| MeSH term | MeSH ID | Detail |
|---|---|---|
| Weight Gain | D015430 | 101 associated lipids |
| Cell Transformation, Neoplastic | D002471 | 126 associated lipids |
| Edema | D004487 | 152 associated lipids |
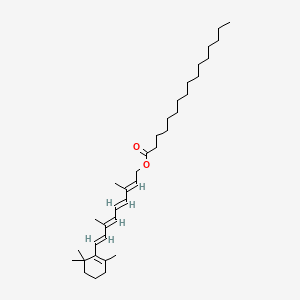
all-trans-retinyl Palmitate
All-trans-retinyl palmitate is a lipid of Prenol Lipids (PR) class. All-trans-retinyl palmitate is associated with abnormalities such as Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of all-trans-retinyl Palmitate, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with all-trans-retinyl Palmitate?
all-trans-retinyl Palmitate is suspected in and other diseases in descending order of the highest number of associated sentences.
Related references are mostly published in these journals:
| Disease | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literature |
|---|
Possible diseases from mapped MeSH terms on references
We collected disease MeSH terms mapped to the references associated with all-trans-retinyl Palmitate
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with all-trans-retinyl Palmitate
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with all-trans-retinyl Palmitate?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
What functions are associated with all-trans-retinyl Palmitate?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
What lipids are associated with all-trans-retinyl Palmitate?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
What genes are associated with all-trans-retinyl Palmitate?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
What common seen animal models are associated with all-trans-retinyl Palmitate?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
NCBI Entrez Crosslinks
All references with all-trans-retinyl Palmitate
Download all related citations| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reinersdorff DV et al. | Plasma kinetics of vitamin A in humans after a single oral dose of [8,9,19-13C]retinyl palmitate. | 1996 | J. Lipid Res. | pmid:8895053 |
| Apgar J et al. | Reproducibility of relative dose response (RDR) test and serum retinol and retinyl ester concentrations in children after a 2-week interval. | 1996 | J Am Coll Nutr | pmid:8892170 |
| Piersma AH et al. | Teratogenicity of a single oral dose of retinyl palmitate in the rat, and the role of dietary vitamin A status. | 1996 | Pharmacol. Toxicol. | pmid:8884871 |
| Fex GA et al. | Serum retinoids in retinitis pigmentosa patients treated with vitamin A. | 1996 | Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. | pmid:8871145 |
| Pimstone SN et al. | A frequently occurring mutation in the lipoprotein lipase gene (Asn291Ser) results in altered postprandial chylomicron triglyceride and retinyl palmitate response in normolipidemic carriers. | 1996 | J. Lipid Res. | pmid:8864951 |
| Issing WJ et al. | [High concentrate A-mulsin, a new therapy concept in laryngeal leukoplakia]. | 1996 | Laryngorhinootologie | pmid:8851116 |
| Bast A et al. | Beta-carotene as antioxidant. | 1996 | Eur J Clin Nutr | pmid:8841774 |
| Meyer E et al. | Abnormal postprandial apolipoprotein B-48 and triglyceride responses in normolipidemic women with greater than 70% stenotic coronary artery disease: a case-control study. | 1996 | Atherosclerosis | pmid:8830935 |
| Tzimas G et al. | Embryotoxic doses of vitamin A to rabbits result in low plasma but high embryonic concentrations of all-trans-retinoic acid: risk of vitamin A exposure in humans. | 1996 | J. Nutr. | pmid:8814204 |
| Sundaresan PR et al. | Interactions in indices of vitamin A, zinc and copper status when these nutrients are fed to rats at adequate and increased levels. | 1996 | Br. J. Nutr. | pmid:8774236 |