| MeSH term | MeSH ID | Detail |
|---|---|---|
| Edema | D004487 | 152 associated lipids |
| Weight Gain | D015430 | 101 associated lipids |
| Cell Transformation, Neoplastic | D002471 | 126 associated lipids |
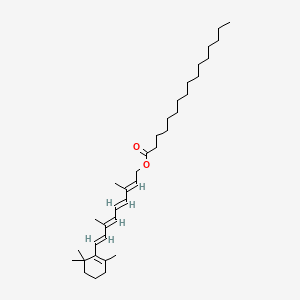
all-trans-retinyl Palmitate
All-trans-retinyl palmitate is a lipid of Prenol Lipids (PR) class. All-trans-retinyl palmitate is associated with abnormalities such as Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of all-trans-retinyl Palmitate, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with all-trans-retinyl Palmitate?
all-trans-retinyl Palmitate is suspected in and other diseases in descending order of the highest number of associated sentences.
Related references are mostly published in these journals:
| Disease | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literature |
|---|
Possible diseases from mapped MeSH terms on references
We collected disease MeSH terms mapped to the references associated with all-trans-retinyl Palmitate
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with all-trans-retinyl Palmitate
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with all-trans-retinyl Palmitate?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
What functions are associated with all-trans-retinyl Palmitate?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
What lipids are associated with all-trans-retinyl Palmitate?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
What genes are associated with all-trans-retinyl Palmitate?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
What common seen animal models are associated with all-trans-retinyl Palmitate?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
NCBI Entrez Crosslinks
All references with all-trans-retinyl Palmitate
Download all related citations| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kohgo T et al. | The enhancing effect of excess retinol palmitate on induction of odontogenic tumors and inhibitory effect on squamous cell carcinoma of the gingiva in hamsters treated with N-methylnitrosourea. | 1999 | Histol. Histopathol. | pmid:9987661 |
| Wang XD et al. | Retinoid signaling and activator protein-1 expression in ferrets given beta-carotene supplements and exposed to tobacco smoke. | 1999 | J. Natl. Cancer Inst. | pmid:9890171 |
| Mizobuchi Y et al. | Retinyl palmitate reduces hepatic fibrosis in rats induced by dimethylnitrosamine or pig serum. | 1998 | J. Hepatol. | pmid:9875640 |
| Velasquez-Pereira J et al. | Effects on performance, tissue integrity, and metabolism of vitamin E supplementation for beef heifers fed a diet that contains gossypol. | 1998 | J. Anim. Sci. | pmid:9856398 |
| Solomons NW | Plant sources of vitamin A and human nutrition: red palm oil does the job. | 1998 | Nutr. Rev. | pmid:9810811 |
| Ritchie HE et al. | Model predicting the teratogenic potential of retinyl palmitate, using a combined in vivo/in vitro approach. | 1998 Sep-Oct | Teratology | pmid:9802191 |
| Lemieux S et al. | Apolipoprotein B-48 and retinyl palmitate are not equivalent markers of postprandial intestinal lipoproteins. | 1998 | J. Lipid Res. | pmid:9788242 |
| von Reinersdorff D et al. | Development of a compartmental model describing the dynamics of vitamin A metabolism in men. | 1998 | Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. | pmid:9781391 |
| Montilla PL et al. | Protective role of melatonin and retinol palmitate in oxidative stress and hyperlipidemic nephropathy induced by adriamycin in rats. | 1998 | J. Pineal Res. | pmid:9755029 |
| Li T et al. | Effect of vitamin A supplementation on rhodopsin mutants threonine-17 --> methionine and proline-347 --> serine in transgenic mice and in cell cultures. | 1998 | Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. | pmid:9751768 |