| MeSH term | MeSH ID | Detail |
|---|---|---|
| Lymphedema | D008209 | 4 associated lipids |
| Neoplasms, Experimental | D009374 | 10 associated lipids |
| Encephalitis | D004660 | 15 associated lipids |
| Neoplasm Invasiveness | D009361 | 23 associated lipids |
| Cystitis | D003556 | 23 associated lipids |
| Adenoma | D000236 | 40 associated lipids |
| Leukemia P388 | D007941 | 43 associated lipids |
| Lupus Erythematosus, Systemic | D008180 | 43 associated lipids |
| Osteosarcoma | D012516 | 50 associated lipids |
| Asthma | D001249 | 52 associated lipids |
| Weight Loss | D015431 | 56 associated lipids |
| Dermatitis, Contact | D003877 | 59 associated lipids |
| Pain | D010146 | 64 associated lipids |
| Mammary Neoplasms, Experimental | D008325 | 67 associated lipids |
| Melanoma | D008545 | 69 associated lipids |
| Carcinoma, Non-Small-Cell Lung | D002289 | 72 associated lipids |
| Hyperlipidemias | D006949 | 73 associated lipids |
| Stomach Ulcer | D013276 | 75 associated lipids |
| Pancreatic Neoplasms | D010190 | 77 associated lipids |
| Diabetes Mellitus, Experimental | D003921 | 85 associated lipids |
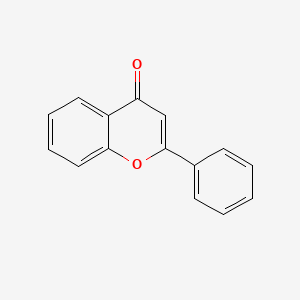
FLAVONE
FLAVONE is a lipid of Polyketides (PK) class. Flavone is associated with abnormalities such as Cardiovascular Diseases, Cerebrovascular accident, DERMATITIS HERPETIFORMIS, FAMILIAL, Hyperinsulinism and Inflammatory disorder. The involved functions are known as Oxidation-Reduction, Metabolic Inhibition, Inflammation, Phosphorylation and antioxidant activity. Flavone often locates in Endothelium, Hepatic, Protoplasm, Body tissue and Extracellular. The associated genes with FLAVONE are ICAM1 gene, BCL2L1 gene, MYC gene, TP53 gene and cytochrome c''. The related lipids are Promega, Steroids and Total cholesterol. The related experimental models are Knock-out, Disease model and Animal Disease Models.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of FLAVONE, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with FLAVONE?
FLAVONE is suspected in Diabetes Mellitus, Non-Insulin-Dependent, Obesity, Chronic Disease, Disintegration, Cardiovascular Diseases, Cerebrovascular accident and other diseases in descending order of the highest number of associated sentences.
Related references are mostly published in these journals:
| Disease | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literature |
|---|
Possible diseases from mapped MeSH terms on references
We collected disease MeSH terms mapped to the references associated with FLAVONE
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with FLAVONE
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with FLAVONE?
Visualization in cellular structure
Associated locations are in red color. Not associated locations are in black.
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Location | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What functions are associated with FLAVONE?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with FLAVONE?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Lipid concept | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What genes are associated with FLAVONE?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Gene | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What common seen animal models are associated with FLAVONE?
Knock-out
Knock-out are used in the study 'MATE2 mediates vacuolar sequestration of flavonoid glycosides and glycoside malonates in Medicago truncatula.' (Zhao J et al., 2011) and Knock-out are used in the study 'How can research on plants contribute to promoting human health?' (Martin C et al., 2011).
Disease model
Disease model are used in the study 'How can research on plants contribute to promoting human health?' (Martin C et al., 2011).
Animal Disease Models
Animal Disease Models are used in the study 'How can research on plants contribute to promoting human health?' (Martin C et al., 2011).
