| MeSH term | MeSH ID | Detail |
|---|---|---|
| Atherosclerosis | D050197 | 85 associated lipids |
| Prostatic Neoplasms | D011471 | 126 associated lipids |
| Neuroblastoma | D009447 | 66 associated lipids |
| Melanoma | D008545 | 69 associated lipids |
| Carcinoma, Hepatocellular | D006528 | 140 associated lipids |
| Glioma | D005910 | 112 associated lipids |
| Alopecia | D000505 | 14 associated lipids |
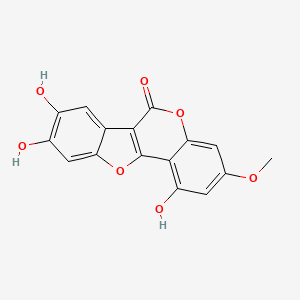
Wedelolactone
Wedelolactone is a lipid of Polyketides (PK) class. Wedelolactone is associated with abnormalities such as CLEFT LIP, CONGENITAL HEALED and Hepatitis. The involved functions are known as Signal Transduction, Cell Cycle Arrest, Apoptosis, luciferase activity and Metabolic Inhibition. Wedelolactone often locates in Protoplasm and Smooth muscle (tissue). The associated genes with Wedelolactone are CFB gene, Candidate Disease Gene, JAK2 gene, STAT2 gene and STAT3 gene.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of Wedelolactone, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with Wedelolactone?
Wedelolactone is suspected in CLEFT LIP, CONGENITAL HEALED, Hepatitis and other diseases in descending order of the highest number of associated sentences.
Related references are mostly published in these journals:
| Disease | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literature |
|---|
Possible diseases from mapped MeSH terms on references
We collected disease MeSH terms mapped to the references associated with Wedelolactone
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with Wedelolactone
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with Wedelolactone?
Visualization in cellular structure
Associated locations are in red color. Not associated locations are in black.
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Location | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What functions are associated with Wedelolactone?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with Wedelolactone?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
What genes are associated with Wedelolactone?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Gene | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What common seen animal models are associated with Wedelolactone?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
NCBI Entrez Crosslinks
All references with Wedelolactone
Download all related citations| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sarveswaran S et al. | Wedelolactone, a medicinal plant-derived coumestan, induces caspase-dependent apoptosis in prostate cancer cells via downregulation of PKCε without inhibiting Akt. | 2012 | Int. J. Oncol. | pmid:23076676 |
| Benedetti G et al. | TNF-α-mediated NF-κB survival signaling impairment by cisplatin enhances JNK activation allowing synergistic apoptosis of renal proximal tubular cells. | 2013 | Biochem. Pharmacol. | pmid:23103562 |
| Golub AG et al. | Discovery of new scaffolds for rational design of HCV NS5B polymerase inhibitors. | 2012 | Eur J Med Chem | pmid:23127989 |
| Lim WS et al. | Tumour necrosis factor alpha down-regulates the expression of peroxisome proliferator activated receptor alpha (PPARα) in human hepatocarcinoma HepG2 cells by activation of NF-κB pathway. | 2013 | Cytokine | pmid:23141142 |
| Chen Z et al. | Wedelolactone, a naturally occurring coumestan, enhances interferon-γ signaling through inhibiting STAT1 protein dephosphorylation. | 2013 | J. Biol. Chem. | pmid:23580655 |
| Xia Y et al. | Wedelolactone exhibits anti-fibrotic effects on human hepatic stellate cell line LX-2. | 2013 | Eur. J. Pharmacol. | pmid:23791612 |
| Patil AA et al. | Optimization of sample preparation variables for wedelolactone from Eclipta alba using Box-Behnken experimental design followed by HPLC identification. | 2013 | Ann Pharm Fr | pmid:23835023 |
| Buldak RJ et al. | Exogenous administration of visfatin affects cytokine secretion and increases oxidative stress in human malignant melanoma Me45 cells. | 2013 | J. Physiol. Pharmacol. | pmid:23959735 |
| Yuan F et al. | Wedelolactone inhibits LPS-induced pro-inflammation via NF-kappaB pathway in RAW 264.7 cells. | 2013 | J. Biomed. Sci. | pmid:24176090 |
| Wong SM et al. | Wedelolactone and coumestan derivatives as new antihepatotoxic and antiphlogistic principles. | 1988 | Arzneimittelforschung | pmid:2458108 |