| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pmid:12236678 | ||||
| You J et al. | Role of cytoplasmic phospholipase A2 in endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor dilations of rat middle cerebral arteries. | 2002 | J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. | pmid:12368663 |
| Burlando B et al. | Essential role of Ca2+ -dependent phospholipase A2 in estradiol-induced lysosome activation. | 2002 | Am. J. Physiol., Cell Physiol. | pmid:12372807 |
| pmid:12409148 | ||||
| pmid:12423404 | ||||
| Kothari SK et al. | Weed control in rose-scented geranium (Pelargonium spp). | 2002 | Pest Manag. Sci. | pmid:12477000 |
| Tommasini I et al. | Peroxynitrite stimulates the activity of cytosolic phospholipase A2 in U937 cells: the extent of arachidonic acid formation regulates the balance between cell survival or death. | 2002 | Cell Death Differ. | pmid:12478474 |
| Nagase T et al. | A potent inhibitor of cytosolic phospholipase A2, arachidonyl trifluoromethyl ketone, attenuates LPS-induced lung injury in mice. | 2003 | Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. | pmid:12505870 |
| pmid:12507867 | ||||
| Kolko M et al. | Neuronal damage by secretory phospholipase A2: modulation by cytosolic phospholipase A2, platelet-activating factor, and cyclooxygenase-2 in neuronal cells in culture. | 2003 | Neurosci. Lett. | pmid:12566178 |
| pmid:12573536 | ||||
| Athawale V et al. | Effect of reaction parameters on synthesis of citronellyl methacrylate by lipase-catalyzed transesterification. | 2003 Mar-Apr | Biotechnol. Prog. | pmid:12675563 |
| Shalit M et al. | Volatile ester formation in roses. Identification of an acetyl-coenzyme A. Geraniol/Citronellol acetyltransferase in developing rose petals. | 2003 | Plant Physiol. | pmid:12692346 |
| Wuryatmo E et al. | Inhibition of citrus postharvest pathogens by vapor of citral and related compounds in culture. | 2003 | J. Agric. Food Chem. | pmid:12696950 |
| King AJ and Dickinson JR | Biotransformation of hop aroma terpenoids by ale and lager yeasts. | 2003 | FEMS Yeast Res. | pmid:12702246 |
| Bostan M et al. | Phospholipase A2 modulates respiratory burst developed by neutrophils in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. | 2003 Jan-Mar | J. Cell. Mol. Med. | pmid:12767262 |
| El-Mowafy AM and Alkhalaf M | Resveratrol activates adenylyl-cyclase in human breast cancer cells: a novel, estrogen receptor-independent cytostatic mechanism. | 2003 | Carcinogenesis | pmid:12771030 |
| Shin S | Anti-Aspergillus activities of plant essential oils and their combination effects with ketoconazole or amphotericin B. | 2003 | Arch. Pharm. Res. | pmid:12785735 |
| pmid:12797753 | ||||
| Fiorini S et al. | 17Beta-eEstradiol stimulates arachidonate release from human amnion-like WISH cells through a rapid mechanism involving a membrane receptor. | 2003 | Endocrinology | pmid:12865314 |
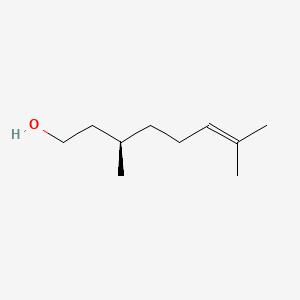
beta-Citronellol
Beta-citronellol is a lipid of Prenol Lipids (PR) class. The involved functions are known as Glycolysis.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of beta-Citronellol, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with beta-Citronellol?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
No disease MeSH terms mapped to the current reference collection.
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with beta-Citronellol
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with beta-Citronellol?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
What functions are associated with beta-Citronellol?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with beta-Citronellol?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
What genes are associated with beta-Citronellol?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
What common seen animal models are associated with beta-Citronellol?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.