| MeSH term | MeSH ID | Detail |
|---|---|---|
| Hemolysis | D006461 | 131 associated lipids |
| Adenocarcinoma | D000230 | 166 associated lipids |
| Lung Neoplasms | D008175 | 171 associated lipids |
| Reperfusion Injury | D015427 | 65 associated lipids |
| Colonic Neoplasms | D003110 | 161 associated lipids |
| Sarcoma 180 | D012510 | 21 associated lipids |
| Body Weight | D001835 | 333 associated lipids |
| Edema | D004487 | 152 associated lipids |
| Precancerous Conditions | D011230 | 48 associated lipids |
| Liver Diseases | D008107 | 31 associated lipids |
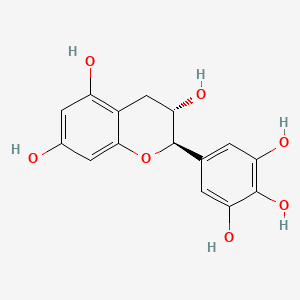
Gallocatechin
(+)-gallocatechin is a lipid of Polyketides (PK) class. The involved functions are known as inhibitors and Cell Survival. The associated genes with (+)-Gallocatechin are TERT gene.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of Gallocatechin, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with Gallocatechin?
Gallocatechin is suspected in Hyperinsulinism, nervous system disorder, Obesity, Parkinson Disease, Transient ischemia and other diseases in descending order of the highest number of associated sentences.
Related references are mostly published in these journals:
| Disease | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literature |
|---|
Possible diseases from mapped MeSH terms on references
We collected disease MeSH terms mapped to the references associated with Gallocatechin
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with Gallocatechin
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with Gallocatechin?
Visualization in cellular structure
Associated locations are in red color. Not associated locations are in black.
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Location | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What functions are associated with Gallocatechin?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with Gallocatechin?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Lipid concept | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What genes are associated with Gallocatechin?
Related references are published most in these journals:
- Drug Metab. Dispos. (4)
- Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. (2)
- Am. J. Physiol., Cell Physiol. (1)
- Others (7)
| Gene | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What common seen animal models are associated with Gallocatechin?
Transgenic Model
Transgenic Model are used in the study 'Dietary (-)-epicatechin as a potent inhibitor of βγ-secretase amyloid precursor protein processing.' (Cox CJ et al., 2015).
Rodent Model
Rodent Model are used in the study 'Dietary (-)-epicatechin as a potent inhibitor of βγ-secretase amyloid precursor protein processing.' (Cox CJ et al., 2015).
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Model | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
NCBI Entrez Crosslinks
All references with Gallocatechin
Download all related citations| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tawaha K et al. | A bioactive prodelphinidin from Mangifera indica leaf extract. | 2010 May-Jun | Z. Naturforsch., C, J. Biosci. | pmid:20653233 |
| Nakayama K et al. | Storage and allogeneic transplantation of peripheral nerve using a green tea polyphenol solution in a canine model. | 2010 | J Brachial Plex Peripher Nerve Inj | pmid:21110896 |
| Lee JE et al. | Geographical and climatic dependencies of green tea (Camellia sinensis) metabolites: a (1)H NMR-based metabolomics study. | 2010 | J. Agric. Food Chem. | pmid:20828156 |
| Lin SF et al. | Synthesis and structure-activity relationship of 3-O-acylated (-)-epigallocatechins as 5α-reductase inhibitors. | 2010 | Eur J Med Chem | pmid:21044810 |
| Ikeda H et al. | [Mechanism of interaction between risperidone and tea catechin(1)complex formation of risperidone with epigallocatechin gallate]. | 2010 | Yakugaku Zasshi | pmid:21048420 |
