| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hoshino N et al. | Damage to the cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli by catechin-copper (II) complexes. | 1999 | Free Radic. Biol. Med. | pmid:10641717 |
| Manach C et al. | Comparison of the bioavailability of quercetin and catechin in rats. | 1999 | Free Radic. Biol. Med. | pmid:10641719 |
| Guo Q et al. | Electron spin resonance study of free radicals formed from a procyanidin-rich pine (Pinus maritima) bark extract, pycnogenol. | 1999 | Free Radic. Biol. Med. | pmid:10641725 |
| Bors W and Michel C | Antioxidant capacity of flavanols and gallate esters: pulse radiolysis studies. | 1999 | Free Radic. Biol. Med. | pmid:10641736 |
| Pan MH et al. | Suppression of lipopolysaccharide-induced nuclear factor-kappaB activity by theaflavin-3,3'-digallate from black tea and other polyphenols through down-regulation of IkappaB kinase activity in macrophages. | 2000 | Biochem. Pharmacol. | pmid:10644043 |
| Rimbach G et al. | Effect of procyanidins from Pinus maritima on glutathione levels in endothelial cells challenged by 3-morpholinosydnonimine or activated macrophages. | 1999 | Redox Rep. | pmid:10658822 |
| Van Dyke K et al. | Green tea extract and its polyphenols markedly inhibit luminol-dependent chemiluminescence activated by peroxynitrite or SIN-1. | 2000 Jan-Feb | Luminescence | pmid:10660664 |
| Bickii J et al. | In vitro antimalarial activity of limonoids from Khaya grandifoliola C.D.C. (Meliaceae). | 2000 | J Ethnopharmacol | pmid:10661881 |
| Hashimoto T et al. | Interaction of tea catechins with lipid bilayers investigated with liposome systems. | 1999 | Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. | pmid:10664864 |
| Bors W et al. | Electron paramagnetic resonance studies of radical species of proanthocyanidins and gallate esters. | 2000 | Arch. Biochem. Biophys. | pmid:10666317 |
| Yang TT and Koo MW | Chinese green tea lowers cholesterol level through an increase in fecal lipid excretion. | 2000 | Life Sci. | pmid:10670829 |
| Abe I et al. | Green tea polyphenols: novel and potent inhibitors of squalene epoxidase. | 2000 | Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. | pmid:10679280 |
| Tanaka T et al. | Oxidation and epimerization of epigallocatechin in banana fruits. | 2000 | Phytochemistry | pmid:10680189 |
| Higashimoto M et al. | Inhibitory effects of tea extracts on the mutagenicity of 1-methyl-1, 2,3,4-tetrahydro-beta-carboline-3-carboxylic acid on treatment with nitrite in the presence of ethanol. | 2000 | Food Chem. Toxicol. | pmid:10685009 |
| Ma C et al. | Inhibitory effects on HIV-1 protease of constituents from the wood of Xanthoceras sorbifolia. | 2000 | J. Nat. Prod. | pmid:10691716 |
| Kao YH et al. | Modulation of endocrine systems and food intake by green tea epigallocatechin gallate. | 2000 | Endocrinology | pmid:10698173 |
| Amarowicz R et al. | Antibacterial activity of green tea polyphenols against Escherichia coli K 12. | 2000 | Nahrung | pmid:10703004 |
| Saeki K et al. | Importance of a pyrogallol-type structure in catechin compounds for apoptosis-inducing activity. | 2000 | Phytochemistry | pmid:10703063 |
| Lee MJ et al. | An improved method for the determination of green and black tea polyphenols in biomatrices by high-performance liquid chromatography with coulometric array detection. | 2000 | Anal. Biochem. | pmid:10706785 |
| Sadzuka Y et al. | Efficacies of tea components on doxorubicin induced antitumor activity and reversal of multidrug resistance. | 2000 | Toxicol. Lett. | pmid:10713480 |
| Demeule M et al. | Matrix metalloproteinase inhibition by green tea catechins. | 2000 | Biochim. Biophys. Acta | pmid:10719174 |
| Li C et al. | Structural identification of two metabolites of catechins and their kinetics in human urine and blood after tea ingestion. | 2000 | Chem. Res. Toxicol. | pmid:10725114 |
| Merken HM and Beecher GR | Measurement of food flavonoids by high-performance liquid chromatography: A review. | 2000 | J. Agric. Food Chem. | pmid:10725120 |
| Tringali C et al. | Bioactive constituents of the bark of Parkia biglobosa. | 2000 | Fitoterapia | pmid:10727806 |
| Tachibana H et al. | Identification of a methylated tea catechin as an inhibitor of degranulation in human basophilic KU812 cells. | 2000 | Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. | pmid:10737211 |
| Gupta S et al. | Growth inhibition, cell-cycle dysregulation, and induction of apoptosis by green tea constituent (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate in androgen-sensitive and androgen-insensitive human prostate carcinoma cells. | 2000 | Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. | pmid:10739747 |
