| MeSH term | MeSH ID | Detail |
|---|---|---|
| Melanoma | D008545 | 69 associated lipids |
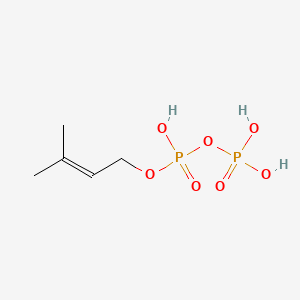
Dimethylallyl pyrophosphate
Dimethylallyl pyrophosphate is a lipid of Prenol Lipids (PR) class. Dimethylallyl pyrophosphate is associated with abnormalities such as Consumption-archaic term for TB and Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome. The involved functions are known as Anabolism, Biochemical Pathway, Oxidation, Process and Chelating Activity [MoA]. Dimethylallyl pyrophosphate often locates in Chloroplasts, Plastids, chloroplast stroma, Cytosol and Cell membrane. The associated genes with Dimethylallyl pyrophosphate are IRF6 wt Allele and ADRBK1 gene. The related lipids are Sterols.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of Dimethylallyl pyrophosphate, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with Dimethylallyl pyrophosphate?
Dimethylallyl pyrophosphate is suspected in and other diseases in descending order of the highest number of associated sentences.
Related references are mostly published in these journals:
| Disease | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literature |
|---|
Possible diseases from mapped MeSH terms on references
We collected disease MeSH terms mapped to the references associated with Dimethylallyl pyrophosphate
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with Dimethylallyl pyrophosphate
Lipid pathways are not clear in current pathway databases. We organized associated pathways with Dimethylallyl pyrophosphate through full-text articles, including metabolic pathways or pathways of biological mechanisms.
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Pathway name | Related literatures |
|---|
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with Dimethylallyl pyrophosphate?
Visualization in cellular structure
Associated locations are in red color. Not associated locations are in black.
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Location | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What functions are associated with Dimethylallyl pyrophosphate?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with Dimethylallyl pyrophosphate?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Lipid concept | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What genes are associated with Dimethylallyl pyrophosphate?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Gene | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What common seen animal models are associated with Dimethylallyl pyrophosphate?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
NCBI Entrez Crosslinks
All references with Dimethylallyl pyrophosphate
Download all related citations| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Xu W et al. | A closer look at the spectroscopic properties of possible reaction intermediates in wild-type and mutant (E)-4-hydroxy-3-methylbut-2-enyl diphosphate reductase. | 2012 | Biochemistry | pmid:22646150 |
| Fu X et al. | Plastid structure and carotenogenic gene expression in red- and white-fleshed loquat (Eriobotrya japonica) fruits. | 2012 | J. Exp. Bot. | pmid:21994170 |
| Span I et al. | Discovery of acetylene hydratase activity of the iron-sulphur protein IspH. | 2012 | Nat Commun | pmid:22948824 |
| Bitok JK and Meyers CF | 2C-Methyl-d-erythritol 4-phosphate enhances and sustains cyclodiphosphate synthase IspF activity. | 2012 | ACS Chem. Biol. | pmid:22839733 |
| Diaz ME et al. | Characterization of an isopentenyl diphosphate isomerase involved in the juvenile hormone pathway in Aedes aegypti. | 2012 | Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. | pmid:22782071 |
| Wu S et al. | Engineering triterpene metabolism in tobacco. | 2012 | Planta | pmid:22729821 |
| Caballero MC et al. | Characterization of acyl carrier protein and LytB in Babesia bovis apicoplast. | 2012 | Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. | pmid:22057350 |
| Fowler DW et al. | Mycobacteria activate γδ T-cell anti-tumour responses via cytokines from type 1 myeloid dendritic cells: a mechanism of action for cancer immunotherapy. | 2012 | Cancer Immunol. Immunother. | pmid:22002242 |
| Türsen U | Pathophysiology of the Behçet's Disease. | 2012 | Patholog Res Int | pmid:21977335 |
| Lamsen EN and Atsumi S | Recent progress in synthetic biology for microbial production of C3-C10 alcohols. | 2012 | Front Microbiol | pmid:22701113 |
| Nes WD | Biosynthesis of cholesterol and other sterols. | 2011 | Chem. Rev. | pmid:21902244 |
| Sivy TL et al. | Evidence of isoprenoid precursor toxicity in Bacillus subtilis. | 2011 | Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. | pmid:22146731 |
| Artz JD et al. | Molecular characterization of a novel geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate synthase from Plasmodium parasites. | 2011 | J. Biol. Chem. | pmid:21084289 |
| Peralta-Yahya PP et al. | Identification and microbial production of a terpene-based advanced biofuel. | 2011 | Nat Commun | pmid:21952217 |
| Lu J et al. | Human ovarian tumor cells escape γδ T cell recognition partly by down regulating surface expression of MICA and limiting cell cycle related molecules. | 2011 | PLoS ONE | pmid:21935360 |
| Battilana J et al. | Functional effect of grapevine 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate synthase substitution K284N on Muscat flavour formation. | 2011 | J. Exp. Bot. | pmid:21868399 |
| Nair SC and Striepen B | What do human parasites do with a chloroplast anyway? | 2011 | PLoS Biol. | pmid:21912515 |
| Yeh E and DeRisi JL | Chemical rescue of malaria parasites lacking an apicoplast defines organelle function in blood-stage Plasmodium falciparum. | 2011 | PLoS Biol. | pmid:21912516 |
| Nordqvist A et al. | Synthesis of functionalized cinnamaldehyde derivatives by an oxidative Heck reaction and their use as starting materials for preparation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis 1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate reductoisomerase inhibitors. | 2011 | J. Org. Chem. | pmid:21936546 |
| Yu Q et al. | Plant carotene cis-trans isomerase CRTISO: a new member of the FAD(RED)-dependent flavoproteins catalyzing non-redox reactions. | 2011 | J. Biol. Chem. | pmid:21209101 |