| Monobe M et al. | Effect on the epigallocatechin gallate/epigallocatechin ratio in a green tea (Camellia sinensis L.) extract of different extraction temperatures and its effect on IgA production in mice. | 2010 | Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. | pmid:21150115 |
| Mori T et al. | Covalent binding of tea catechins to protein thiols: the relationship between stability and electrophilic reactivity. | 2010 | Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. | pmid:21150116 |
| Ziaedini A et al. | Extraction of antioxidants and caffeine from green tea (Camelia sinensis) leaves: kinetics and modeling. | 2010 | Food Sci Technol Int | pmid:21339166 |
| Minoda K et al. | Influence of the galloyl moiety in tea catechins on binding affinity for human serum albumin. | 2010 | J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. | pmid:21228505 |
| Schmidt CA et al. | Catechin derivatives from Parapiptadenia rigida with in vitro wound-healing properties. | 2010 | J. Nat. Prod. | pmid:21080642 |
| Del Rio D et al. | Bioavailability of catechins from ready-to-drink tea. | 2010 | Nutrition | pmid:19765952 |
| Nakamura H et al. | Green tea catechin inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced bone resorption in vivo. | 2010 | J. Periodont. Res. | pmid:19602116 |
| Luo J et al. | Urinary polyphenols and breast cancer risk: results from the Shanghai Women's Health Study. | 2010 | Breast Cancer Res. Treat. | pmid:19653095 |
| Wang CJ et al. | (-)-epigallocatechin gallate inhibits endothelin-1-induced C-reactive protein production in vascular smooth muscle cells. | 2010 | Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. | pmid:20346058 |
| Hurst SM et al. | Blackcurrant proanthocyanidins augment IFN-gamma-induced suppression of IL-4 stimulated CCL26 secretion in alveolar epithelial cells. | 2010 | Mol Nutr Food Res | pmid:20229526 |
| Cao P et al. | Effect of green tea catechins and hydrolyzable tannins on benzo[a]pyrene-induced DNA adducts and structure-activity relationship. | 2010 | Chem. Res. Toxicol. | pmid:20218540 |
| Stalmach A et al. | Absorption, metabolism, and excretion of green tea flavan-3-ols in humans with an ileostomy. | 2010 | Mol Nutr Food Res | pmid:19937856 |
| Das A et al. | Flavonoids activated caspases for apoptosis in human glioblastoma T98G and U87MG cells but not in human normal astrocytes. | 2010 | Cancer | pmid:19894226 |
| Korte G et al. | Tea catechins' affinity for human cannabinoid receptors. | 2010 | Phytomedicine | pmid:19897346 |
| Ishii T et al. | Binding affinity of tea catechins for HSA: characterization by high-performance affinity chromatography with immobilized albumin column. | 2010 | Mol Nutr Food Res | pmid:20013883 |
| Li Y et al. | Reaction of the black tea pigment theaflavin during enzymatic oxidation of tea catechins. | 2010 | J. Nat. Prod. | pmid:20014758 |
| Jun X et al. | Separation of major catechins from green tea by ultrahigh pressure extraction. | 2010 | Int J Pharm | pmid:19874878 |
| Iwasaki M et al. | Plasma tea polyphenol levels and subsequent risk of breast cancer among Japanese women: a nested case-control study. | 2010 | Breast Cancer Res. Treat. | pmid:20440552 |
| Feng W et al. | Green tea catechins are potent sensitizers of ryanodine receptor type 1 (RyR1). | 2010 | Biochem. Pharmacol. | pmid:20471964 |
| Takagaki A and Nanjo F | Metabolism of (-)-epigallocatechin gallate by rat intestinal flora. | 2010 | J. Agric. Food Chem. | pmid:20043675 |
| Shen YX et al. | A new chromone derivative from Berchemia lineata. | 2010 | Yao Xue Xue Bao | pmid:21348425 |
| Ueda M et al. | Tea catechins modulate the glucose transport system in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. | 2010 | Food Funct | pmid:21776468 |
| Wang YH et al. | Development of a whole-organism model to screen new compounds for sun protection. | 2009 May-Jun | Mar. Biotechnol. | pmid:19005726 |