| Li HC et al. | Green tea polyphenols induce apoptosis in vitro in peripheral blood T lymphocytes of adult T-cell leukemia patients. | 2000 | Jpn. J. Cancer Res. | pmid:10744042 |
| Kang KS et al. | Preventive effect of epicatechin and ginsenoside Rb(2) on the inhibition of gap junctional intercellular communication by TPA and H(2)O(2). | 2000 | Cancer Lett. | pmid:10754211 |
| Fujiki H et al. | A new concept of tumor promotion by tumor necrosis factor-alpha, and cancer preventive agents (-)-epigallocatechin gallate and green tea--a review. | 2000 | Cancer Detect. Prev. | pmid:10757128 |
| Sachinidis A et al. | Green tea compounds inhibit tyrosine phosphorylation of PDGF beta-receptor and transformation of A172 human glioblastoma. | 2000 | FEBS Lett. | pmid:10760511 |
| Sakamoto K | Synergistic effects of thearubigin and genistein on human prostate tumor cell (PC-3) growth via cell cycle arrest. | 2000 | Cancer Lett. | pmid:10766429 |
| Islam S et al. | Involvement of caspase-3 in epigallocatechin-3-gallate-mediated apoptosis of human chondrosarcoma cells. | 2000 | Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. | pmid:10772904 |
| Ren F et al. | Tea polyphenols down-regulate the expression of the androgen receptor in LNCaP prostate cancer cells. | 2000 | Oncogene | pmid:10773882 |
| Zhu N et al. | Identification of oxidation products of (-)-epigallocatechin gallate and (-)-epigallocatechin with H(2)O(2). | 2000 | J. Agric. Food Chem. | pmid:10775337 |
| Ahmad N et al. | Green tea polyphenol epigallocatechin-3-gallate differentially modulates nuclear factor kappaB in cancer cells versus normal cells. | 2000 | Arch. Biochem. Biophys. | pmid:10775421 |
| Coetzee J et al. | Structure and synthesis of the first procassinidin dimers based on epicatechin, and gallo- and epigallo-catechin. | 2000 | Phytochemistry | pmid:10783985 |
| Yee YK and Koo MW | Anti-Helicobacter pylori activity of Chinese tea: in vitro study. | 2000 | Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. | pmid:10792128 |
| Maeda-Yamamoto M et al. | Effects of tea polyphenols on the invasion and matrix metalloproteinases activities of human fibrosarcoma HT1080 cells. | 1999 | J. Agric. Food Chem. | pmid:10794635 |
| Lee MH et al. | EBV DNA polymerase inhibition of tannins from Eugenia uniflora. | 2000 | Cancer Lett. | pmid:10806300 |
| Liberto M and Cobrinik D | Growth factor-dependent induction of p21(CIP1) by the green tea polyphenol, epigallocatechin gallate. | 2000 | Cancer Lett. | pmid:10806303 |
| Johnson MK and Loo G | Effects of epigallocatechin gallate and quercetin on oxidative damage to cellular DNA. | 2000 | Mutat. Res. | pmid:10812333 |
| Schwinger RH et al. | Crataegus special extract WS 1442 increases force of contraction in human myocardium cAMP-independently. | 2000 | J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. | pmid:10813370 |
| Castillo J et al. | Antioxidant activity and radioprotective effects against chromosomal damage induced in vivo by X-rays of flavan-3-ols (Procyanidins) from grape seeds (Vitis vinifera): comparative study versus other phenolic and organic compounds. | 2000 | J. Agric. Food Chem. | pmid:10820088 |
| Arts IC et al. | Catechin contents of foods commonly consumed in The Netherlands. 1. Fruits, vegetables, staple foods, and processed foods. | 2000 | J. Agric. Food Chem. | pmid:10820089 |
| Arts IC et al. | Catechin contents of foods commonly consumed in The Netherlands. 2. Tea, wine, fruit juices, and chocolate milk. | 2000 | J. Agric. Food Chem. | pmid:10820090 |
| Wang JN et al. | Procyanidins from the seeds of Vitis amurensis. | 2000 | Phytochemistry | pmid:10820838 |
| Aucamp JP et al. | Simultaneous analysis of tea catechins, caffeine, gallic acid, theanine and ascorbic acid by micellar electrokinetic capillary chromatography. | 2000 | J Chromatogr A | pmid:10823519 |
| Mukhtar H and Ahmad N | Tea polyphenols: prevention of cancer and optimizing health. | 2000 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:10837321 |
| Shi X et al. | Antioxidant properties of (-)-epicatechin-3-gallate and its inhibition of Cr(VI)-induced DNA damage and Cr(IV)- or TPA-stimulated NF-kappaB activation. | 2000 | Mol. Cell. Biochem. | pmid:10839202 |
| Reguant C et al. | Influence of phenolic compounds on the physiology of Oenococcus oeni from wine. | 2000 | J. Appl. Microbiol. | pmid:10849183 |
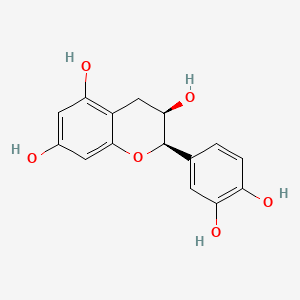
(-)-Epicatechin
(-)-Epicatechin is a lipid of Polyketides (PK) class.