| MeSH term | MeSH ID | Detail |
|---|---|---|
| Adenocarcinoma | D000230 | 166 associated lipids |
| Arthritis, Experimental | D001169 | 24 associated lipids |
| Asthma | D001249 | 52 associated lipids |
| Astrocytoma | D001254 | 15 associated lipids |
| Autoimmune Diseases | D001327 | 27 associated lipids |
| Body Weight | D001835 | 333 associated lipids |
| Cell Transformation, Neoplastic | D002471 | 126 associated lipids |
| Chlamydia Infections | D002690 | 7 associated lipids |
| Colonic Neoplasms | D003110 | 161 associated lipids |
| Cystic Fibrosis | D003550 | 65 associated lipids |
| Diabetes Mellitus, Experimental | D003921 | 85 associated lipids |
| Diabetes Mellitus, Type 2 | D003924 | 87 associated lipids |
| Diabetic Nephropathies | D003928 | 39 associated lipids |
| Edema | D004487 | 152 associated lipids |
| Glioblastoma | D005909 | 27 associated lipids |
| Glioma | D005910 | 112 associated lipids |
| Glomerulonephritis | D005921 | 35 associated lipids |
| Cardiomegaly | D006332 | 31 associated lipids |
| Hypertrophy | D006984 | 16 associated lipids |
| Kidney Diseases | D007674 | 29 associated lipids |
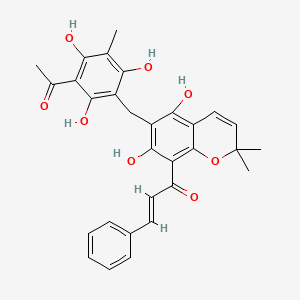
rottlerin
Rottlerin is a lipid of Polyketides (PK) class. Rottlerin is associated with abnormalities such as PARAGANGLIOMAS 2, Hyperostosis, Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal, Virus Diseases, Perisylvian syndrome and Autoimmune disease (systemic) NOS. The involved functions are known as Apoptosis, Regulation, Signal Transduction, inhibitors and Proteasome Inhibitors [MoA]. Rottlerin often locates in Clone, Membrane, Body tissue, Plasma membrane and soluble. The associated genes with Rottlerin are XIAP gene, GAPDH gene, ICAM1 gene, P4HTM gene and TNFSF10 gene. The related lipids are Promega, Fatty Acids, Sphingolipids, Lipopolysaccharides and Saponin. The related experimental models are Mouse Model, Xenograft Model and Cancer Model.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of rottlerin, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with rottlerin?
rottlerin is suspected in Infection, Morphologically altered structure, Ischemia, Pulmonary Edema, Asthma, Cardiovascular Diseases and other diseases in descending order of the highest number of associated sentences.
Related references are mostly published in these journals:
- J. Biol. Chem. (5)
- Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. (3)
- Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. (3)
- Others (19)
| Disease | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literature |
|---|
Possible diseases from mapped MeSH terms on references
We collected disease MeSH terms mapped to the references associated with rottlerin
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with rottlerin
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with rottlerin?
Visualization in cellular structure
Associated locations are in red color. Not associated locations are in black.
Related references are published most in these journals:
- J. Biol. Chem. (9)
- J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. (4)
- Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. (3)
- Others (42)
| Location | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What functions are associated with rottlerin?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with rottlerin?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Lipid concept | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What genes are associated with rottlerin?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Gene | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What common seen animal models are associated with rottlerin?
Cancer Model
Cancer Model are used in the study 'Rottlerin stimulates apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells through interactions with proteins of the Bcl-2 family.' (Ohno I et al., 2010) and Cancer Model are used in the study 'Rottlerin induces Wnt co-receptor LRP6 degradation and suppresses both Wnt/β-catenin and mTORC1 signaling in prostate and breast cancer cells.' (Lu W et al., 2014).
Mouse Model
Mouse Model are used in the study 'Neuroprotective effect of protein kinase C delta inhibitor rottlerin in cell culture and animal models of Parkinson's disease.' (Zhang D et al., 2007).
Xenograft Model
Xenograft Model are used in the study 'Rottlerin stimulates apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells through interactions with proteins of the Bcl-2 family.' (Ohno I et al., 2010).
