| MeSH term | MeSH ID | Detail |
|---|---|---|
| Alopecia | D000505 | 14 associated lipids |
| Prostatic Neoplasms | D011471 | 126 associated lipids |
| Melanoma | D008545 | 69 associated lipids |
| Glioma | D005910 | 112 associated lipids |
| Neuroblastoma | D009447 | 66 associated lipids |
| Carcinoma, Hepatocellular | D006528 | 140 associated lipids |
| Atherosclerosis | D050197 | 85 associated lipids |
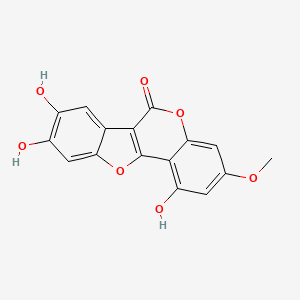
Wedelolactone
Wedelolactone is a lipid of Polyketides (PK) class. Wedelolactone is associated with abnormalities such as CLEFT LIP, CONGENITAL HEALED and Hepatitis. The involved functions are known as Signal Transduction, Cell Cycle Arrest, Apoptosis, luciferase activity and Metabolic Inhibition. Wedelolactone often locates in Protoplasm and Smooth muscle (tissue). The associated genes with Wedelolactone are CFB gene, Candidate Disease Gene, JAK2 gene, STAT2 gene and STAT3 gene.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of Wedelolactone, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with Wedelolactone?
Wedelolactone is suspected in CLEFT LIP, CONGENITAL HEALED, Hepatitis and other diseases in descending order of the highest number of associated sentences.
Related references are mostly published in these journals:
| Disease | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literature |
|---|
Possible diseases from mapped MeSH terms on references
We collected disease MeSH terms mapped to the references associated with Wedelolactone
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with Wedelolactone
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with Wedelolactone?
Visualization in cellular structure
Associated locations are in red color. Not associated locations are in black.
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Location | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What functions are associated with Wedelolactone?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with Wedelolactone?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
What genes are associated with Wedelolactone?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Gene | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What common seen animal models are associated with Wedelolactone?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
NCBI Entrez Crosslinks
All references with Wedelolactone
Download all related citations| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lefas G and Chaconas G | High-throughput screening identifies three inhibitor classes of the telomere resolvase from the lyme disease spirochete. | 2009 | Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. | pmid:19596868 |
| Idris AI et al. | Pharmacologic inhibitors of IkappaB kinase suppress growth and migration of mammary carcinosarcoma cells in vitro and prevent osteolytic bone metastasis in vivo. | 2009 | Mol. Cancer Ther. | pmid:19671767 |
| Tsai CH et al. | Herbal extract of Wedelia chinensis attenuates androgen receptor activity and orthotopic growth of prostate cancer in nude mice. | 2009 | Clin. Cancer Res. | pmid:19690196 |
| Rowe DL et al. | Modulation of the BRCA1 Protein and Induction of Apoptosis in Triple Negative Breast Cancer Cell Lines by the Polyphenolic Compound Curcumin. | 2009 | Breast Cancer (Auckl) | pmid:19809577 |
| Melo PA et al. | Ability of a synthetic coumestan to antagonize Bothrops snake venom activities. | 2010 Feb-Mar | Toxicon | pmid:19883675 |
| Tanabe K et al. | Mechanisms of tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced interleukin-6 synthesis in glioma cells. | 2010 | J Neuroinflammation | pmid:20205746 |
| Huang LH et al. | Lipid soluble smoke particles upregulate endothelin receptors in rat basilar artery. | 2010 | Toxicol. Lett. | pmid:20561571 |
| Yang JH et al. | [Regulation of NF-κB signal transduction pathway on cytokines in cultured nasal epithelium]. | 2010 | Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi | pmid:21055061 |
| Chen QW et al. | Cigarette smoke extract promotes human vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and survival through ERK1/2- and NF-κB-dependent pathways. | 2010 | ScientificWorldJournal | pmid:21057728 |
| Maalouf SW et al. | Inflammatory responses in epithelia: endotoxin-induced IL-6 secretion and iNOS/NO production are differentially regulated in mouse mammary epithelial cells. | 2010 | J Inflamm (Lond) | pmid:21118556 |