| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lewinsohn E et al. | Wound-inducible pinene cyclase from grand fir: purification, characterization, and renaturation after SDS-PAGE. | 1992 | Arch. Biochem. Biophys. | pmid:1731633 |
| Wheeler CJ et al. | Uncompetitive inhibition of monoterpene cyclases by an analog of the substrate geranyl pyrophosphate and inhibition of monoterpene biosynthesis in vivo by an analog of geraniol. | 1990 | Arch. Biochem. Biophys. | pmid:2350172 |
| Croteau R et al. | Biosynthesis of monoterpenes: stereochemistry of the coupled isomerization and cyclization of geranyl pyrophosphate to camphane and isocamphane monoterpenes. | 1990 | Arch. Biochem. Biophys. | pmid:2178556 |
| Hallahan TW and Croteau R | Monoterpene biosynthesis: mechanism and stereochemistry of the enzymatic cyclization of geranyl pyrophosphate to (+)-cis- and (+)-trans-sabinene hydrate. | 1989 | Arch. Biochem. Biophys. | pmid:2916845 |
| Hallahan TW and Croteau R | Monoterpene biosynthesis: demonstration of a geranyl pyrophosphate:sabinene hydrate cyclase in soluble enzyme preparations from sweet marjoram (Majorana hortensis). | 1988 | Arch. Biochem. Biophys. | pmid:3401015 |
| Croteau R et al. | Biosynthesis of monoterpenes: preliminary characterization of i-endo-fenchol synthetase from fennel (Foeniculum vulgare) and evidence that no free intermediate is involved in the cyclization of geranyl pyrophosphate to the rearranged product. | 1980 | Arch. Biochem. Biophys. | pmid:7436421 |
| Pichersky E et al. | Purification and characterization of S-linalool synthase, an enzyme involved in the production of floral scent in Clarkia breweri. | 1995 | Arch. Biochem. Biophys. | pmid:7864636 |
| Wagschal KC et al. | Monoterpene biosynthesis: isotope effects associated with bicyclic olefin formation catalyzed by pinene synthases from sage (Salvia officinalis). | 1994 | Arch. Biochem. Biophys. | pmid:8109978 |
| Pyun HJ et al. | Stereochemistry of the proton elimination in the formation of (+)- and (-)-alpha-pinene by monoterpene cyclases from sage (Salvia officinalis). | 1994 | Arch. Biochem. Biophys. | pmid:8109979 |
| Kjonaas R and Croteau R | Demonstration that limonene is the first cyclic intermediate in the biosynthesis of oxygenated p-menthane monoterpenes in Mentha piperita and other Mentha species. | 1983 | Arch. Biochem. Biophys. | pmid:6830247 |
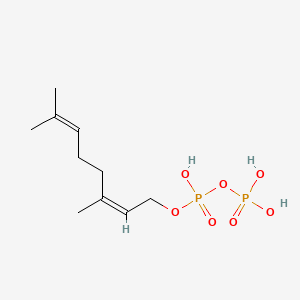
Neryl diphosphate
Neryl diphosphate is a lipid of Prenol Lipids (PR) class. The involved functions are known as Phenomenon. Neryl diphosphate often locates in Chloroplasts and Head. The associated genes with Neryl diphosphate are IPP gene.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of Neryl diphosphate, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with Neryl diphosphate?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
No disease MeSH terms mapped to the current reference collection.
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with Neryl diphosphate
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with Neryl diphosphate?
Visualization in cellular structure
Associated locations are in red color. Not associated locations are in black.
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Location | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What functions are associated with Neryl diphosphate?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with Neryl diphosphate?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
What genes are associated with Neryl diphosphate?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Gene | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What common seen animal models are associated with Neryl diphosphate?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.