| MeSH term | MeSH ID | Detail |
|---|---|---|
| Cerebellar Diseases | D002526 | 2 associated lipids |
| Cerebral Hemorrhage | D002543 | 13 associated lipids |
| Hypoglycemia | D007003 | 13 associated lipids |
| Bacteroides Infections | D001442 | 1 associated lipids |
| Clostridium Infections | D003015 | 5 associated lipids |
| Fusobacterium Infections | D005674 | 3 associated lipids |
| Sepsis | D018805 | 11 associated lipids |
| Thiamine Deficiency | D013832 | 4 associated lipids |
| Pancytopenia | D010198 | 6 associated lipids |
| Nervous System Diseases | D009422 | 37 associated lipids |
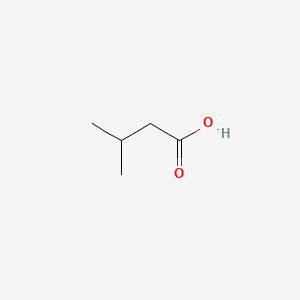
ISOVALERIC ACID
ISOVALERIC ACID is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. Isovaleric acid is associated with abnormalities such as Infection, Lymphocele, Cyst, Abscess and Subgingival plaque. The involved functions are known as Biochemical Reaction, 5-(carboxyamino)imidazole ribonucleotide mutase activity, nitrate reductase activity, urease activity and colony morphology. Isovaleric acid often locates in Skeleton, Abdomen, Chromosomes, Tissue membrane and Microsomes. The associated genes with ISOVALERIC ACID are trypticase, Operon, KCNT1 gene, Genome and Reverse primer. The related lipids are Fatty Acids, Propionate, Fatty Acids, Unsaturated, Steroids and Promega. The related experimental models are Knock-out.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of ISOVALERIC ACID, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with ISOVALERIC ACID?
ISOVALERIC ACID is suspected in Exanthema, Isovaleryl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency, Subgingival plaque, Dehydration, MAJOR DEPRESSIVE DISORDER 1, MAJOR DEPRESSIVE DISORDER 2 and other diseases in descending order of the highest number of associated sentences.
Related references are mostly published in these journals:
| Disease | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literature |
|---|
Possible diseases from mapped MeSH terms on references
We collected disease MeSH terms mapped to the references associated with ISOVALERIC ACID
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with ISOVALERIC ACID
Lipid pathways are not clear in current pathway databases. We organized associated pathways with ISOVALERIC ACID through full-text articles, including metabolic pathways or pathways of biological mechanisms.
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Pathway name | Related literatures |
|---|
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with ISOVALERIC ACID?
Visualization in cellular structure
Associated locations are in red color. Not associated locations are in black.
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Location | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What functions are associated with ISOVALERIC ACID?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with ISOVALERIC ACID?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Lipid concept | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What genes are associated with ISOVALERIC ACID?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Gene | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What common seen animal models are associated with ISOVALERIC ACID?
Knock-out
Knock-out are used in the study '3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A (CoA) synthase is involved in biosynthesis of isovaleryl-CoA in the myxobacterium Myxococcus xanthus during fruiting body formation.' (Bode HB et al., 2006) and Knock-out are used in the study 'Ethanol hypersensitivity and olfactory discrimination defect in mice lacking a homolog of Drosophila neuralized.' (Ruan Y et al., 2001).
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Model | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
NCBI Entrez Crosslinks
All references with ISOVALERIC ACID
Download all related citations| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paczkowski S and Schütz S | Post-mortem volatiles of vertebrate tissue. | 2011 | Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. | pmid:21720824 |
| Serrazanetti DI et al. | Acid stress-mediated metabolic shift in Lactobacillus sanfranciscensis LSCE1. | 2011 | Appl. Environ. Microbiol. | pmid:21335381 |
| Shank RA et al. | Current and future experimental strategies for structural analysis of trichothecene mycotoxins--a prospectus. | 2011 | Toxins (Basel) | pmid:22295175 |
| Schmidt J et al. | Selective orthosteric free fatty acid receptor 2 (FFA2) agonists: identification of the structural and chemical requirements for selective activation of FFA2 versus FFA3. | 2011 | J. Biol. Chem. | pmid:21220428 |
| Arora R et al. | Potential of Complementary and Alternative Medicine in Preventive Management of Novel H1N1 Flu (Swine Flu) Pandemic: Thwarting Potential Disasters in the Bud. | 2011 | Evid Based Complement Alternat Med | pmid:20976081 |
| Nes WD | Biosynthesis of cholesterol and other sterols. | 2011 | Chem. Rev. | pmid:21902244 |
| Wroblewska M et al. | Physiological properties of beetroot crisps applied in standard and dyslipidaemic diets of rats. | 2011 | Lipids Health Dis | pmid:21995671 |
| Ukhanov K et al. | Phosphoinositide 3-kinase-dependent antagonism in mammalian olfactory receptor neurons. | 2011 | J. Neurosci. | pmid:21209212 |
| Downes J and Wade WG | Prevotella fusca sp. nov. and Prevotella scopos sp. nov., isolated from the human oral cavity. | 2011 | Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. | pmid:20495041 |
| Holzmann I et al. | Evaluation of Behavioral and Pharmacological Effects of Hydroalcoholic Extract of Valeriana prionophylla Standl. from Guatemala. | 2011 | Evid Based Complement Alternat Med | pmid:21754942 |
| Zasloff M | Observations on the remarkable (and mysterious) wound-healing process of the bottlenose dolphin. | 2011 | J. Invest. Dermatol. | pmid:21776005 |
| Hansen CF et al. | A high dietary concentration of inulin is necessary to reduce the incidence of swine dysentery in pigs experimentally challenged with Brachyspira hyodysenteriae. | 2011 | Br. J. Nutr. | pmid:21736788 |
| Chin ST et al. | Identification of potent odourants in wine and brewed coffee using gas chromatography-olfactometry and comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography. | 2011 | J Chromatogr A | pmid:21741655 |
| Kappers IF et al. | Variation in herbivory-induced volatiles among cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) varieties has consequences for the attraction of carnivorous natural enemies. | 2011 | J. Chem. Ecol. | pmid:21249432 |
| Prakash S et al. | Gut microbiota: next frontier in understanding human health and development of biotherapeutics. | 2011 | Biologics | pmid:21847343 |
| Verhulst NO et al. | Improvement of a synthetic lure for Anopheles gambiae using compounds produced by human skin microbiota. | 2011 | Malar. J. | pmid:21303496 |
| Busman M et al. | Observation of T-2 toxin and HT-2 toxin glucosides from Fusarium sporotrichioides by liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). | 2011 | Toxins (Basel) | pmid:22295176 |
| Scadding G et al. | Diagnostic tools in Rhinology EAACI position paper. | 2011 | Clin Transl Allergy | pmid:22410181 |
| Rolls ET | Chemosensory learning in the cortex. | 2011 | Front Syst Neurosci | pmid:21954379 |
| Wilson AD and Baietto M | Advances in electronic-nose technologies developed for biomedical applications. | 2011 | Sensors (Basel) | pmid:22346620 |