| MeSH term | MeSH ID | Detail |
|---|---|---|
| Starvation | D013217 | 47 associated lipids |
| Tuberculosis, Multidrug-Resistant | D018088 | 6 associated lipids |
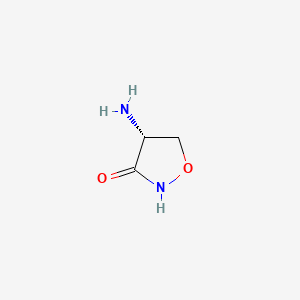
D-cycloserine
D-cycloserine is a lipid of Polyketides (PK) class. D-cycloserine is associated with abnormalities such as Inflammatory disorder, Asthma, Rheumatoid Arthritis, Multiple Sclerosis and Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. The involved functions are known as Cellular Infiltration, Vascular Permeability, Stimulus, antagonists and Kinase Inhibitors [MoA]. D-cycloserine often locates in Tissue membrane, Body tissue, Protoplasm, Endothelium and Cell Wall. The associated genes with D-cycloserine are Genome, serine O-sulfate, Polypeptides, alpha-aminobutyric acid, (S)-isomer and Genes, Reporter. The related lipids are Sphingolipids, Fatty Acids, Sterols, 25-hydroxycholesterol and Fatty Acids, Unsaturated.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of D-cycloserine, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with D-cycloserine?
D-cycloserine is suspected in Tuberculosis, Inflammatory disorder, Asthma, Rheumatoid Arthritis, Multiple Sclerosis, Inflammatory Bowel Diseases and other diseases in descending order of the highest number of associated sentences.
Related references are mostly published in these journals:
| Disease | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literature |
|---|
Possible diseases from mapped MeSH terms on references
We collected disease MeSH terms mapped to the references associated with D-cycloserine
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with D-cycloserine
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with D-cycloserine?
Visualization in cellular structure
Associated locations are in red color. Not associated locations are in black.
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Location | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What functions are associated with D-cycloserine?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with D-cycloserine?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Lipid concept | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What genes are associated with D-cycloserine?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Gene | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What common seen animal models are associated with D-cycloserine?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
NCBI Entrez Crosslinks
All references with D-cycloserine
Download all related citations| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pmid:16296047 | ||||
| Baghaei P et al. | Adverse effects of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis treatment with a standardized regimen: a report from Iran. | Am J Ther | pmid:20019591 | |
| pmid:23342661 | ||||
| pmid: | ||||
| Nadeau SE et al. | A pilot randomized controlled trial of D-cycloserine and distributed practice as adjuvants to constraint-induced movement therapy after stroke. | Neurorehabil Neural Repair | pmid:24769437 | |
| Sharma B et al. | Cycloserine-induced psychosis in a young female with drug-resistant tuberculosis. | Gen Hosp Psychiatry | pmid:24766906 | |
| CYCLOSERINE. | 1955 | Br Med J | pmid:14363816 | |
| STEENKEN W and WOLINSKY E | Cycloserine: antituberculous activity in vitro and in the experimental animal. | 1956 | Am Rev Tuberc | pmid:13302684 |
| NEILANDS JB | Metal and hydrogen-ion binding properties of cycloserine. | 1956 | Arch. Biochem. Biophys. | pmid:13314649 |
| WOODSIDE JM et al. | Spectrophotometric determination of cycloserine and isoniazid in pharmaceutical preparations. | 1957 | J Am Pharm Assoc Am Pharm Assoc | pmid:13491492 |
| HERROLD RD | Some considerations in the administration of novobiocin and cycloserine. | 1957 | J. Urol. | pmid:13439702 |
| ANDREJEW A et al. | [Effect of d-cycloserine & isonicotinic acid hydrazide on the catalase activity of Mycobacteria]. | 1958 | Biochim. Biophys. Acta | pmid:13584402 |
| HUGHES J et al. | Cycloserine in chronic urinary infections. | 1958 | J. Urol. | pmid:13564591 |
| WEISERT O | Some investigations relating to resistance determination of tubercle bacilli on cycloserine-containing Lowenstein-Jensen medium. | 1958 | Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand | pmid:13532707 |
| HEIN J and BERTHOLD H | [On cycloserine-therapy]. | 1959 | Schweiz Z Tuberc Pneumonol | pmid:14400685 |
| HOLMES CX et al. | The role of the cycloserine (seromycin) blood level in the treatment of pulmonary tuberculosis and the prevention and control of cycloserine (seromycin) toxicity. | 1959 | Dis Chest | pmid:14402775 |
| DUMON G | [New antibiotics and pulmonary tuberculosis (viomycin, cycloserine, neomycin)]. | 1959 | Mars Med | pmid:13818595 |
| ROGNATO C et al. | [Hematic levels of cycloserine in relation to seasonal temperature]. | 1959 | Arcisp S Anna Ferrara | pmid:13854547 |
| ROGNATO C and ZAMPINI N | [Urinary elimination of cycloserine in man]. | 1959 | Arcisp S Anna Ferrara | pmid:13854548 |
| LEITES V | Cycloserine-isoniazid in the ambulatory treatment of active tuberculosis after failure of previous chemotherapy. | 1959 | Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. | pmid:13670395 |