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Model | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
NCBI Entrez Crosslinks
All references with FLAVONE
Download all related citations| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Göpfert JC et al. | Identification, functional characterization and developmental regulation of sesquiterpene synthases from sunflower capitate glandular trichomes. | 2009 | BMC Plant Biol. | pmid:19580670 |
| Guttikonda SK et al. | Whole genome co-expression analysis of soybean cytochrome P450 genes identifies nodulation-specific P450 monooxygenases. | 2010 | BMC Plant Biol. | pmid:21062474 |
| Luo H et al. | Comparison of 454-ESTs from Huperzia serrata and Phlegmariurus carinatus reveals putative genes involved in lycopodium alkaloid biosynthesis and developmental regulation. | 2010 | BMC Plant Biol. | pmid:20854695 |
| Galla G et al. | Computational annotation of genes differentially expressed along olive fruit development. | 2009 | BMC Plant Biol. | pmid:19852839 |
| Heller G et al. | Transcriptional analysis of Pinus sylvestris roots challenged with the ectomycorrhizal fungus Laccaria bicolor. | 2008 | BMC Plant Biol. | pmid:18298811 |
| Zabala G et al. | Transcriptome changes in the phenylpropanoid pathway of Glycine max in response to Pseudomonas syringae infection. | 2006 | BMC Plant Biol. | pmid:17083738 |
| Opassiri R et al. | Analysis of rice glycosyl hydrolase family 1 and expression of Os4bglu12 beta-glucosidase. | 2006 | BMC Plant Biol. | pmid:17196101 |
| Parravicini C et al. | Forced unbinding of GPR17 ligands from wild type and R255I mutant receptor models through a computational approach. | 2010 | BMC Struct. Biol. | pmid:20233425 |
| NORTHOVER BJ and SUBRAMANIAN G | A study of possible mediators of inflammatory reactions in the mouse foot. | 1962 | Br J Pharmacol Chemother | pmid:14480419 |
| Ching LM et al. | Relationship between tumour endothelial cell apoptosis and tumour blood flow shutdown following treatment with the antivascular agent DMXAA in mice. | 2004 | Br. J. Cancer | pmid:14970872 |
| Jameson MB et al. | Clinical aspects of a phase I trial of 5,6-dimethylxanthenone-4-acetic acid (DMXAA), a novel antivascular agent. | 2003 | Br. J. Cancer | pmid:12799625 |
| Rustin GJ et al. | 5,6-dimethylxanthenone-4-acetic acid (DMXAA), a novel antivascular agent: phase I clinical and pharmacokinetic study. | 2003 | Br. J. Cancer | pmid:12698178 |
| Ching LM et al. | Induction of endothelial cell apoptosis by the antivascular agent 5,6-Dimethylxanthenone-4-acetic acid. | 2002 | Br. J. Cancer | pmid:12085190 |
| Peterson J et al. | Flavonoid intake and breast cancer risk: a case--control study in Greece. | 2003 | Br. J. Cancer | pmid:14520456 |
| Kerr DJ et al. | Phase II trials of flavone acetic acid in advanced malignant melanoma and colorectal carcinoma. | 1989 | Br. J. Cancer | pmid:2803908 |
| Murray JC et al. | Flavone acetic acid induces a coagulopathy in mice. | 1989 | Br. J. Cancer | pmid:2803949 |
| Newell DR et al. | Professor Tom Connors and the development of novel cancer therapies by the Phase I/II Clinical Trials Committee of Cancer Research UK. | 2003 | Br. J. Cancer | pmid:12888809 |
| Giavazzi R et al. | Response to flavone acetic acid (NSC 347512) of primary and metastatic human colorectal carcinoma xenografts. | 1988 | Br. J. Cancer | pmid:3355765 |
| Hinnen P and Eskens FA | Vascular disrupting agents in clinical development. | 2007 | Br. J. Cancer | pmid:17375046 |
| Lévy V et al. | A phase I dose-finding and pharmacokinetic study of subcutaneous semisynthetic homoharringtonine (ssHHT) in patients with advanced acute myeloid leukaemia. | 2006 | Br. J. Cancer | pmid:16847470 |