| MeSH term | MeSH ID | Detail |
|---|---|---|
| Diabetes Mellitus, Type 1 | D003922 | 56 associated lipids |
| Alzheimer Disease | D000544 | 76 associated lipids |
| Colonic Neoplasms | D003110 | 161 associated lipids |
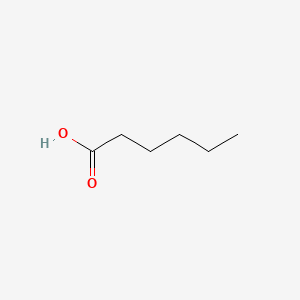
HEXANOIC ACID
HEXANOIC ACID is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. Hexanoic acid is associated with abnormalities such as Obesity, Ileoanal Pouches, Ulcerative Colitis, Ulcerative colitis, quiescent and Diabetes Mellitus, Non-Insulin-Dependent. The involved functions are known as Binding (Molecular Function), Anabolism, Adjudication, enzyme activity and Process. Hexanoic acid often locates in Membrane, Tissue membrane, Microsomes, Liver, Microsomes and Mitochondria. The associated genes with HEXANOIC ACID are SH2D1A gene, Fusion Protein and MAPK3 gene. The related lipids are hexanoic acid, Fatty Acids, Butyric Acid, Propionate and Palmitates.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of HEXANOIC ACID, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with HEXANOIC ACID?
HEXANOIC ACID is suspected in Obesity, Ileoanal Pouches, Ulcerative Colitis, Ulcerative colitis, quiescent, Diabetes Mellitus, Non-Insulin-Dependent, Gastroesophageal reflux disease and other diseases in descending order of the highest number of associated sentences.
Related references are mostly published in these journals:
| Disease | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literature |
|---|
Possible diseases from mapped MeSH terms on references
We collected disease MeSH terms mapped to the references associated with HEXANOIC ACID
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with HEXANOIC ACID
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with HEXANOIC ACID?
Visualization in cellular structure
Associated locations are in red color. Not associated locations are in black.
Related references are published most in these journals:
- Drug Metab. Dispos. (2)
- J. Biol. Chem. (2)
- Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. (1)
- Others (1)
| Location | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What functions are associated with HEXANOIC ACID?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with HEXANOIC ACID?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Lipid concept | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What genes are associated with HEXANOIC ACID?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Gene | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What common seen animal models are associated with HEXANOIC ACID?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
NCBI Entrez Crosslinks
All references with HEXANOIC ACID
Download all related citations| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Doody AM et al. | Characterizing the structure/function parameter space of hydrocarbon-conjugated branched polyethylenimine for DNA delivery in vitro. | 2006 | J Control Release | pmid:16963143 |
| Hidalgo-Fernández P et al. | Avidin and streptavidin ligands based on the glycoluril bicyclic system. | 2006 | Org. Biomol. Chem. | pmid:16886084 |
| Yu HQ and Mu Y | Biological hydrogen production in a UASB reactor with granules. II: Reactor performance in 3-year operation. | 2006 | Biotechnol. Bioeng. | pmid:16615161 |
| Röck F et al. | Comparative analysis of volatile constituents from mice and their urine. | 2006 | J. Chem. Ecol. | pmid:16770722 |
| Vandieken V et al. | Desulfotomaculum arcticum sp. nov., a novel spore-forming, moderately thermophilic, sulfate-reducing bacterium isolated from a permanently cold fjord sediment of Svalbard. | 2006 | Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. | pmid:16585677 |
| Vitali M et al. | Exposure to organic solvents among handicraft car painters: A pilot study in Italy. | 2006 | Ind Health | pmid:16716010 |
| Benton R et al. | Atypical membrane topology and heteromeric function of Drosophila odorant receptors in vivo. | 2006 | PLoS Biol. | pmid:16402857 |
| Miyazawa M and Kawata J | Composition of the essential oil of rootstock from Cimicifuga simplex. | 2006 | Nat. Prod. Res. | pmid:16835085 |
| Okere IC et al. | Differential effects of heptanoate and hexanoate on myocardial citric acid cycle intermediates following ischemia-reperfusion. | 2006 | J. Appl. Physiol. | pmid:16141384 |
| Jin T et al. | Identification of human dim1 as a peptidase with autocleavage activity. | 2006 | Chem Biol Drug Des | pmid:17177886 |
| Tao F et al. | Competition and coadsorption of di-acids and carboxylic acid solvents on HOPG. | 2006 | J Phys Chem B | pmid:17004820 |
| BÅ‚aszczyk A et al. | Genotoxic and antioxidant activities of ethoxyquin salts evaluated by the comet assay. | 2006 | Chem. Biol. Interact. | pmid:16959229 |
| Spickenreither M et al. | Novel 6-O-acylated vitamin C derivatives as hyaluronidase inhibitors with selectivity for bacterial lyases. | 2006 | Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. | pmid:16908142 |
| Williams CR et al. | Geographic variation in attraction to human odor compounds by Aedes aegypti mosquitoes (Diptera: Culicidae): a laboratory study. | 2006 | J. Chem. Ecol. | pmid:16868835 |
| Kendall MM et al. | Butyrate- and propionate-degrading syntrophs from permanently cold marine sediments in Skan Bay, Alaska, and description of Algorimarina butyrica gen. nov., sp. nov. | 2006 | FEMS Microbiol. Lett. | pmid:16907746 |
| Jiracek J et al. | S-alkylated homocysteine derivatives: new inhibitors of human betaine-homocysteine S-methyltransferase. | 2006 | J. Med. Chem. | pmid:16789755 |
| Cometto-Muñiz JE et al. | Cutoff in detection of eye irritation from vapors of homologous carboxylic acids and aliphatic aldehydes. | 2007 | Neuroscience | pmid:17270354 |
| Giroux HJ et al. | Characterization of hydrophobic flavor release profile in oil-in-water emulsions. | 2007 | J. Food Sci. | pmid:17995853 |
| Soule MC et al. | Effects of atmospherically important solvated ions on organic acid adsorption at the surface of aqueous solutions. | 2007 | J Phys Chem B | pmid:18004833 |
| Cao SL et al. | A novel nasal delivery system of a Chinese traditional medicine, Radix Bupleuri, based on the concept of ion-activated in situ gel. | 2007 | Arch. Pharm. Res. | pmid:17879756 |