| MeSH term | MeSH ID | Detail |
|---|---|---|
| Gastritis | D005756 | 27 associated lipids |
| Byssinosis | D002095 | 11 associated lipids |
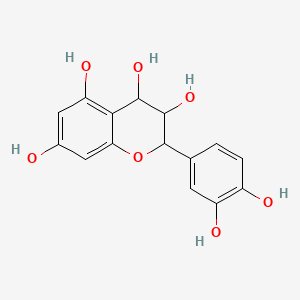
Leucocyanidin
Leucocyanidin is a lipid of Polyketides (PK) class. Leucocyanidin is associated with abnormalities such as Dehydration. The involved functions are known as Pigment, enzyme activity, proanthocyanidin biosynthetic process, Sterility and Signal. Leucocyanidin often locates in Body tissue, Autonomic nervous system, Cytosol, Vacuole and insoluble fraction. The associated genes with Leucocyanidin are F3 gene and Orthologous Gene. The related lipids are Butanols.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of Leucocyanidin, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with Leucocyanidin?
Leucocyanidin is suspected in Dehydration and other diseases in descending order of the highest number of associated sentences.
Related references are mostly published in these journals:
| Disease | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literature |
|---|
Possible diseases from mapped MeSH terms on references
We collected disease MeSH terms mapped to the references associated with Leucocyanidin
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with Leucocyanidin
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with Leucocyanidin?
Visualization in cellular structure
Associated locations are in red color. Not associated locations are in black.
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Location | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What functions are associated with Leucocyanidin?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with Leucocyanidin?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Lipid concept | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What genes are associated with Leucocyanidin?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Gene | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What common seen animal models are associated with Leucocyanidin?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
NCBI Entrez Crosslinks
All references with Leucocyanidin
Download all related citations| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pmid: | ||||
| Lewis DA et al. | A natural flavonoid present in unripe plantain banana pulp (Musa sapientum L. var. paradisiaca) protects the gastric mucosa from aspirin-induced erosions. | 1999 | J Ethnopharmacol | pmid:10404428 |
| Nakajima J et al. | Reaction mechanism from leucoanthocyanidin to anthocyanidin 3-glucoside, a key reaction for coloring in anthocyanin biosynthesis. | 2001 | J. Biol. Chem. | pmid:11316805 |
| Lans C et al. | Medicinal and ethnoveterinary remedies of hunters in Trinidad. | 2001 | BMC Complement Altern Med | pmid:11737880 |
| Ray H et al. | Expression of anthocyanins and proanthocyanidins after transformation of alfalfa with maize Lc. | 2003 | Plant Physiol. | pmid:12857826 |
| Abrahams S et al. | The Arabidopsis TDS4 gene encodes leucoanthocyanidin dioxygenase (LDOX) and is essential for proanthocyanidin synthesis and vacuole development. | 2003 | Plant J. | pmid:12940955 |
| FORSYTH WG and ROBERTS JB | Cacao polyphenolic substances. 5. The structure of cacao 'leucocyanidin 1. | 1960 | Biochem. J. | pmid:13824051 |
| Turnbull JJ et al. | The C-4 stereochemistry of leucocyanidin substrates for anthocyanidin synthase affects product selectivity. | 2003 | Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. | pmid:14552794 |
| Xie DY et al. | Molecular and biochemical analysis of two cDNA clones encoding dihydroflavonol-4-reductase from Medicago truncatula. | 2004 | Plant Physiol. | pmid:14976232 |
| Pang Y et al. | Early steps in proanthocyanidin biosynthesis in the model legume Medicago truncatula. | 2007 | Plant Physiol. | pmid:17885080 |
| Louie GV et al. | Structure and reaction mechanism of basil eugenol synthase. | 2007 | PLoS ONE | pmid:17912370 |
| Matsuda M et al. | Biotransformation of (+)-catechin into taxifolin by a two-step oxidation: primary stage of (+)-catechin metabolism by a novel (+)-catechin-degrading bacteria, Burkholderia sp. KTC-1, isolated from tropical peat. | 2008 | Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. | pmid:18068670 |
| Park JS et al. | Arabidopsis R2R3-MYB transcription factor AtMYB60 functions as a transcriptional repressor of anthocyanin biosynthesis in lettuce (Lactuca sativa). | 2008 | Plant Cell Rep. | pmid:18317777 |
| Xu F et al. | Molecular cloning and function analysis of an anthocyanidin synthase gene from Ginkgo biloba, and its expression in abiotic stress responses. | 2008 | Mol. Cells | pmid:18779661 |
| Chemler JA et al. | Improving NADPH availability for natural product biosynthesis in Escherichia coli by metabolic engineering. | 2010 | Metab. Eng. | pmid:19628048 |
| Hoorens B et al. | Neighbour identity hardly affects litter-mixture effects on decomposition rates of New Zealand forest species. | 2010 | Oecologia | pmid:19756760 |
| Auger B et al. | Brassica orthologs from BANYULS belong to a small multigene family, which is involved in procyanidin accumulation in the seed. | 2009 | Planta | pmid:19760260 |
| Han Y et al. | Ectopic expression of apple F3'H genes contributes to anthocyanin accumulation in the Arabidopsis tt7 mutant grown under nitrogen stress. | 2010 | Plant Physiol. | pmid:20357139 |
| Metwally AM et al. | Phytochemical investigation and antimicrobial activity of Psidium guajava L. leaves. | 2010 | Pharmacogn Mag | pmid:20931082 |
| Ponnusamy S et al. | Evaluation of traditional Indian antidiabetic medicinal plants for human pancreatic amylase inhibitory effect in vitro. | 2011 | Evid Based Complement Alternat Med | pmid:20953430 |