| MeSH term | MeSH ID | Detail |
|---|---|---|
| Body Weight | D001835 | 333 associated lipids |
| Abnormalities, Multiple | D000015 | 13 associated lipids |
| Adrenoleukodystrophy | D000326 | 29 associated lipids |
| Refsum Disease | D012035 | 19 associated lipids |
| Cholestasis | D002779 | 23 associated lipids |
| Lipid Metabolism, Inborn Errors | D008052 | 26 associated lipids |
| Brain Diseases, Metabolic, Inborn | D020739 | 10 associated lipids |
| Peroxisomal Disorders | D018901 | 5 associated lipids |
| Brain Damage, Chronic | D001925 | 6 associated lipids |
| Chondrodysplasia Punctata | D002806 | 8 associated lipids |
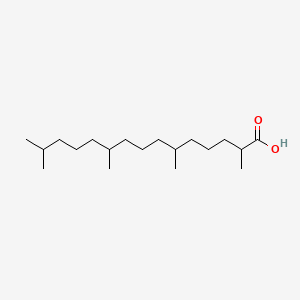
Pristanic acid
Pristanic acid is a lipid of Prenol Lipids (PR) class. Pristanic acid is associated with abnormalities such as Refsum Disease, Peroxisomal Disorders, Hereditary Diseases, Peripheral Neuropathy and Sensory neuropathy. The involved functions are known as physiological aspects, Regulation, Pathogenesis, Oxidation and Peroxisome Proliferator-activated Receptor Activity [MoA]. Pristanic acid often locates in peroxisome, Body tissue, Mitochondria, Membrane of peroxisome and Organelles. The associated genes with Pristanic acid are PSG5 gene, LGALS4 gene, PEX2 gene, ACSL4 gene and ACSL1 Gene. The related lipids are pristanic acid, Fatty Acids, branched chain fatty acid, Plasmalogens and 3-hydroxypristanic acid.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of Pristanic acid, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with Pristanic acid?
Pristanic acid is suspected in Peroxisomal Disorders, Refsum Disease, Protein Deficiency, Retinitis Pigmentosa, Enzyme Deficiency, Hereditary Diseases and other diseases in descending order of the highest number of associated sentences.
Related references are mostly published in these journals:
| Disease | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literature |
|---|
Possible diseases from mapped MeSH terms on references
We collected disease MeSH terms mapped to the references associated with Pristanic acid
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with Pristanic acid
Lipid pathways are not clear in current pathway databases. We organized associated pathways with Pristanic acid through full-text articles, including metabolic pathways or pathways of biological mechanisms.
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Pathway name | Related literatures |
|---|
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with Pristanic acid?
Visualization in cellular structure
Associated locations are in red color. Not associated locations are in black.
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Location | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What functions are associated with Pristanic acid?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with Pristanic acid?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Lipid concept | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What genes are associated with Pristanic acid?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Gene | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What common seen animal models are associated with Pristanic acid?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
NCBI Entrez Crosslinks
All references with Pristanic acid
Download all related citations| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Schmitt K et al. | [Zellweger syndrome, neonatal adrenoleukodystrophy or infantile Refsum's disease in a case with generalized peroxisome defect?]. | 1993 | Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. | pmid:7687405 |
| Straube R et al. | Membrane differential filtration is safe and effective for the long-term treatment of Refsum syndrome--an update of treatment modalities and pathophysiological cognition. | 2003 | Transfus. Apher. Sci. | pmid:12877898 |
| Mackie JT et al. | Phytol-induced hepatotoxicity in mice. | 2009 | Toxicol Pathol | pmid:19188468 |
| Kase BF and Björkhem I | Studies on the degradation of [U-3H]-phytanic acid and [U-3H]-pristanic acid in cultured fibroblasts from children with peroxisomal disorders. | 1996 | Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Invest. | pmid:8761525 |
| Verhoeven NM and Jakobs C | Human metabolism of phytanic acid and pristanic acid. | 2001 | Prog. Lipid Res. | pmid:11591435 |
| Wanders RJ et al. | Activation and oxidation of pristanic acid in rat liver: identification of a distinct, clofibrate non-inducible pristanoyl-CoA oxidase. | 1992 | Prog. Clin. Biol. Res. | pmid:1438370 |
| Wanders RJ et al. | Molecular analysis of disorders of peroxisomal beta-oxidation. | 1992 | Prog. Clin. Biol. Res. | pmid:1438395 |
| Villarroya F et al. | PPARs in the Control of Uncoupling Proteins Gene Expression. | 2007 | PPAR Res | pmid:17389766 |
| Astarita G et al. | Deficient liver biosynthesis of docosahexaenoic acid correlates with cognitive impairment in Alzheimer's disease. | 2010 | PLoS ONE | pmid:20838618 |
| ten Brink HJ et al. | In vivo study of phytanic acid alpha-oxidation in classic Refsum's disease and chondrodysplasia punctata. | 1992 | Pediatr. Res. | pmid:1282700 |
| McMillan HJ et al. | Specific combination of compound heterozygous mutations in 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 4 (HSD17B4) defines a new subtype of D-bifunctional protein deficiency. | 2012 | Orphanet J Rare Dis | pmid:23181892 |
| Sevin C et al. | Autosomal recessive cerebellar ataxia caused by mutations in the PEX2 gene. | 2011 | Orphanet J Rare Dis | pmid:21392394 |
| Klein CJ et al. | Plasma fatty acids in premature infants with hyperbilirubinemia: before-and-after nutrition support with fish oil emulsion. | 2013 | Nutr Clin Pract | pmid:23319354 |
| Pyper SR et al. | PPARalpha: energy combustion, hypolipidemia, inflammation and cancer. | 2010 | Nucl Recept Signal | pmid:20414453 |
| Gootjes J et al. | Biochemical markers predicting survival in peroxisome biogenesis disorders. | 2002 | Neurology | pmid:12473763 |
| Clarke CE et al. | Tremor and deep white matter changes in alpha-methylacyl-CoA racemase deficiency. | 2004 | Neurology | pmid:15249642 |
| Kapina V et al. | Relapsing rhabdomyolysis due to peroxisomal alpha-methylacyl-coa racemase deficiency. | 2010 | Neurology | pmid:20921516 |
| Busanello EN et al. | Neurochemical evidence that pristanic acid impairs energy production and inhibits synaptic Na(+), K(+)-ATPase activity in brain of young rats. | 2011 | Neurochem. Res. | pmid:21445584 |
| Kruska N and Reiser G | Phytanic acid and pristanic acid, branched-chain fatty acids associated with Refsum disease and other inherited peroxisomal disorders, mediate intracellular Ca2+ signaling through activation of free fatty acid receptor GPR40. | 2011 | Neurobiol. Dis. | pmid:21570468 |
| Rönicke S et al. | The influence of the branched-chain fatty acids pristanic acid and Refsum disease-associated phytanic acid on mitochondrial functions and calcium regulation of hippocampal neurons, astrocytes, and oligodendrocytes. | 2009 | Neurobiol. Dis. | pmid:19703563 |