| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Xie W et al. | Initiation of rubber biosynthesis: In vitro comparisons of benzophenone-modified diphosphate analogues in three rubber-producing species. | 2008 | Phytochemistry | pmid:18799172 |
| Tringali G et al. | Lovastatin and mevastatin reduce basal and cytokine-stimulated production of prostaglandins from rat microglial cells in vitro: evidence for a mechanism unrelated to the inhibition of hydroxy-methyl-glutaryl CoA reductase. | 2004 | Neurosci. Lett. | pmid:14698450 |
| Appelkvist EL et al. | Regulation of coenzyme Q biosynthesis. | 1994 | Mol. Aspects Med. | pmid:7752843 |
| Sagami H and Ogura K | Geranylpyrophosphate synthetase-geranylgeranylpyrophosphate synthetase from Micrococcus luteus. | 1985 | Meth. Enzymol. | pmid:4021813 |
| Saito A et al. | Simvastatin inhibits growth via apoptosis and the induction of cell cycle arrest in human melanoma cells. | 2008 | Melanoma Res. | pmid:18337644 |
| Chen KH et al. | A fluorescence sensor for detection of geranyl pyrophosphate by the chemo-ensemble method. | 2009 | J. Org. Chem. | pmid:19049370 |
| Hsieh FL et al. | Enhanced specificity of mint geranyl pyrophosphate synthase by modifying the R-loop interactions. | 2010 | J. Mol. Biol. | pmid:20965200 |
| Chang KC and Chuang NN | GTPase stimulation in shrimp Ras(Q(61)K) with geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate but not mammalian GAP. | 2001 | J. Exp. Zool. | pmid:11748613 |
| Gambliel H and Croteau R | Biosynthesis of (+/-)-alpha-pinene and (-)-beta-pinene from geranyl pyrophosphate by a soluble enzyme system from sage (Salvia officinalis). | 1982 | J. Biol. Chem. | pmid:7037765 |
| Wise ML et al. | Monoterpene synthases from common sage (Salvia officinalis). cDNA isolation, characterization, and functional expression of (+)-sabinene synthase, 1,8-cineole synthase, and (+)-bornyl diphosphate synthase. | 1998 | J. Biol. Chem. | pmid:9614092 |
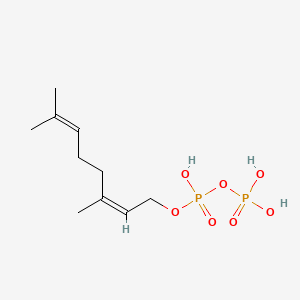
Neryl diphosphate
Neryl diphosphate is a lipid of Prenol Lipids (PR) class. The involved functions are known as Phenomenon. Neryl diphosphate often locates in Chloroplasts and Head. The associated genes with Neryl diphosphate are IPP gene.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of Neryl diphosphate, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with Neryl diphosphate?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
No disease MeSH terms mapped to the current reference collection.
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with Neryl diphosphate
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with Neryl diphosphate?
Visualization in cellular structure
Associated locations are in red color. Not associated locations are in black.
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Location | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What functions are associated with Neryl diphosphate?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with Neryl diphosphate?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
What genes are associated with Neryl diphosphate?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Gene | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What common seen animal models are associated with Neryl diphosphate?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.