| MeSH term | MeSH ID | Detail |
|---|---|---|
| Hemolysis | D006461 | 131 associated lipids |
| Colitis, Ulcerative | D003093 | 24 associated lipids |
| Stomach Ulcer | D013276 | 75 associated lipids |
| Diarrhea | D003967 | 32 associated lipids |
| Diabetes Mellitus | D003920 | 90 associated lipids |
| Uterine Cervical Neoplasms | D002583 | 10 associated lipids |
| Lead Poisoning | D007855 | 4 associated lipids |
| Hypoxia | D000860 | 23 associated lipids |
| Arrhythmias, Cardiac | D001145 | 42 associated lipids |
| Neovascularization, Pathologic | D009389 | 39 associated lipids |
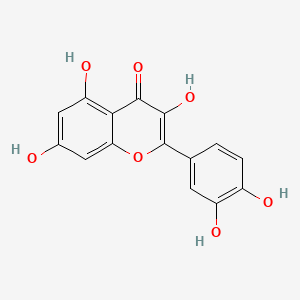
quercetin
quercetin is a lipid of Polyketides (PK) class. Quercetin is associated with abnormalities such as Coronary heart disease, Myocardial Infarction, Cirrhosis, Coronary Arteriosclerosis and Vascular ring. The involved functions are known as Vasodilation, physiological aspects, Fermentation, Process and Ingredient. Quercetin often locates in Arterial system, Endothelium, Skin, Endothelium, Vascular and Tissue specimen. The associated genes with quercetin are P4HTM gene, SULT gene, UGT1A1 gene, ARHGAP26 gene and PLXNB1 gene. The related lipids are blood lipid, Promega, Steroids, Phosphatidylserines and Fatty Acids. The related experimental models are Knock-out, Mouse Model, Xenograft Model, Tissue Model and Cancer Model.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of quercetin, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with quercetin?
quercetin is suspected in Hypertensive disease, Cardiovascular Diseases, Atherosclerosis, Infection, Obesity, Coronary heart disease and other diseases in descending order of the highest number of associated sentences.
Related references are mostly published in these journals:
| Disease | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literature |
|---|
Possible diseases from mapped MeSH terms on references
We collected disease MeSH terms mapped to the references associated with quercetin
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with quercetin
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with quercetin?
Visualization in cellular structure
Associated locations are in red color. Not associated locations are in black.
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Location | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What functions are associated with quercetin?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with quercetin?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Lipid concept | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What genes are associated with quercetin?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Gene | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What common seen animal models are associated with quercetin?
Mouse Model
Mouse Model are used in the study 'Hepatic cytochrome P-450 reductase-null mice show reduced transcriptional response to quercetin and reveal physiological homeostasis between jejunum and liver.' (Mutch DM et al., 2006), Mouse Model are used in the study 'Heat shock protein 70 increases tumorigenicity and inhibits apoptosis in pancreatic adenocarcinoma.' (Aghdassi A et al., 2007), Mouse Model are used in the study 'Proatherogenic macrophage activities are targeted by the flavonoid quercetin.' (Lara-Guzman OJ et al., 2012) and Mouse Model are used in the study 'Identification of brain-targeted bioactive dietary quercetin-3-O-glucuronide as a novel intervention for Alzheimer's disease.' (Ho L et al., 2013).
Xenograft Model
Xenograft Model are used in the study 'Quercetin induces tumor-selective apoptosis through downregulation of Mcl-1 and activation of Bax.' (Cheng S et al., 2010) and Xenograft Model are used in the study 'Inhibition of carcinogenesis by polyphenols: evidence from laboratory investigations.' (Lambert JD et al., 2005).
Cancer Model
Cancer Model are used in the study 'Modulation of aberrant crypt foci and apoptosis by dietary herbal supplements (quercetin, curcumin, silymarin, ginseng and rutin).' (Volate SR et al., 2005).
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Model | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
NCBI Entrez Crosslinks
All references with quercetin
Download all related citations| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blardi P et al. | Stimulation of endogenous adenosine release by oral administration of quercetin and resveratrol in man. | 1999 | Drugs Exp Clin Res | pmid:10370871 |
| Miodini P et al. | The two phyto-oestrogens genistein and quercetin exert different effects on oestrogen receptor function. | 1999 | Br. J. Cancer | pmid:10376965 |
| Pelletier MK et al. | Disruption of specific flavonoid genes enhances the accumulation of flavonoid enzymes and end-products in Arabidopsis seedlings. | 1999 | Plant Mol. Biol. | pmid:10394944 |
| Lee E et al. | Anti-allergic actions of the leaves of Castanea crenata and isolation of an active component responsible for the inhibition of mast cell degranulation. | 1999 | Arch. Pharm. Res. | pmid:10403140 |
| Alexandrakis M et al. | Differential effect of flavonoids on inhibition of secretion and accumulation of secretory granules in rat basophilic leukemia cells. | 1999 | Int. J. Immunopharmacol. | pmid:10405873 |
| Ghosh JC et al. | Effects of protein kinase inhibitors on the accumulation kinetics of p53 protein in normal human embryo cells following X-irradiation. | 1999 | J. Radiat. Res. | pmid:10408175 |
| Crespy V et al. | Part of quercetin absorbed in the small intestine is conjugated and further secreted in the intestinal lumen. | 1999 | Am. J. Physiol. | pmid:10409158 |
| Roth A et al. | Phytoestrogen kaempferol (3,4',5,7-tetrahydroxyflavone) protects PC12 and T47D cells from beta-amyloid-induced toxicity. | 1999 | J. Neurosci. Res. | pmid:10412031 |
| Nail SL et al. | Structure of aluminum hydroxide gel III: mechanism of stabilization by sorbitol. | 1976 | J Pharm Sci | pmid:10415 |
| Johnson ET et al. | Cymbidium hybrida dihydroflavonol 4-reductase does not efficiently reduce dihydrokaempferol to produce orange pelargonidin-type anthocyanins. | 1999 | Plant J. | pmid:10417729 |