| MeSH term | MeSH ID | Detail |
|---|---|---|
| Adenocarcinoma | D000230 | 166 associated lipids |
| Neoplasms | D009369 | 13 associated lipids |
| Lung Neoplasms | D008175 | 171 associated lipids |
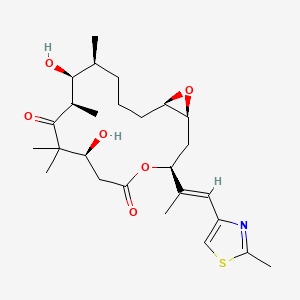
Epothilone A
Epothilone a is a lipid of Polyketides (PK) class. Epothilone a is associated with abnormalities such as abnormal fragmented structure and Hyperostosis, Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal. The involved functions are known as Polymerization, Mutation, Depolymerization, Musculoskeletal torsion, function and Negative Regulation of Microtubule Depolymerization. Epothilone a often locates in Microtubules, soluble, Nuclear Structure and Microtubule cytoskeleton. The associated genes with Epothilone A are C9 gene, SLC33A1 gene, KIF2C gene and HMHA1 gene.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of Epothilone A, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with Epothilone A?
Epothilone A is suspected in and other diseases in descending order of the highest number of associated sentences.
Related references are mostly published in these journals:
| Disease | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literature |
|---|
Possible diseases from mapped MeSH terms on references
We collected disease MeSH terms mapped to the references associated with Epothilone A
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with Epothilone A
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with Epothilone A?
Visualization in cellular structure
Associated locations are in red color. Not associated locations are in black.
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Location | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What functions are associated with Epothilone A?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with Epothilone A?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
What genes are associated with Epothilone A?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Gene | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What common seen animal models are associated with Epothilone A?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
NCBI Entrez Crosslinks
All references with Epothilone A
Download all related citations| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pmid: | ||||
| Kamel K and Kolinski A | Computational study of binding of epothilone A to β-tubulin. | 2011 | Acta Biochim. Pol. | pmid:21633729 |
| Hu W et al. | A high-throughput model for screening anti-tumor agents capable of promoting polymerization of tubulin in vitro. | 2004 | Acta Pharmacol. Sin. | pmid:15169631 |
| Carlomagno T et al. | The high-resolution solution structure of epothilone A bound to tubulin: an understanding of the structure-activity relationships for a powerful class of antitumor agents. | 2003 | Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. | pmid:12800173 |
| Carlomagno T et al. | Derivation of dihedral angles from CH-CH dipolar-dipolar cross-correlated relaxation rates: a C-C torsion involving a quaternary carbon atom in epothilone A bound to tubulin. | 2003 | Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. | pmid:12800174 |
| Reese M et al. | Structural basis of the activity of the microtubule-stabilizing agent epothilone a studied by NMR spectroscopy in solution. | 2007 | Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. | pmid:17274084 |
| Heinz DW et al. | Much anticipated--the bioactive conformation of epothilone and its binding to tubulin. | 2005 | Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. | pmid:15714588 |
| Sánchez-Pedregal VM et al. | The INPHARMA method: protein-mediated interligand NOEs for pharmacophore mapping. | 2005 | Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. | pmid:15929149 |
| Rogalska A et al. | Effects of Epothilone A in Combination with the Antidiabetic Drugs Metformin and Sitagliptin in HepG2 Human Hepatocellular Cancer Cells: Role of Transcriptional Factors NF-κB and p53. | 2016 | Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. | pmid:27039825 |
| Hamel E et al. | The coral-derived natural products eleutherobin and sarcodictyins A and B: effects on the assembly of purified tubulin with and without microtubule-associated proteins and binding at the polymer taxoid site. | 1999 | Biochemistry | pmid:10220336 |