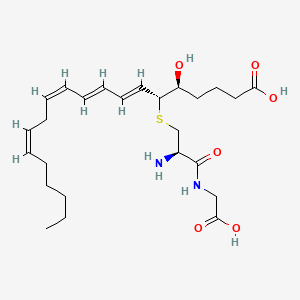
LTD4
Ltd4 is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. Ltd4 is associated with abnormalities such as Inflammatory Bowel Diseases, Inflammatory disorder, Asthma, Pneumonia and Allergic asthma. The involved functions are known as inhibitors, Signal Transduction, Cell Survival, antagonists and Phosphorylation. Ltd4 often locates in Membrane, Tissue membrane, Protoplasm, Cytoplasmic matrix and membrane fraction. The associated genes with LTD4 are ALOX5 gene, UMOD gene, P4HTM gene, RAF1 gene and Homologous Gene. The related lipids are Lipopolysaccharides.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of LTD4, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with LTD4?
LTD4 is suspected in Asthma, Inflammatory Bowel Diseases, Inflammatory disorder, Pneumonia, Allergic asthma, Virus Diseases and other diseases in descending order of the highest number of associated sentences.
Related references are mostly published in these journals:
| Disease | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literature |
|---|
Possible diseases from mapped MeSH terms on references
We collected disease MeSH terms mapped to the references associated with LTD4
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with LTD4
Lipid pathways are not clear in current pathway databases. We organized associated pathways with LTD4 through full-text articles, including metabolic pathways or pathways of biological mechanisms.
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Pathway name | Related literatures |
|---|
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with LTD4?
Visualization in cellular structure
Associated locations are in red color. Not associated locations are in black.
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Location | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What functions are associated with LTD4?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with LTD4?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Lipid concept | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What genes are associated with LTD4?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Gene | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What common seen animal models are associated with LTD4?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
NCBI Entrez Crosslinks
All references with LTD4
Download all related citations| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ohshima N et al. | A functional study on CysLT(1) receptors in human eosinophils. | 2002 | Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. | pmid:12373000 |
| Uemura M et al. | Cysteinyl leukotrienes in the bile of patients with obstructive jaundice. | 2002 | J. Gastroenterol. | pmid:12424566 |
| Kurogi Y | Mesangial cell proliferation inhibitors for the treatment of proliferative glomerular disease. | 2003 | Med Res Rev | pmid:12424751 |
| Sheller J et al. | The prostaglandin E agonist, misoprostol, inhibits airway IL-5 production in atopic asthmatics. | 2002 | Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. | pmid:12428688 |
| Shahbazian A et al. | Differential peristaltic motor effects of prostanoid (DP, EP, IP, TP) and leukotriene receptor agonists in the guinea-pig isolated small intestine. | 2002 | Br. J. Pharmacol. | pmid:12429577 |
| Evans JF | Cysteinyl leukotriene receptors. | 2002 | Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. | pmid:12432945 |
| Walch L et al. | Pharmacological evidence for a novel cysteinyl-leukotriene receptor subtype in human pulmonary artery smooth muscle. | 2002 | Br. J. Pharmacol. | pmid:12466244 |
| Wikström K et al. | The anti-apoptotic effect of leukotriene D4 involves the prevention of caspase 8 activation and Bid cleavage. | 2003 | Biochem. J. | pmid:12482325 |
| Nagase T et al. | A potent inhibitor of cytosolic phospholipase A2, arachidonyl trifluoromethyl ketone, attenuates LPS-induced lung injury in mice. | 2003 | Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. | pmid:12505870 |
| Liu P et al. | Cysteinyl leukotriene-dependent [Ca2+]i responses to angiotensin II in cardiomyocytes. | 2003 | Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. | pmid:12531730 |
| Peters SP | Leukotriene receptor antagonists in asthma therapy. | 2003 | J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. | pmid:12532087 |
| Mazzetti L et al. | The ACh-induced contraction in rat aortas is mediated by the Cys Lt1 receptor via intracellular calcium mobilization in smooth muscle cells. | 2003 | Br. J. Pharmacol. | pmid:12598425 |
| Mizutani N | [Studies on the experimental allergic rhinitis induced by Japanese cedar pollen--role of cysteinyl leukotrienes in nasal allergic symptoms]. | 2003 | Yakugaku Zasshi | pmid:12607939 |
| Smyth TP et al. | A substrate variant as a high-affinity, reversible inhibitor: insight from the X-ray structure of cilastatin bound to membrane dipeptidase. | 2003 | Bioorg. Med. Chem. | pmid:12614884 |
| Hattori T et al. | Effects of H2O2 on membrane potential of smooth muscle cells in rabbit mesenteric resistance artery. | 2003 | Eur. J. Pharmacol. | pmid:12620501 |
| Klegeris A and McGeer PL | Toxicity of human monocytic THP-1 cells and microglia toward SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells is reduced by inhibitors of 5-lipoxygenase and its activating protein FLAP. | 2003 | J. Leukoc. Biol. | pmid:12629151 |
| Stelmach I et al. | The effect of inhaled heparin on airway responsiveness to histamine and leukotriene D4. | 2003 Jan-Feb | Allergy Asthma Proc | pmid:12635579 |
| Vargaftig BB and Singer M | Leukotrienes mediate murine bronchopulmonary hyperreactivity, inflammation, and part of mucosal metaplasia and tissue injury induced by recombinant murine interleukin-13. | 2003 | Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. | pmid:12654629 |
| Thodeti CK and Sjölander A | Leukotriene D4-induced calcium signaling in human intestinal epithelial cells. | 2002 | Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. | pmid:12664584 |
| Chibana K et al. | Up-regulation of cysteinyl leukotriene 1 receptor by IL-13 enables human lung fibroblasts to respond to leukotriene C4 and produce eotaxin. | 2003 | J. Immunol. | pmid:12682264 |