| MeSH term | MeSH ID | Detail |
|---|---|---|
| Starvation | D013217 | 47 associated lipids |
| Tuberculosis, Multidrug-Resistant | D018088 | 6 associated lipids |
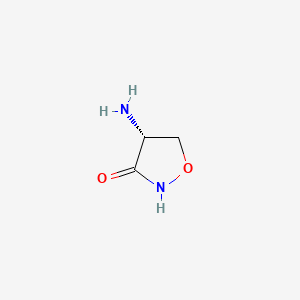
D-cycloserine
D-cycloserine is a lipid of Polyketides (PK) class. D-cycloserine is associated with abnormalities such as Inflammatory disorder, Asthma, Rheumatoid Arthritis, Multiple Sclerosis and Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. The involved functions are known as Cellular Infiltration, Vascular Permeability, Stimulus, antagonists and Kinase Inhibitors [MoA]. D-cycloserine often locates in Tissue membrane, Body tissue, Protoplasm, Endothelium and Cell Wall. The associated genes with D-cycloserine are Genome, serine O-sulfate, Polypeptides, alpha-aminobutyric acid, (S)-isomer and Genes, Reporter. The related lipids are Sphingolipids, Fatty Acids, Sterols, 25-hydroxycholesterol and Fatty Acids, Unsaturated.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of D-cycloserine, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with D-cycloserine?
D-cycloserine is suspected in Tuberculosis, Inflammatory disorder, Asthma, Rheumatoid Arthritis, Multiple Sclerosis, Inflammatory Bowel Diseases and other diseases in descending order of the highest number of associated sentences.
Related references are mostly published in these journals:
| Disease | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literature |
|---|
Possible diseases from mapped MeSH terms on references
We collected disease MeSH terms mapped to the references associated with D-cycloserine
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with D-cycloserine
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with D-cycloserine?
Visualization in cellular structure
Associated locations are in red color. Not associated locations are in black.
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Location | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What functions are associated with D-cycloserine?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with D-cycloserine?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Lipid concept | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What genes are associated with D-cycloserine?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Gene | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What common seen animal models are associated with D-cycloserine?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
NCBI Entrez Crosslinks
All references with D-cycloserine
Download all related citations| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vamvakides A | [Inactivity of imipramine in the forced swimming test on old mice or on young mice undergone chronic glycinergic treatment]. | 1996 | Ann Pharm Fr | pmid:9008899 |
| Peloquin CA et al. | Pharmacokinetics of para-aminosalicylic acid granules under four dosing conditions. | 2001 | Ann Pharmacother | pmid:11724078 |
| FLOCH H and FLOCH T | [THE CHEMOTHERAPY OF LEPROSY]. | 1964 | Ann Soc Belges Med Trop Parasitol Mycol | pmid:14211530 |
| Srednicka-Zajac D et al. | [Resistance of tubercle bacilli to cycloserine, viomycin and ethionamide in patients suffering from pulmonary tuberculosis]. | 1967 | Ann Univ Mariae Curie Sklodowska Med | pmid:4308440 |
| van Dongen JT et al. | Transcript and metabolite profiling of the adaptive response to mild decreases in oxygen concentration in the roots of arabidopsis plants. | 2009 | Ann. Bot. | pmid:18660497 |
| Venho VM and Koskinen R | The effect of pyrazinamide, rifampicin and cycloserine on the blood levels and urinary excretion of isoniazid. | 1971 | Ann. Clin. Res. | pmid:5156629 |
| Aukee S et al. | Drug absorption in patients with T-tube after cholecystectomy. | 1975 | Ann. Clin. Res. | pmid:1155910 |
| Murty MV and Venkitasubramanian TA | Evidence for the synthesis of peptidoglycan by spheroplasts of Mycobacterium smegmatis ATCC-14468. | 1984 May-Jun | Ann. Microbiol. (Paris) | pmid:6465738 |
| Iandolo JJ | Repair of stress-induced macromolecular alterations in S. aureus. | 1974 | Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. | pmid:4529248 |
| Cohen AC | Pyridoxine in the prevention and treatment of convulsions and neurotoxicity due to cycloserine. | 1969 | Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. | pmid:5262029 |
| Jones RW et al. | Effects of NMDA modulation in scopolamine dementia. | 1991 | Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. | pmid:1837979 |
| Kantak KM and Nic Dhonnchadha BÃ | Pharmacological enhancement of drug cue extinction learning: translational challenges. | 2011 | Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. | pmid:21272016 |
| Pyle MM | Ethambutol in the retreatment and primary treatment of tuberculosis: a four-year clinical investigation. | 1966 | Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. | pmid:5220243 |
| Kass I | Kanamycin in the therapy of pulmonary tuberculosis in the United States. | 1966 | Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. | pmid:4960375 |
| Dye WE | Bacteriology of tuberculosis with special reference to kanamycin and related drugs. | 1966 | Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. | pmid:4290030 |
| Rapp A et al. | Treatment of pediatric anxiety disorders. | 2013 | Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. | pmid:24279893 |
| Kutt H | Biochemical and genetic factors regulating dilantin metabolism in man. | 1971 | Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. | pmid:4105796 |
| Fonnum F et al. | Role of glutamate and glutamate receptors in memory function and Alzheimer's disease. | 1995 | Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. | pmid:7611704 |
| Tomasz A | The role of autolysins in cell death. | 1974 | Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. | pmid:4153141 |
| de Repentigny J and Mathieu LG | Metabolism and pathogenicity in Staphylococcus single and mixed cultures and infections. | 1974 | Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. | pmid:4213698 |