| MeSH term | MeSH ID | Detail |
|---|---|---|
| Alopecia | D000505 | 14 associated lipids |
| Neuroblastoma | D009447 | 66 associated lipids |
| Melanoma | D008545 | 69 associated lipids |
| Atherosclerosis | D050197 | 85 associated lipids |
| Glioma | D005910 | 112 associated lipids |
| Prostatic Neoplasms | D011471 | 126 associated lipids |
| Carcinoma, Hepatocellular | D006528 | 140 associated lipids |
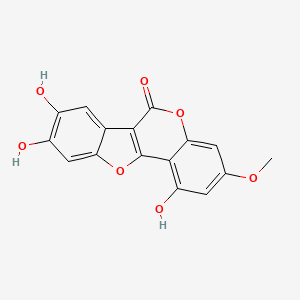
Wedelolactone
Wedelolactone is a lipid of Polyketides (PK) class. Wedelolactone is associated with abnormalities such as CLEFT LIP, CONGENITAL HEALED and Hepatitis. The involved functions are known as Signal Transduction, Cell Cycle Arrest, Apoptosis, luciferase activity and Metabolic Inhibition. Wedelolactone often locates in Protoplasm and Smooth muscle (tissue). The associated genes with Wedelolactone are CFB gene, Candidate Disease Gene, JAK2 gene, STAT2 gene and STAT3 gene.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of Wedelolactone, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with Wedelolactone?
Wedelolactone is suspected in CLEFT LIP, CONGENITAL HEALED, Hepatitis and other diseases in descending order of the highest number of associated sentences.
Related references are mostly published in these journals:
| Disease | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literature |
|---|
Possible diseases from mapped MeSH terms on references
We collected disease MeSH terms mapped to the references associated with Wedelolactone
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with Wedelolactone
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with Wedelolactone?
Visualization in cellular structure
Associated locations are in red color. Not associated locations are in black.
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Location | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What functions are associated with Wedelolactone?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with Wedelolactone?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
What genes are associated with Wedelolactone?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Gene | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What common seen animal models are associated with Wedelolactone?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
NCBI Entrez Crosslinks
All references with Wedelolactone
Download all related citations| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nehybová T et al. | Wedelolactone Acts as Proteasome Inhibitor in Breast Cancer Cells. | 2017 | Int J Mol Sci | pmid:28353647 |
| Ferrari D et al. | Cyanidin-3-O-glucoside inhibits NF-kB signalling in intestinal epithelial cells exposed to TNF-α and exerts protective effects via Nrf2 pathway activation. | 2016 | Toxicol. Lett. | pmid:27793764 |
| Liu YQ et al. | Wedelolactone enhances osteoblastogenesis by regulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway but suppresses osteoclastogenesis by NF-κB/c-fos/NFATc1 pathway. | 2016 | Sci Rep | pmid:27558652 |
| Sarveswaran S et al. | Wedelolactone, an Anti-inflammatory Botanical, Interrupts c-Myc Oncogenic Signaling and Synergizes with Enzalutamide to Induce Apoptosis in Prostate Cancer Cells. | 2016 | Mol. Cancer Ther. | pmid:27474149 |
| Ali F et al. | Wedelolactone mitigates UVB induced oxidative stress, inflammation and early tumor promotion events in murine skin: plausible role of NFkB pathway. | 2016 | Eur. J. Pharmacol. | pmid:27164422 |
| Li L et al. | Wedelolactone metabolism in rats through regioselective glucuronidation catalyzed by uridine diphosphate-glucuronosyltransferases 1As (UGT1As). | 2016 | Phytomedicine | pmid:27002404 |
| Lu Y et al. | Protective effect of wedelolactone against CCl4-induced acute liver injury in mice. | 2016 | Int. Immunopharmacol. | pmid:26921731 |
| Berrak Ö et al. | The inhibition of PI3K and NFκB promoted curcumin-induced cell cycle arrest at G2/M via altering polyamine metabolism in Bcl-2 overexpressing MCF-7 breast cancer cells. | 2016 | Biomed. Pharmacother. | pmid:26796279 |
| Alquézar C et al. | Progranulin deficiency induces overactivation of WNT5A expression via TNF-α/NF-κB pathway in peripheral cells from frontotemporal dementia-linked granulin mutation carriers. | 2016 | J Psychiatry Neurosci | pmid:26624524 |
| Fratantonio D et al. | Palmitate-induced endothelial dysfunction is attenuated by cyanidin-3-O-glucoside through modulation of Nrf2/Bach1 and NF-κB pathways. | 2015 | Toxicol. Lett. | pmid:26422990 |