| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ling Y et al. | The farnesyl-diphosphate/geranylgeranyl-diphosphate synthase of Toxoplasma gondii is a bifunctional enzyme and a molecular target of bisphosphonates. | 2007 | J. Biol. Chem. | pmid:17724033 |
| Glickman JF and Schmid A | Farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase: real-time kinetics and inhibition by nitrogen-containing bisphosphonates in a scintillation assay. | 2007 | Assay Drug Dev Technol | pmid:17477829 |
| Komatsu M et al. | Identification and functional analysis of genes controlling biosynthesis of 2-methylisoborneol. | 2008 | Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. | pmid:18492804 |
| Davidovich-Rikanati R et al. | Overexpression of the lemon basil alpha-zingiberene synthase gene increases both mono- and sesquiterpene contents in tomato fruit. | 2008 | Plant J. | pmid:18643974 |
| Schmidt A and Gershenzon J | Cloning and characterization of two different types of geranyl diphosphate synthases from Norway spruce (Picea abies). | 2008 | Phytochemistry | pmid:17673268 |
| Gilg AB et al. | Unique animal prenyltransferase with monoterpene synthase activity. | 2009 | Naturwissenschaften | pmid:19277597 |
| Navia-Giné WG et al. | Medicago truncatula (E)-beta-ocimene synthase is induced by insect herbivory with corresponding increases in emission of volatile ocimene. | 2009 | Plant Physiol. Biochem. | pmid:19249223 |
| Vandermoten S et al. | Structural features conferring dual geranyl/farnesyl diphosphate synthase activity to an aphid prenyltransferase. | 2009 | Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. | pmid:19720147 |
| Xiao Y et al. | Prenyltransferase substrate binding pocket flexibility and its application in isoprenoid profiling. | 2009 | Mol Biosyst | pmid:19668852 |
| Sillero MA et al. | Synthesis of ATP derivatives of compounds of the mevalonate pathway (isopentenyl di- and triphosphate; geranyl di- and triphosphate, farnesyl di- and triphosphate, and dimethylallyl diphosphate) catalyzed by T4 RNA ligase, T4 DNA ligase and other ligases Potential relationship with the effect of bisphosphonates on osteoclasts. | 2009 | Biochem. Pharmacol. | pmid:19414000 |
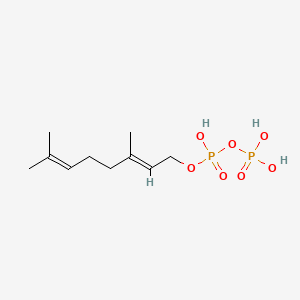
Geranyl diphosphate
Geranyl diphosphate is a lipid of Prenol Lipids (PR) class. The involved functions are known as Prenylation, Anabolism, Biochemical Pathway and Methylation. Geranyl diphosphate often locates in Membrane and Plastids. The associated genes with Geranyl diphosphate are GGPS1 gene, NKS1 gene, COQ2 gene and MIB1 gene.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of Geranyl diphosphate, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with Geranyl diphosphate?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
No disease MeSH terms mapped to the current reference collection.
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with Geranyl diphosphate
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with Geranyl diphosphate?
Visualization in cellular structure
Associated locations are in red color. Not associated locations are in black.
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Location | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What functions are associated with Geranyl diphosphate?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with Geranyl diphosphate?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
What genes are associated with Geranyl diphosphate?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Gene | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What common seen animal models are associated with Geranyl diphosphate?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.