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Model | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
NCBI Entrez Crosslinks
All references with rottlerin
Download all related citations| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Contreras X et al. | IL-10 production induced by HIV-1 Tat stimulation of human monocytes is dependent on the activation of PKC beta(II) and delta isozymes. | 2004 | Microbes Infect. | pmid:15488737 |
| Ikewaki N et al. | Regulation of CD93 cell surface expression by protein kinase C isoenzymes. | 2006 | Microbiol. Immunol. | pmid:16490927 |
| Woo SM et al. | Rottlerin induces cyclooxygenase-2 upregulation through an ATF4 and reactive oxygen species-independent pathway in HEI-OC1 cells. | 2016 | Mol Med Rep | pmid:27222046 |
| Liao YF et al. | Dibenzoylmethane, hydroxydibenzoylmethane and hydroxymethyldibenzoylmethane inhibit phorbol-12-myristate 13-acetate‑induced breast carcinoma cell invasion. | 2015 | Mol Med Rep | pmid:25650742 |
| Shi J et al. | Rottlerin inhibits cell growth, induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest, and inhibits cell invasion in human hepatocellular carcinoma. | 2018 | Mol Med Rep | pmid:29115596 |
| Liu ZC et al. | Translocation of protein kinase C δ contributes to the moderately high glucose-, but not hypoxia-induced proliferation in primary cultured human retinal endothelial cells. | 2014 | Mol Med Rep | pmid:24626810 |
| Song J et al. | Rottlerin promotes autophagy and apoptosis in gastric cancer cell lines. | 2018 | Mol Med Rep | pmid:30015872 |
| Masur K et al. | High PKC alpha and low E-cadherin expression contribute to high migratory activity of colon carcinoma cells. | 2001 | Mol. Biol. Cell | pmid:11451996 |
| Wiedłocha A et al. | Phosphorylation-regulated nucleocytoplasmic trafficking of internalized fibroblast growth factor-1. | 2005 | Mol. Biol. Cell | pmid:15574884 |
| Panaretakis T et al. | Doxorubicin requires the sequential activation of caspase-2, protein kinase Cdelta, and c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase to induce apoptosis. | 2005 | Mol. Biol. Cell | pmid:15917298 |
| Lima F et al. | Connexin43 potentiates osteoblast responsiveness to fibroblast growth factor 2 via a protein kinase C-delta/Runx2-dependent mechanism. | 2009 | Mol. Biol. Cell | pmid:19339281 |
| Lladó A et al. | Protein kinaseCdelta-calmodulin crosstalk regulates epidermal growth factor receptor exit from early endosomes. | 2004 | Mol. Biol. Cell | pmid:15342779 |
| Latorre E et al. | Downregulation of HuR as a new mechanism of doxorubicin resistance in breast cancer cells. | 2012 | Mol. Cancer | pmid:22436134 |
| Kumar D et al. | Rottlerin-induced autophagy leads to the apoptosis in breast cancer stem cells: molecular mechanisms. | 2013 | Mol. Cancer | pmid:24359639 |
| Akar U et al. | Tissue transglutaminase inhibits autophagy in pancreatic cancer cells. | 2007 | Mol. Cancer Res. | pmid:17374730 |
| Kumar Biswas S et al. | Down-regulation of Bcl-2 is associated with cisplatin resistance in human small cell lung cancer H69 cells. | 2004 | Mol. Cancer Ther. | pmid:15026553 |
| McCracken MA et al. | Protein kinase C delta is a prosurvival factor in human breast tumor cell lines. | 2003 | Mol. Cancer Ther. | pmid:12657722 |
| Johnson CL et al. | Regulation of p53 stabilization by DNA damage and protein kinase C. | 2002 | Mol. Cancer Ther. | pmid:12492119 |
| Thomas R and Kim MH | Targeting the hypoxia inducible factor pathway with mitochondrial uncouplers. | 2007 | Mol. Cell. Biochem. | pmid:16924414 |
| Pandur S et al. | Combined incubation of colon carcinoma cells with phorbol ester and mitochondrial uncoupling agents results in synergic elevated reactive oxygen species levels and increased γ-glutamyltransferase expression. | 2014 | Mol. Cell. Biochem. | pmid:24281857 |