| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zhang W et al. | Solution NMR structure of putidaredoxin-cytochrome P450cam complex via a combined residual dipolar coupling-spin labeling approach suggests a role for Trp106 of putidaredoxin in complex formation. | 2008 | J. Mol. Biol. | pmid:18835276 |
| Bell SG et al. | Engineering the CYP101 system for in vivo oxidation of unnatural substrates. | 2001 | Protein Eng. | pmid:11739899 |
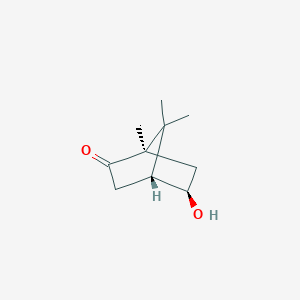
(+)-exo-5-hydroxycamphor
(+)-exo-5-hydroxycamphor is a lipid of Prenol Lipids (PR) class. The associated genes with (+)-exo-5-hydroxycamphor are putidaredoxin.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of (+)-exo-5-hydroxycamphor, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with (+)-exo-5-hydroxycamphor?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
No disease MeSH terms mapped to the current reference collection.
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with (+)-exo-5-hydroxycamphor
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with (+)-exo-5-hydroxycamphor?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
What functions are associated with (+)-exo-5-hydroxycamphor?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
What lipids are associated with (+)-exo-5-hydroxycamphor?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
What genes are associated with (+)-exo-5-hydroxycamphor?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Gene | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What common seen animal models are associated with (+)-exo-5-hydroxycamphor?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.