| Tanaka T et al. | Chemistry of secondary polyphenols produced during processing of tea and selected foods. | 2009 | Int J Mol Sci | pmid:20161999 |
| Yang CH et al. | Supplementary catechins attenuate cooking-oil-fumes-induced oxidative stress in rat lung. | 2009 | Chin J Physiol | pmid:19777801 |
| Neyestani TR et al. | Selective effects of tea extract and its phenolic compounds on human peripheral blood mononuclear cell cytokine secretions. | 2009 | Int J Food Sci Nutr | pmid:18686109 |
| Ozyürek M et al. | Measurement of xanthine oxidase inhibition activity of phenolics and flavonoids with a modified cupric reducing antioxidant capacity (CUPRAC) method. | 2009 | Anal. Chim. Acta | pmid:19231354 |
| Shin BC et al. | The protective effects of green tea extract against L-arginine toxicity to cultured human mesangial cells. | 2009 | J. Korean Med. Sci. | pmid:19194554 |
| Al-Bloushi S et al. | Green tea modulates reserpine toxicity in animal models. | 2009 | J Toxicol Sci | pmid:19182437 |
| Hu J et al. | Preparation and antioxidant activity of green tea extract enriched in epigallocatechin (EGC) and epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG). | 2009 | J. Agric. Food Chem. | pmid:19182914 |
| Ku HC et al. | Green tea (-)-epigallocatechin gallate inhibits insulin stimulation of 3T3-L1 preadipocyte mitogenesis via the 67-kDa laminin receptor pathway. | 2009 | Am. J. Physiol., Cell Physiol. | pmid:19176763 |
| Stalmach A et al. | Absorption, metabolism and excretion of Choladi green tea flavan-3-ols by humans. | 2009 | Mol Nutr Food Res | pmid:18979506 |
| Ni HY and Zhang ZH | [Studies on the chemical constituents of Xanthoceras sorbifolia]. | 2009 | Zhong Yao Cai | pmid:19771840 |
| Jin SL et al. | Protective effect of epigallocatechin gallate on the immune function of dendritic cells after ultraviolet B irradiation. | 2009 | J Cosmet Dermatol | pmid:19735514 |
| Grace MH et al. | Phytochemical characterization of an adaptogenic preparation from Rhodiola heterodonta. | 2009 | Nat Prod Commun | pmid:19768982 |
| Thomas F et al. | Dihydrotestosterone sensitises LNCaP cells to death induced by epigallocatechin-3-Gallate (EGCG) or an IGF-I receptor inhibitor. | 2009 | Prostate | pmid:18942120 |
| Wei Y et al. | Separation of epigallocatechin and flavonoids from Hypericum perforatum L. by high-speed counter-current chromatography and preparative high-performance liquid chromatography. | 2009 | J Chromatogr A | pmid:19150073 |
| Ochiai H et al. | Epigallocatechin-3-gallate is an inhibitor of Na+, K(+)-ATPase by favoring the E1 conformation. | 2009 | Biochem. Pharmacol. | pmid:19539611 |
| Han DH and Kim JH | Difference in growth suppression and apoptosis induction of EGCG and EGC on human promyelocytic leukemia HL-60 cells. | 2009 | Arch. Pharm. Res. | pmid:19407972 |
| Kushima Y et al. | Inhibitory effect of (-)-epigallocatechin and (-)-epigallocatechin gallate against heregulin beta1-induced migration/invasion of the MCF-7 breast carcinoma cell line. | 2009 | Biol. Pharm. Bull. | pmid:19420761 |
| Severino JF et al. | Free radicals generated during oxidation of green tea polyphenols: electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy combined with density functional theory calculations. | 2009 | Free Radic. Biol. Med. | pmid:19439236 |
| Chang KC et al. | (-)Epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits the spontaneous firing of rat locus coeruleus neuron. | 2009 | Neurosci. Lett. | pmid:19383428 |
| Liu J et al. | Borate complexation-assisted field-enhanced sample injection for on-line preconcentration of cis-diol-containing compounds in capillary electrophoresis. | 2009 | Talanta | pmid:19836518 |
| Sato K and Toriyama M | Depigmenting effect of catechins. | 2009 | Molecules | pmid:19924076 |
| Park JH et al. | Ambivalent role of gallated catechins in glucose tolerance in humans: a novel insight into non-absorbable gallated catechin-derived inhibitors of glucose absorption. | 2009 | J. Physiol. Pharmacol. | pmid:20065503 |