| MeSH term | MeSH ID | Detail |
|---|---|---|
| Uremia | D014511 | 33 associated lipids |
| Colonic Neoplasms | D003110 | 161 associated lipids |
| Diabetes Mellitus, Type 1 | D003922 | 56 associated lipids |
| Arthritis | D001168 | 41 associated lipids |
| Leukemia, Erythroblastic, Acute | D004915 | 41 associated lipids |
| Alzheimer Disease | D000544 | 76 associated lipids |
| Arthritis, Infectious | D001170 | 8 associated lipids |
| Clostridium Infections | D003015 | 5 associated lipids |
| Starvation | D013217 | 47 associated lipids |
| Riboflavin Deficiency | D012257 | 10 associated lipids |
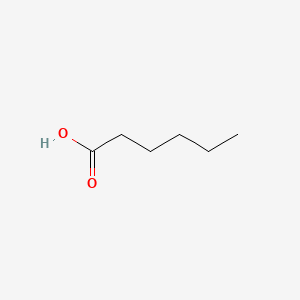
HEXANOIC ACID
HEXANOIC ACID is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. Hexanoic acid is associated with abnormalities such as Obesity, Ileoanal Pouches, Ulcerative Colitis, Ulcerative colitis, quiescent and Diabetes Mellitus, Non-Insulin-Dependent. The involved functions are known as Binding (Molecular Function), Anabolism, Adjudication, enzyme activity and Process. Hexanoic acid often locates in Membrane, Tissue membrane, Microsomes, Liver, Microsomes and Mitochondria. The associated genes with HEXANOIC ACID are SH2D1A gene, Fusion Protein and MAPK3 gene. The related lipids are hexanoic acid, Fatty Acids, Butyric Acid, Propionate and Palmitates.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of HEXANOIC ACID, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with HEXANOIC ACID?
HEXANOIC ACID is suspected in Obesity, Ileoanal Pouches, Ulcerative Colitis, Ulcerative colitis, quiescent, Diabetes Mellitus, Non-Insulin-Dependent, Gastroesophageal reflux disease and other diseases in descending order of the highest number of associated sentences.
Related references are mostly published in these journals:
| Disease | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literature |
|---|
Possible diseases from mapped MeSH terms on references
We collected disease MeSH terms mapped to the references associated with HEXANOIC ACID
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with HEXANOIC ACID
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with HEXANOIC ACID?
Visualization in cellular structure
Associated locations are in red color. Not associated locations are in black.
Related references are published most in these journals:
- Drug Metab. Dispos. (2)
- J. Biol. Chem. (2)
- Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. (1)
- Others (1)
| Location | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What functions are associated with HEXANOIC ACID?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with HEXANOIC ACID?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Lipid concept | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What genes are associated with HEXANOIC ACID?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Gene | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What common seen animal models are associated with HEXANOIC ACID?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
NCBI Entrez Crosslinks
All references with HEXANOIC ACID
Download all related citations| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sundqvist KE et al. | Metabolic effects of propionate, hexanoate and propionylcarnitine in normoxia, ischaemia and reperfusion. Does an anaplerotic substrate protect the ischaemic myocardium? | 1994 | Eur. Heart J. | pmid:8070485 |
| Ishiwata K et al. | Synthesis and preliminary evaluation of [1-11C]hexanoate as a PET tracer of fatty acid metabolism. | 1995 | Ann Nucl Med | pmid:7779532 |
| Amblard M et al. | Synthesis and biological evaluation of cholecystokinin analogs in which the Asp-Phe-NH2 moiety has been replaced by a 3-amino-7-phenylheptanoic acid or a 3-amino-6-(phenyloxy)hexanoic acid. | 1993 | J. Med. Chem. | pmid:7692048 |
| Madden MC et al. | Acylcarnitine accumulation does not correlate with reperfusion recovery in palmitate-perfused rat hearts. | 1995 | Am. J. Physiol. | pmid:7611501 |
| Varani J et al. | Comparison of cell attachment and caseinolytic activities of five tumour cell types. | 1978 | J. Cell. Sci. | pmid:748334 |
| Hoshi A et al. | Antitumor activity of metabolites of 1-hexylcarbamoyl-5-fluorouracil and related compounds against L1210 leukemia in vivo and L5178Y lymphoma cells in vitro. | 1980 | J. Pharmacobio-dyn. | pmid:7463306 |
| Kølvraa S et al. | Excretion of short-chain N-acylglycines in the urine of a patient with D-glyceric acidemia. | 1980 | Clin. Chim. Acta | pmid:7408214 |
| Lee IY and McMenamy RH | Location of the medium chain fatty acid site on human serum albumin. Residues involved and relationship to the indole site. | 1980 | J. Biol. Chem. | pmid:7391008 |
| Brook I et al. | Abnormalities in synovial fluid of patients with septic arthritis detected by gas-liquid chromatography. | 1980 | Ann. Rheum. Dis. | pmid:7387221 |
| Morio M et al. | Quantitative analysis of trifluoroacetate in the urine and blood by isotachophoresis. | 1980 | Anesthesiology | pmid:7386909 |