| MeSH term | MeSH ID | Detail |
|---|---|---|
| Cell Transformation, Neoplastic | D002471 | 126 associated lipids |
| Edema | D004487 | 152 associated lipids |
| Weight Gain | D015430 | 101 associated lipids |
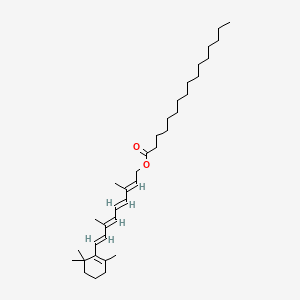
all-trans-retinyl Palmitate
All-trans-retinyl palmitate is a lipid of Prenol Lipids (PR) class. All-trans-retinyl palmitate is associated with abnormalities such as Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of all-trans-retinyl Palmitate, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with all-trans-retinyl Palmitate?
all-trans-retinyl Palmitate is suspected in and other diseases in descending order of the highest number of associated sentences.
Related references are mostly published in these journals:
| Disease | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literature |
|---|
Possible diseases from mapped MeSH terms on references
We collected disease MeSH terms mapped to the references associated with all-trans-retinyl Palmitate
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with all-trans-retinyl Palmitate
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with all-trans-retinyl Palmitate?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
What functions are associated with all-trans-retinyl Palmitate?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
What lipids are associated with all-trans-retinyl Palmitate?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
What genes are associated with all-trans-retinyl Palmitate?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
What common seen animal models are associated with all-trans-retinyl Palmitate?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
NCBI Entrez Crosslinks
All references with all-trans-retinyl Palmitate
Download all related citations| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surman SL et al. | Oral retinyl palmitate or retinoic acid corrects mucosal IgA responses toward an intranasal influenza virus vaccine in vitamin A deficient mice. | 2014 | Vaccine | pmid:24657715 |
| Oliveira MB et al. | Topical application of retinyl palmitate-loaded nanotechnology-based drug delivery systems for the treatment of skin aging. | 2014 | Biomed Res Int | pmid:24772430 |
| McDonald SL et al. | A double blind randomized controlled trial in neonates to determine the effect of vitamin A supplementation on immune responses: The Gambia protocol. | 2014 | BMC Pediatr | pmid:24708735 |
| Pirazzi C et al. | PNPLA3 has retinyl-palmitate lipase activity in human hepatic stellate cells. | 2014 | Hum. Mol. Genet. | pmid:24670599 |
| Surman SL et al. | Intranasal administration of retinyl palmitate with a respiratory virus vaccine corrects impaired mucosal IgA response in the vitamin A-deficient host. | 2014 | Clin. Vaccine Immunol. | pmid:24554696 |
| Jørgensen MJ et al. | The effect of at-birth vitamin A supplementation on differential leucocyte counts and in vitro cytokine production: an immunological study nested within a randomised trial in Guinea-Bissau. | 2013 | Br. J. Nutr. | pmid:23168172 |
| Ambrosini GL et al. | No dose-dependent increase in fracture risk after long-term exposure to high doses of retinol or beta-carotene. | 2013 | Osteoporos Int | pmid:22986930 |
| Heying EK et al. | High-provitamin A carotenoid (Orange) maize increases hepatic vitamin A reserves of offspring in a vitamin A-depleted sow-piglet model during lactation. | 2013 | J. Nutr. | pmid:23719225 |
| Farhangi MA et al. | Vitamin A supplementation and serum Th1- and Th2-associated cytokine response in women. | 2013 | J Am Coll Nutr | pmid:24024773 |
| Clugston RD et al. | Altered hepatic retinyl ester concentration and acyl composition in response to alcohol consumption. | 2013 | Biochim. Biophys. Acta | pmid:24046868 |