| MeSH term | MeSH ID | Detail |
|---|---|---|
| Adenocarcinoma | D000230 | 166 associated lipids |
| Colonic Neoplasms | D003110 | 161 associated lipids |
| Endometriosis | D004715 | 29 associated lipids |
| Leukemia, Erythroblastic, Acute | D004915 | 41 associated lipids |
| Hypercholesterolemia | D006937 | 91 associated lipids |
| Leukemia, Myeloid | D007951 | 52 associated lipids |
| Liver Neoplasms, Experimental | D008114 | 46 associated lipids |
| Protozoan Infections | D011528 | 6 associated lipids |
| Osteosarcoma | D012516 | 50 associated lipids |
| Leukemia-Lymphoma, Adult T-Cell | D015459 | 25 associated lipids |
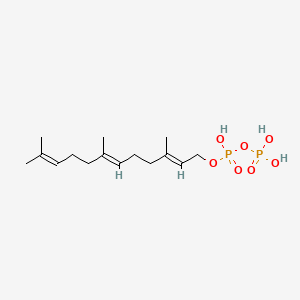
Farnesyl diphosphate
Farnesyl diphosphate is a lipid of Prenol Lipids (PR) class. Farnesyl diphosphate is associated with abnormalities such as Dental caries and Hyperostosis, Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal. The involved functions are known as Regulation, Process, Signal, Anabolism and inhibitors. Farnesyl diphosphate often locates in peroxisome, Cytoplasmic matrix, Plasma membrane, soluble and Mitochondria. The associated genes with Farnesyl diphosphate are HSD3B1 gene, ABRA gene, MATN1 gene, SEPSECS gene and MBD2 gene. The related lipids are Sterols, 22-hydroxycholesterol, dehydrosqualene, SK&F 104976 and 25-hydroxycholesterol.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of Farnesyl diphosphate, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with Farnesyl diphosphate?
Farnesyl diphosphate is suspected in and other diseases in descending order of the highest number of associated sentences.
Related references are mostly published in these journals:
| Disease | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literature |
|---|
Possible diseases from mapped MeSH terms on references
We collected disease MeSH terms mapped to the references associated with Farnesyl diphosphate
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with Farnesyl diphosphate
Lipid pathways are not clear in current pathway databases. We organized associated pathways with Farnesyl diphosphate through full-text articles, including metabolic pathways or pathways of biological mechanisms.
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Pathway name | Related literatures |
|---|
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with Farnesyl diphosphate?
Visualization in cellular structure
Associated locations are in red color. Not associated locations are in black.
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Location | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What functions are associated with Farnesyl diphosphate?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with Farnesyl diphosphate?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Lipid concept | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What genes are associated with Farnesyl diphosphate?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Gene | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What common seen animal models are associated with Farnesyl diphosphate?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
NCBI Entrez Crosslinks
All references with Farnesyl diphosphate
Download all related citations| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Schulz JG et al. | HMG-CoA reductase inhibition causes neurite loss by interfering with geranylgeranylpyrophosphate synthesis. | 2004 | J. Neurochem. | pmid:15030386 |
| Runquist M et al. | Distribution of branch point prenyltransferases in regions of bovine brain. | 1995 | J. Neurochem. | pmid:7595519 |
| Kim SH et al. | Cyclization mechanism of amorpha-4,11-diene synthase, a key enzyme in artemisinin biosynthesis. | 2006 | J. Nat. Prod. | pmid:16724836 |
| Itoh D et al. | Nonequivalent labeling of the phytyl side chain of chlorophyll a in callus of the hornwort Anthoceros punctatus. | 2000 | J. Nat. Prod. | pmid:10978203 |
| Baba TT et al. | Simvastatin suppresses the differentiation of C2C12 myoblast cells via a Rac pathway. | 2008 | J. Muscle Res. Cell. Motil. | pmid:18792797 |
| Hong WK et al. | Characterization of a squalene synthase from the thraustochytrid microalga Aurantiochytrium sp. KRS101. | 2013 | J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. | pmid:23676912 |
| Sanders JM et al. | Pyridinium-1-yl bisphosphonates are potent inhibitors of farnesyl diphosphate synthase and bone resorption. | 2005 | J. Med. Chem. | pmid:15828834 |
| Aoyama T et al. | A new class of highly potent farnesyl diphosphate-competitive inhibitors of farnesyltransferase. | 1998 | J. Med. Chem. | pmid:9457237 |
| Biller SA et al. | Isoprenoid (phosphinylmethyl)phosphonates as inhibitors of squalene synthetase. | 1988 | J. Med. Chem. | pmid:3172121 |
| Williams TM et al. | 2-substituted piperazines as constrained amino acids. Application to the synthesis of potent, non carboxylic acid inhibitors of farnesyltransferase. | 1996 | J. Med. Chem. | pmid:8691462 |