al. | Structural basis of the activity of the microtubule-stabilizing agent epothilone a studied by NMR spectroscopy in solution. | 2007 | Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. | pmid:17274084 |
| Buey RM et al. | Cyclostreptin binds covalently to microtubule pores and lumenal taxoid binding sites. | 2007 | Nat. Chem. Biol. | pmid:17206139 |
| Seyb KI et al. | beta-Amyloid and endoplasmic reticulum stress responses in primary neurons: effects of drugs that interact with the cytoskeleton. | 2006 | J. Mol. Neurosci. | pmid:16679552 |
| Han C et al. | Prostaglandins from a zoanthid: paclitaxel-like neurite-degenerating and microtubule-stabilizating activities. | 2006 | Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. | pmid:16556989 |
| Cachoux F et al. | Total synthesis and biological assessment of benzimidazole-based analogues of epothilone A: ambivalent effects on cancer cell growth inhibition. | 2006 | Chembiochem | pmid:16345113 |
| Ramachandran PV et al. | Studies towards the synthesis of epothilone A via organoboranes. | 2005 | Org. Biomol. Chem. | pmid:16211118 |
| Sánchez-Pedregal VM et al. | The INPHARMA method: protein-mediated interligand NOEs for pharmacophore mapping. | 2005 | Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. | pmid:15929149 |
| Heinz DW et al. | Much anticipated--the bioactive conformation of epothilone and its binding to tubulin. | 2005 | Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. | pmid:15714588 |
| Ogura H et al. | EpoK, a cytochrome P450 involved in biosynthesis of the anticancer agents epothilones A and B. Substrate-mediated rescue of a P450 enzyme. | 2004 | Biochemistry | pmid:15544342 |
| Nettles JH et al. | The binding mode of epothilone A on alpha,beta-tubulin by electron crystallography. | 2004 | Science | pmid:15297674 |
| Hu W et al. | A high-throughput model for screening anti-tumor agents capable of promoting polymerization of tubulin in vitro. | 2004 | Acta Pharmacol. Sin. | pmid:15169631 |
| Kingston DG | What makes epothilones stick? | 2004 | Chem. Biol. | pmid:15123274 |
| Altmann KH et al. | 4. The natural products epothilones A and B as lead structures for anticancer drug discovery: chemistry, biology, and SAR studies. | 2004 | Prog Med Chem | pmid:15003721 |
| Carlomagno T et al. | Derivation of dihedral angles from CH-CH dipolar-dipolar cross-correlated relaxation rates: a C-C torsion involving a quaternary carbon atom in epothilone A bound to tubulin. | 2003 | Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. | pmid:12800174 |
| Carlomagno T et al. | The high-resolution solution structure of epothilone A bound to tubulin: an understanding of the structure-activity relationships for a powerful class of antitumor agents. | 2003 | Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. | pmid:12800173 |
| Walsh CT et al. | Polyketide-nonribosomal peptide epothilone antitumor agents: the EpoA, B, C subunits. | 2003 | J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. | pmid:12707798 |